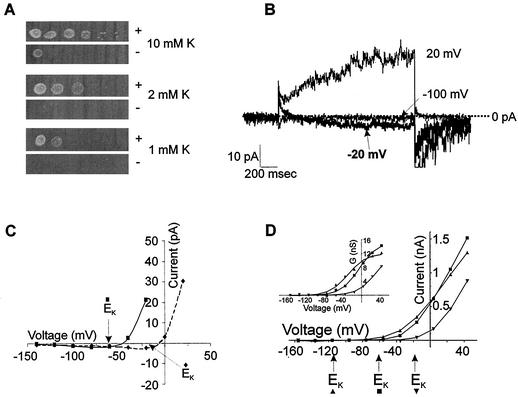
FIG. 5.
(A) Expression of NcTOKA overcomes K+-limited growth phenotype of the WΔ3TOK1Δ yeast mutant. The leftmost spots show patterns of growth after 3 days at 30°C after innoculation with 5 μl of culture at 0.5 × 108 cells/ml. Serial 10-fold dilutions of the first inocula are shown on the right. Growth is on arginine-phosphate medium (33) containing adenine and galactose and supplemented with 1, 2, or 10 mM KCl. “+” and “−” denote WΔ3TOK1Δ cells transformed with pYES2-NcTOKA and pYES2, respectively. (B and C) NcTOKA-mediated inward currents. The pipette solution included the following: 100 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 3 mM K2ATP, 10 mM HEPES, 4 mM EGTA, and 20 mM KOH (pH 7.4). (B) Whole-cell currents recorded by using SBS containing 60 mM KCl and 1 mM CaCl2 resulting from voltage steps to 20, −20, and −100 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV. Note that the EK was −16 mV. (C) Current-voltage relationship of NcTOKA currents from the same cells shown in panel A. Solid and dashed lines represent data from cells in SBS containing 10 and 60 mM K+, respectively. (D) Typical current-voltage relationship of NcTOKA whole-cell currents recorded by using SBS containing 1 (▴), 10 (▪), and 60 (▾) mM KCl. Calculated K+ equilibrium potentials (Erev) for each solution are indicated by arrows below the x axis. (Inset) Relationship between steady-state chord conductance NcTOKA currents and voltage. Chord conductance (G) was calculated as Iss/(Vm − EK), where Iss is the steady-state current at test voltage (Vm). Data were fitted (by using Clampfit 8.1) to a Boltzman equation of the form G = Gmax/[1 + exp(Vm − V0.5)/S], where G is the chord conductance at test voltage (Vm), Gmax is the maximal chord conductance, V0.5 is the voltage at which G is half maximal, and S is the slope factor equivalent to RT/δF, where δ is the apparent gating charge and R, T, and F have their usual meanings. For data presented at 1 mM K+, Gmax = 12.1 nS and V0.5 = −29 mV; at 10 mM K+, Gmax = 15.8 nS and V0.5 = −5.2 mV; and at 60 mM K+, Gmax = 13.1 nS and V0.5 = +32 mV. The δ value for all fittings was 1.2.