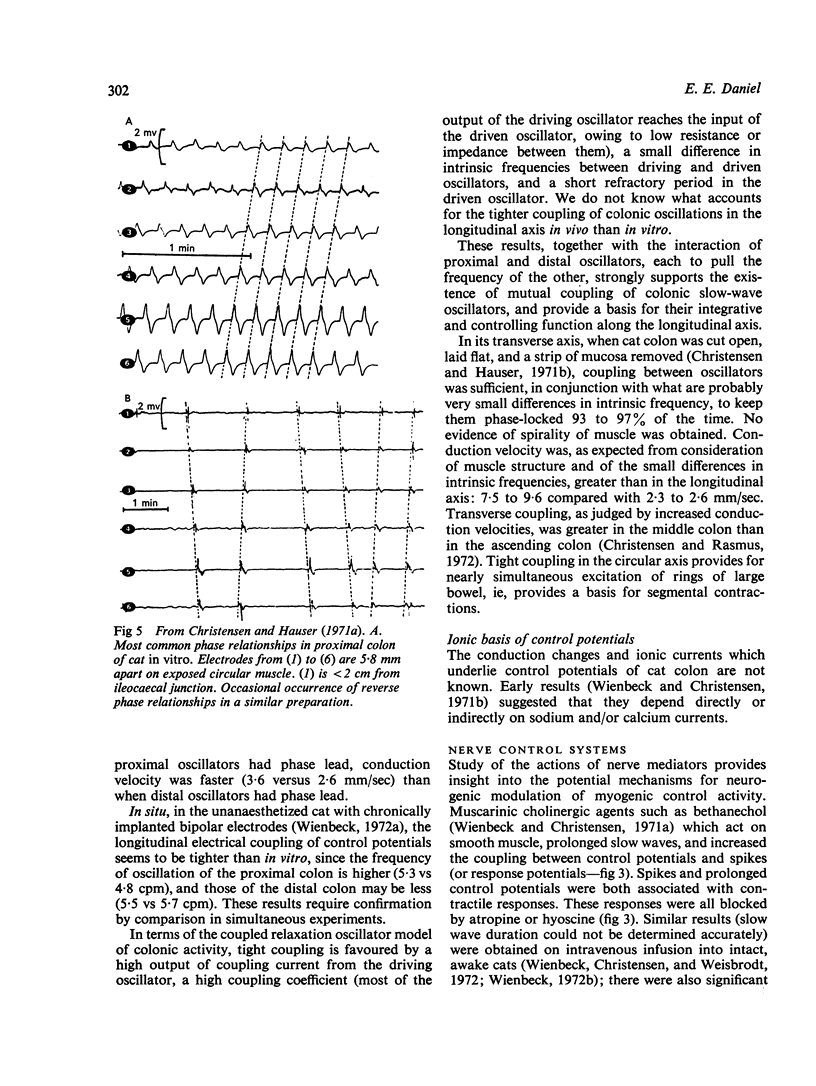
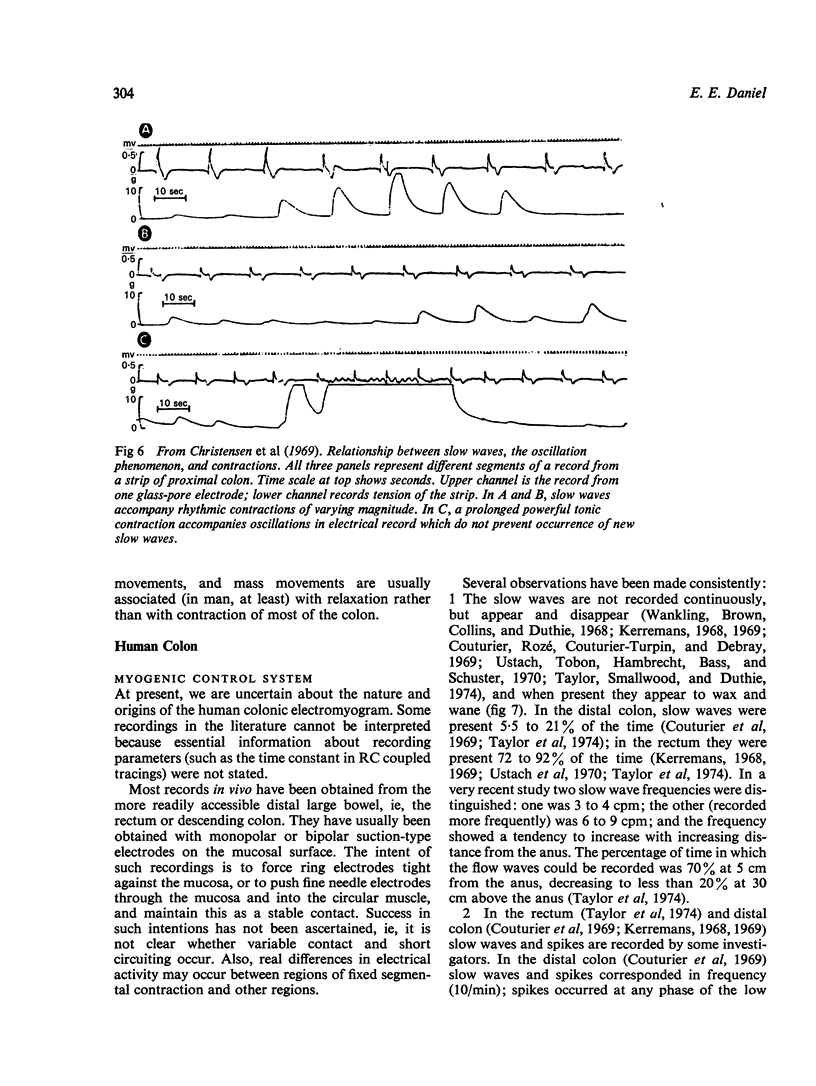
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUCKNELL A., WHITNEY B. A PRELIMINARY INVESTIGATION OF THE PHARMACOLOGY OF THE HUMAN ISOLATED TAENIA COLI PREPARATION. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1964 Aug;23:164–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1964.tb01576.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. D., Jr, Christensen J. Some effects of quinidine and quinine on the electromyogram of the colon. Gastroenterology. 1973 Nov;65(5):773–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belisle S., Gagnon D. J. Stimulating action of catecholamines on isolated preparations of the rat colon and human and rabbit taeniae coli. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Feb;41(2):361–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb08037.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A., Whitney B. A pharmacological study of the motility of the human gastrointestinal tract. Gut. 1966 Aug;7(4):307–316. doi: 10.1136/gut.7.4.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B. On the nature of the oscillations of the membrane potential (slow waves) produced by acetylcholine or carbachol in intestinal smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):403–418. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Sep;24(3):509–581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Anuras S., Hauser R. L. Migrating spike bursts and electrical slow waves in the cat colon: effect of sectioning. Gastroenterology. 1974 Feb;66(2):240–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Caprilli R., Lund G. F. Electric slow waves in circular muscle of cat colon. Am J Physiol. 1969 Sep;217(3):771–776. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.3.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Freeman B. W. Circular muscle electromyogram in the cat colon: local effect of sodium ricinoleate. Gastroenterology. 1972 Dec;63(6):1011–1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Hauser R. L. Circumferential coupling of electric slow waves in circular muscle of cat colon. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1033–1037. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Hauser R. L. Longitudinal axial coupling of slow waves in proximal cat colon. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jul;221(1):246–250. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.1.246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Rasmus S. C. Colon slow waves: size of oscillators and rates of spread. Am J Physiol. 1972 Dec;223(6):1330–1333. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.6.1330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Weisbrodt N. W., Hauser R. L. Electrical slow wave of the proximal colon of the cat in diarrhea. Gastroenterology. 1972 Jun;62(6):1167–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier D., Roze C., Couturier-Turpin M. H., Debray C. Electromyography of the colon in situ. An experimental study in man and in the rabbit. Gastroenterology. 1969 Feb;56(2):317–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsen J., Arey L. B. On spirality in the intestinal wall. Am J Anat. 1966 Jan;118(1):11–20. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001180103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon B. J., Noblet H. R., Burnstock G. Adrenergic innervation of bowel in Hirschsprung's disease. Br Med J. 1969 Aug 9;3(5666):338–340. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5666.330-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett J. R., Howard E. R., Nixon H. H. Autonomic nerves in rectum and colon in Hirschsprung's disease. A cholinesterase and catecholamine histochemical study. Arch Dis Child. 1969 Jun;44(235):406–417. doi: 10.1136/adc.44.235.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grivel M. L., Ruckebusch Y. The propagation of segmental contractions along the small intestine. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(2):611–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard E. R., Garrett J. R. The intrinsic myenteric innervation of the hind-gut and accessory muscles of defaecation in the cat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973;136(1):31–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00307678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerremans R. Electrical activity and motility of the internal anal sphincter: an "in vivo" electrophysiological study in man. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 1968 Jul;31(7):465–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Williams I. Organization of the muscular wall of the human colon. Gut. 1969 May;10(5):352–359. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.5.352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarna S. K., Daniel E. E., Kingma Y. J. Effects of partial cuts on gastric electrical control activity and its computer model. Am J Physiol. 1972 Aug;223(2):332–340. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.2.332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarna S. K., Daniel E. E., Kingma Y. J. Premature control potentials in the dog stomach and in the gastric computer model. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jun;222(6):1518–1523. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.6.1518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarna S. K., Daniel E. E., Kingma Y. J. Simulation of slow-wave electrical activity of small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jul;221(1):166–175. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.1.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarna S. K., Daniel E. E., Kingma Y. J. Simulation of the electric-control activity of the stomach by an array of relaxation oscillators. Am J Dig Dis. 1972 Apr;17(4):299–310. doi: 10.1007/BF02231729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szurszewski J. H. A migrating electric complex of canine small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1969 Dec;217(6):1757–1763. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.6.1757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ustach T. J., Tobon F., Hambrecht T., Bass D. D., Schuster M. M. Electrophysiological aspects of human sphincter function. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jan;49(1):41–48. doi: 10.1172/JCI106220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wankling W. J., Brown B. H., Collins C. D., Duthie H. L. Basal electrical activity in the anal canal in man. Gut. 1968 Aug;9(4):457–460. doi: 10.1136/gut.9.4.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrodt N. W., Christensen J. Electrical activity of the cat duodenum in fasting and vomiting. Gastroenterology. 1972 Dec;63(6):1004–1010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienbeck M., Christensen J. Cationic requirements of colon slow waves in the cat. Am J Physiol. 1971 Feb;220(2):513–519. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.2.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienbeck M., Christensen J. Effects of some drugs on electrical activity of the isolated colon of the cat. Gastroenterology. 1971 Oct;61(4):470–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienbeck M., Christensen J., Weisbrodt N. W. Electromyography of the colon in the unanesthetized cat. Am J Dig Dis. 1972 Apr;17(4):356–362. doi: 10.1007/BF02231738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienbeck M. The electrical activity of the cat colon in vivo. I. The normal electrical activity and its relationship to contractile activity. Res Exp Med (Berl) 1972;158(4):268–279. doi: 10.1007/BF01852210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wienbeck M. The electrical activity of the cat colon in vivo. II. The effects of bethanechol and morphine. Res Exp Med (Berl) 1972;158(4):280–287. doi: 10.1007/BF01852211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]