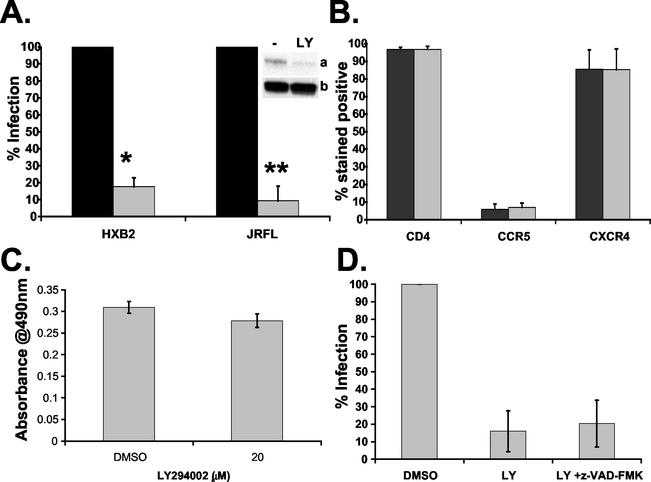
FIG. 3.
Effect of LY294002 on HIV-1 infection of CD4+ T lymphocytes. (A) Activated CD4+ T cells were treated with 20 μM LY294002 (gray bars) or DMSO control (black bars) for 1 h at 37°C prior to infection with either HXB2 (X4) or JRFL (R5) HIV-1-pseudotyped luciferase virus. Luciferase activity was measured 24 h postinfection and normalized to total protein concentration. Uninfected background levels of luciferase were subtracted from total luciferase activity. Results are expressed as a percentage of the DMSO control infection. Data are averages from four or more independent experiments, where * and ** indicate P < 0.0001. Inset, confirmation of PI3-kinase inhibition by immunoblotting for phosphorylated Akt (a) and total Akt protein (b) following LY294002 treatment. (B) Activated CD4+ T cells were treated with DMSO (gray bars) or 20 μM LY294002 (black bars) for 60 min at 37°C prior to staining with allophycyanin-, fluorescein isothiocyanate-, and phycoerythrin-conjugated antibodies against CD4, CCR5, and CXCR4 and their corresponding isotype controls. Fluorescence staining was measured by flow cytometry, and data are averages of two independent experiments, with the ranges indicated. (C) Cell viability of activated CD4+ T lymphocytes incubated with 20 μM LY294002 or DMSO control for 24 h at 37°C measured with the Promega CellTiter96 aqueous MTS assay. Over 90% of cells were viable after 24 h of incubation with 20 μM LY294002 (P > 0.05). (D) Activated CD4+ T cells were treated with 20 μM LY294002 in the absence or presence of 50 μM z-VAD-FMK for 1 h at 37°C prior to infection with HXB2-HIV-1-pseudotyped luciferase virus. Percenta infection was determined as described for A. Data are averages of two independent experiments, with the range indicated by bars.