Abstract
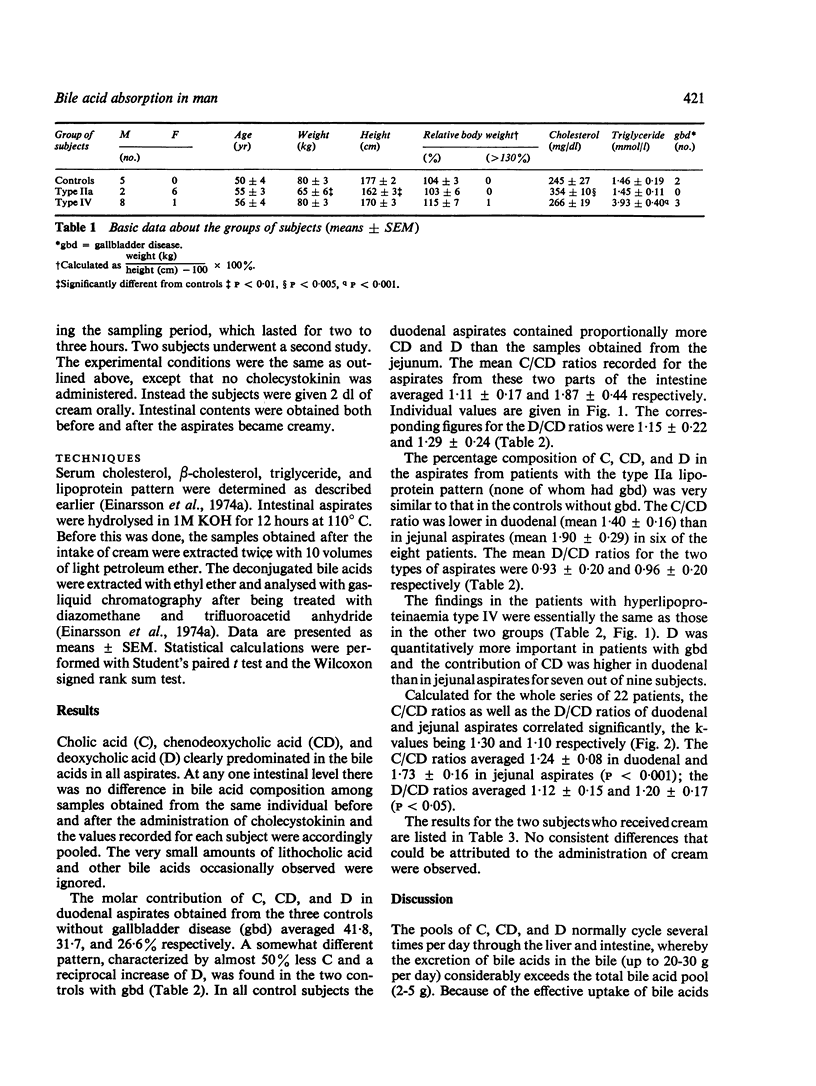
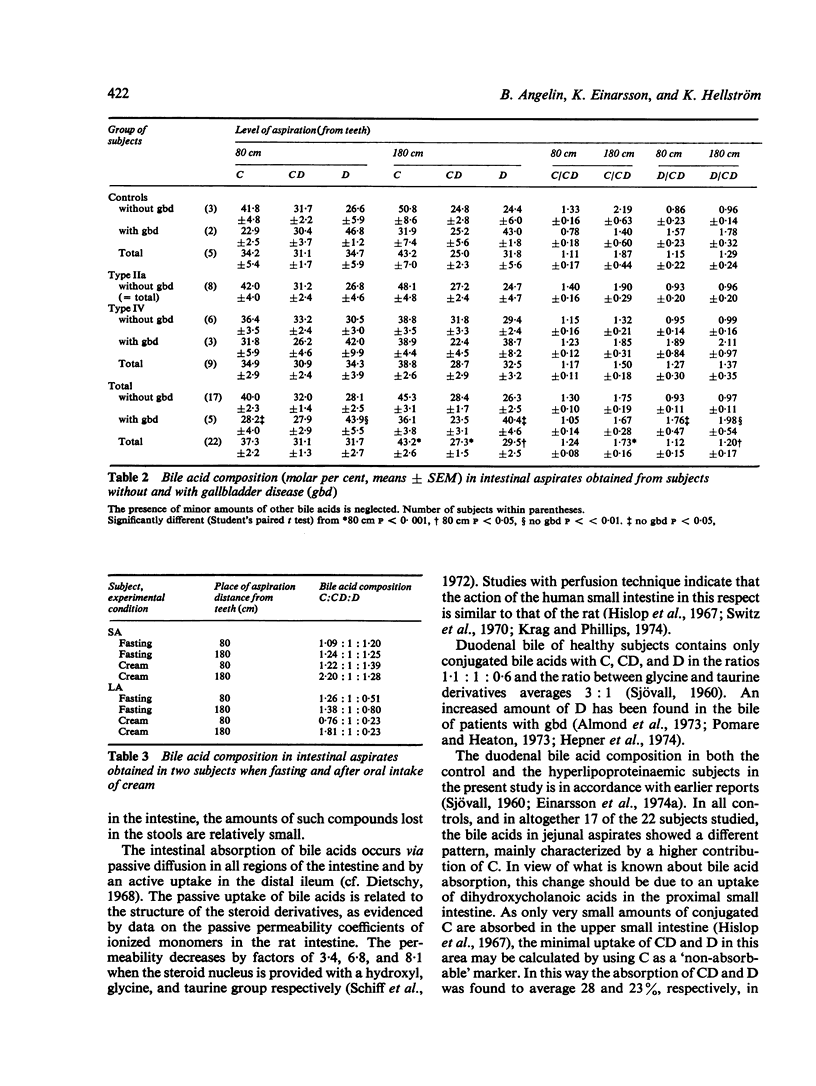
Bile acid composition was determined in duodenal and jejunal aspirates obtained under fasting conditions in normolipidaemic controls and in patients with the type IIa and type IV lipoprotein patterns. In 17 out of the 22 subjects studied, the duodenal as compared with the jejunal aspirates contained proportionally more CD (chenodeoxycholic acid) than C (cholic acid). The two types of aspirates also differed slightly with regard to the D (deoxycholic acid): CD ratio, which was higher in samples drawn from the jejunum. These findings, compatible with an absorpiton of about 30% of CD in the upper small intestine, were approximately the same in all groups of patients. As evidenced by additional experiments in two subjects, an oral intake of cream does not significantly influence the absorption of CD in the upper small intestine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almond H. R., Vlahcevic Z. R., Bell C. C., Jr, Gregory D. H., Swell L. Bile acid pools, kinetics and biliary lipid composition before and after cholecystectomy. N Engl J Med. 1973 Dec 6;289(23):1213–1216. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197312062892302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont J. L., Carlson L. A., Cooper G. R., Fejfar Z., Fredrickson D. S., Strasser T. Classification of hyperlipidaemias and hyperlipoproteinaemias. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(6):891–915. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dam H., Prange I., Jensen M., Kallehauge H. E., Fenger H. J. Studies on human bile. V. Influence of cholestyramine treatment on the composition of bile in healthy subjects. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1971 Apr;10(3):188–197. doi: 10.1007/BF02020930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M. Mechanisms for the intestinal absorption of bile acids. J Lipid Res. 1968 May;9(3):297–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Hellström K., Kallner M. Bile acid kinetics in relation to sex, serum lipids, body weights, and gallbladder disease in patients with various types of hyperlipoproteinemia;. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1301–1311. doi: 10.1172/JCI107876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Hellström K., Kallner M. Effect of cholic acid feeding on bile acid kinetics and neutral fecal steroid excretion in hyperlipoproteinemia (types II and IV). Metabolism. 1974 Sep;23(9):863–873. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(74)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einarsson K., Hellström K. The formation of deoxycholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid in man. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Feb;46(2):183–190. doi: 10.1042/cs0460183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbutt J. T., Kenney T. J. Effect of cholestyramine on bile acid metabolism in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1972 Nov;51(11):2781–2789. doi: 10.1172/JCI107100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepner G. W., Hofmann A. F., Malagelada J. R., Szczepanik P. A., Klein P. D. Increased bacterial degradation of bile acids in cholecystectomized patients. Gastroenterology. 1974 Apr;66(4):556–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepner G. W., Hofmann A. F., Thomas P. J. Metabolism of steroid and amino acid moieties of conjugated bile acids in man. II. Glycine-conjugated dihydroxy bile acids. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jul;51(7):1898–1905. doi: 10.1172/JCI106992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krag E., Phillips S. F. Active and passive bile acid absorption in man. Perfusion studies of the ileum and jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jun;53(6):1686–1694. doi: 10.1172/JCI107720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomare E. W., Heaton K. W. The effect of cholecystectomy on bile salt metabolism. Gut. 1973 Oct;14(10):753–762. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomare E. W., Low-Beer T. S. Measurement and validation of human bile salt pool size and synthesis. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Dec 17;57(3):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff E. R., Small N. C., Dietschy J. M. Characterization of the kinetics of the passive and active transport mechanisms for bile acid absorption in the small intestine and colon of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1351–1362. doi: 10.1172/JCI106931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. D., Shioda R., Estrich D. L., Splitter S. D. Effect of cholestyramine on composition of duodenal bile in obese human subjects. Metabolism. 1972 Feb;21(2):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(72)90062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


