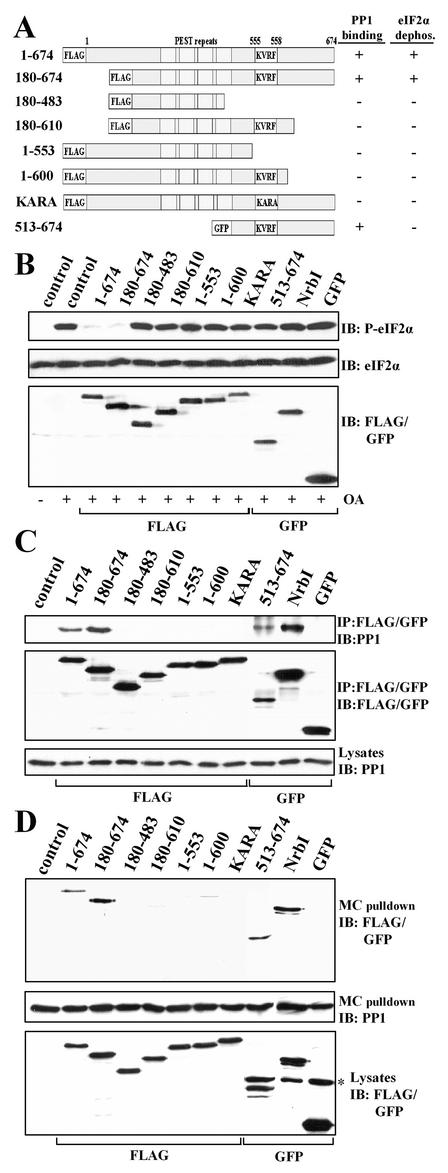
FIG. 3.
Structure-function analysis of GADD34 as a component of a cellular eIF-2α phosphatase. (A) A schematic representation of theGADD34 mutants analyzed in this study, with blocks highlighting the N-terminal tag, the central PEST repeats, and the consensus KVRF PP1-binding motif. The presence and absence of eIF-2α phosphatase activity (panel B) and PP1 binding (panels C and D) displayed by GADD34 proteins are summarized at the right side of panel A: + indicates a positive function and − indicates an absence of function. All proteins were FLAG tagged with the exception of GFP-tagged GADD34(513-674). (B) HEK293T cells expressing the GADD34 proteins were treated with 1 μM OA for 1 h, and eIF-2α phosphorylation was assayed by immunoblotting with an anti-phosphoserine-51-eIF-2α antibody. NrbI represents a fragment of the neuronal actin-binding protein (amino acids 286 to 552) known to bind PP1. Immunoblotting for total eIF-2α demonstrated equal protein loading, and anti-FLAG/GFP immunoblots (IB) showed equivalent expression of GADD34 proteins. Control, lysates of untransfected cells. (C) The GADD34 proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) using anti-FLAG M2 beads or an anti-GFP polyclonal antibody. The immunoprecipitates were subjected to SDS-PAGE, transferred to a PVDF membrane, and immunoblotted (IB) with anti-FLAG, anti-GFP, and anti-PP1 antibodies. Control, lysates of untransfected cells. (D) Cellular PP1 complexes were affinity isolated on microcystin-LR-Sepharose as described in Materials and Methods. The microcystin-bound proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblotting (IB) with anti-FLAG, anti-GFP, and anti-PP1 antibodies. The asterisk indicates a nonspecific band recognized by anti-GFP antibody. Control, lysates of untransfected cells.