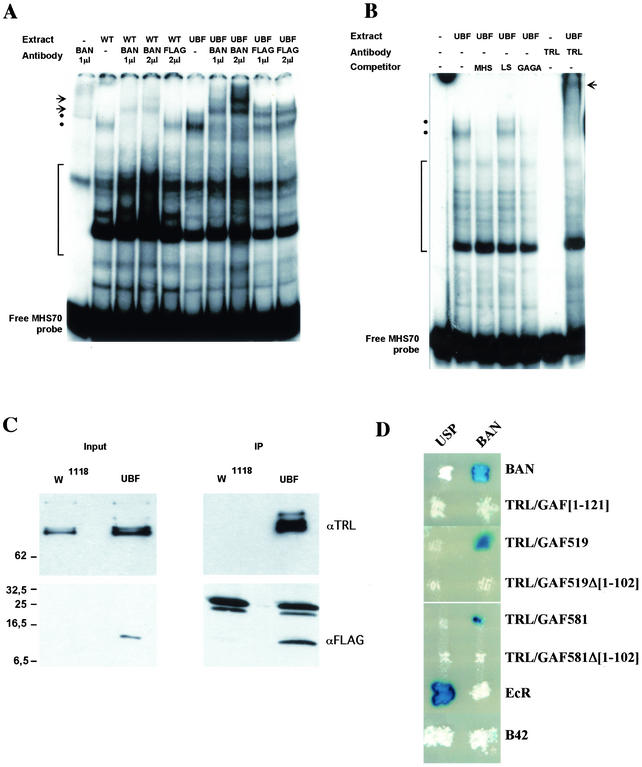
FIG. 6.
(A and B) Gel shift analysis of MHS-70 binding activities. (A) Binding of proteins in nuclear extracts from w1118 embryos (WT) or da:Gal4, UBF/+ embryos (UBF) was analyzed in a gel shift assay using the MHS-70 fragment as a probe in the absence (−) or in the presence of BAN or FLAG antibodies as indicated. The positions of BAN-containing low-mobility complexes in the absence (dots) or the presence (arrows) of BAN antibody are indicated. The position of nonspecific complexes that are not displaced by the addition of unlabeled probe is indicated (bracket). (B) Binding of proteins in a nuclear extract from da:Gal4, UBF/+ embryos (UBF) was analyzed in a gel shift assay using the MHS-70 labeled probe in the absence (−) or in the presence of competitors DNAs or TRL/GAF antibody (TRL) as indicated. Positions of the BAN containing complexes in the absence (dots) or the presence (arrow) of TRL/GAF antibody are indicated. The position of unspecific complexes that are not competed against by a 100-fold molar excess of MHS-70 probe is indicated (bracket). (C) Coimmunoprecipitation of BAN-FLAG with theTRL/GAF. Nuclear protein extracts from w1118 or da:Gal4/UBF (UBF) larvae were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG beads and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-TRL/GAF (TRL) or anti-FLAG (FLAG) antibodies. Aliquots (1/60) of the input extracts (input) were analyzed in parallel using the indicated antibody. The positions of protein molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are shown on the left. (D) Interaction of BAN and GAF in a yeast two-hybrid assay. Each patch corresponds to diploid yeast colonies coexpressing either the BAN protein (right column) or the USP (left column) as a control; both fused to the DNA binding domain of LexA; and BAN, full-length or truncated TRL/GAF isoforms, or EcR, all fused to the B42 transactivation domain (rows). Interactions resulted in the activation of a lacZ reporter gene placed under the control of LexA binding sites and were revealed in a β-galactosidase assay. Interaction (84) between the EcR-B1 isoform (EcR) and USP provided a positive control, while expression of the B42 domain alone served as a negative control.