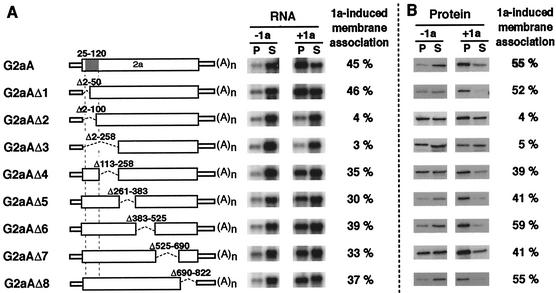
FIG. 6.
Deletion analysis of 2a sequences required for 2a ORF-dependent 1a responsiveness. (A) On the left are schematic diagrams of G2aA and its in-frame deletion derivatives. The previously defined limits of resolution for the region encoding the 1a-interacting domain of the 2a protein are indicated with a shaded box. Membrane association abilities of these RNAs in the absence (−1a) or presence (+1a) of 1a were assessed by cell fractionation to measure RNA distribution in the pellet (P) and supernatant (S) fractions as described in the legend to Fig. 1. Representative Northern blots are shown. As a measure of 1a responsiveness, the difference between the percentage of pelletable RNA in the presence and the absence of 1a was calculated for each RNA. The data shown are averages from three or more independent experiments for each derivative. (B) Western blots showing parallel analysis of the membrane association levels of the corresponding 2a protein derivatives in the absence (−1a) or presence (+1a) of 1a. 2a and 2a derivatives were detected with a mixture of three monoclonal antibodies that recognize epitopes mapped to the C-terminal, central polymerase, and N-terminal regions of 2a (R. Hershberger and P. Ahlquist, unpublished results). As a measure of 1a-induced membrane association, the difference between the percentages of pelletable 2a protein in the presence and the absence of 1a was calculated for each mutant. The data shown are averages from three or more independent experiments for each derivative.