Full text
PDF
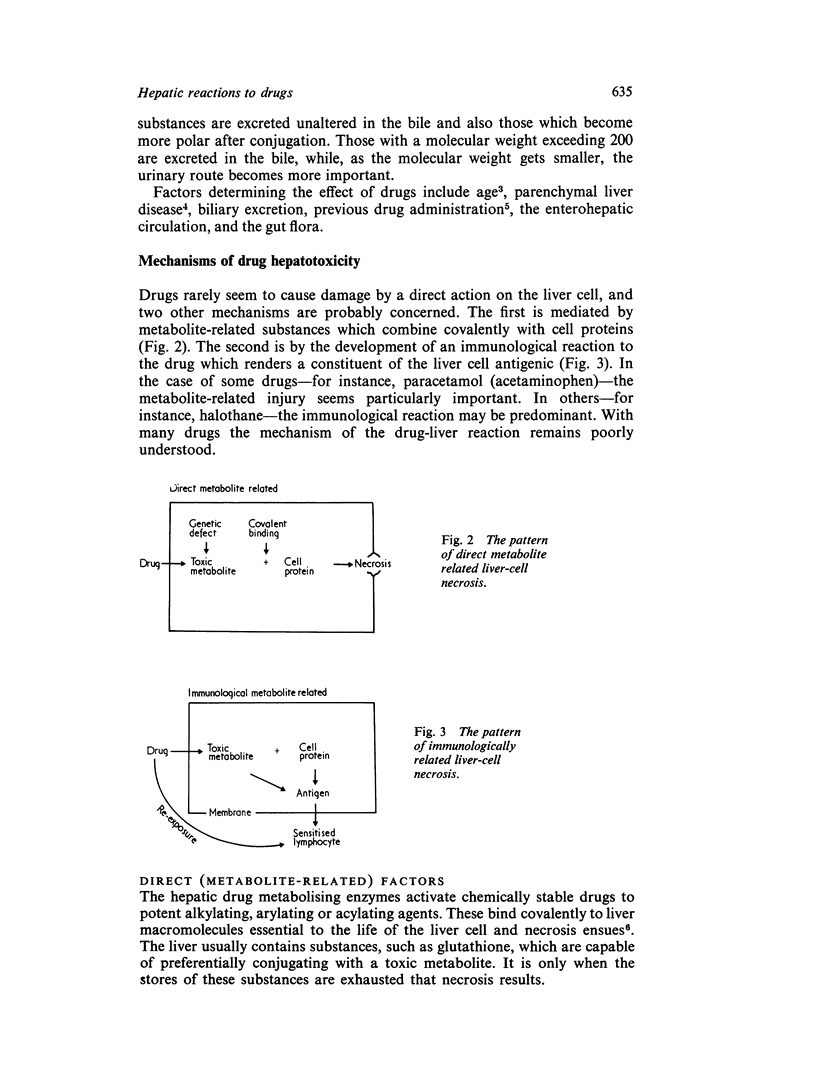

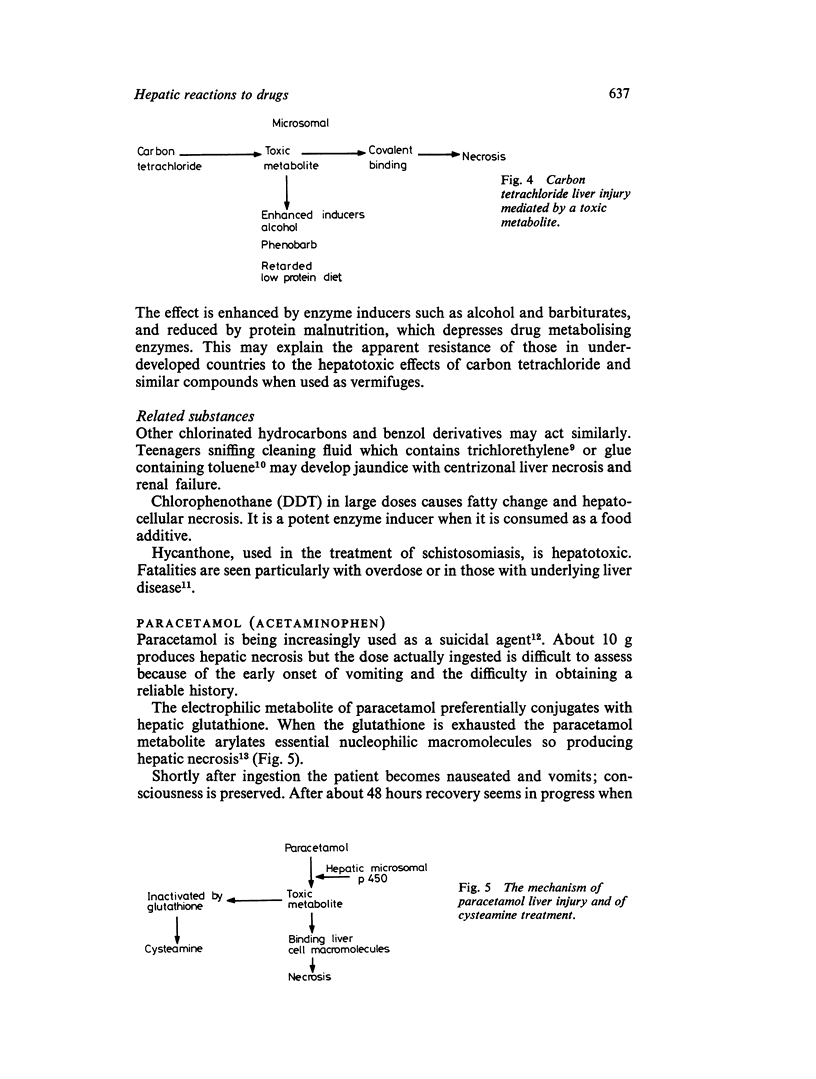




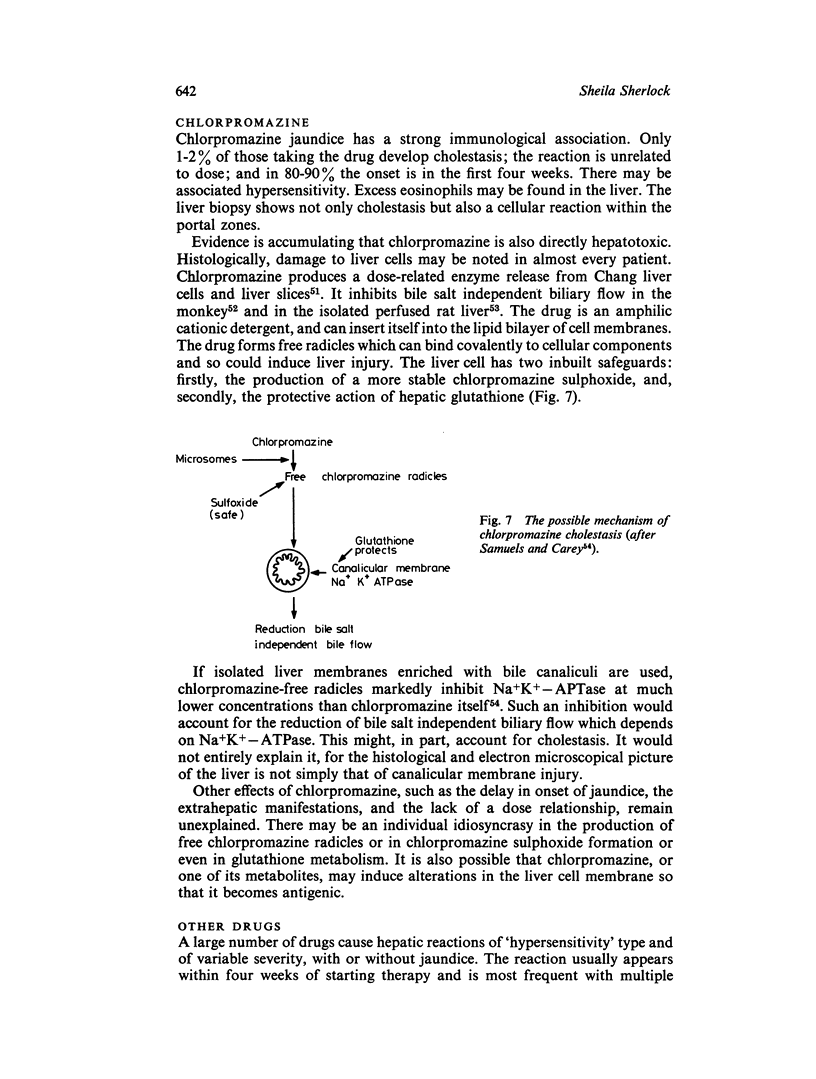

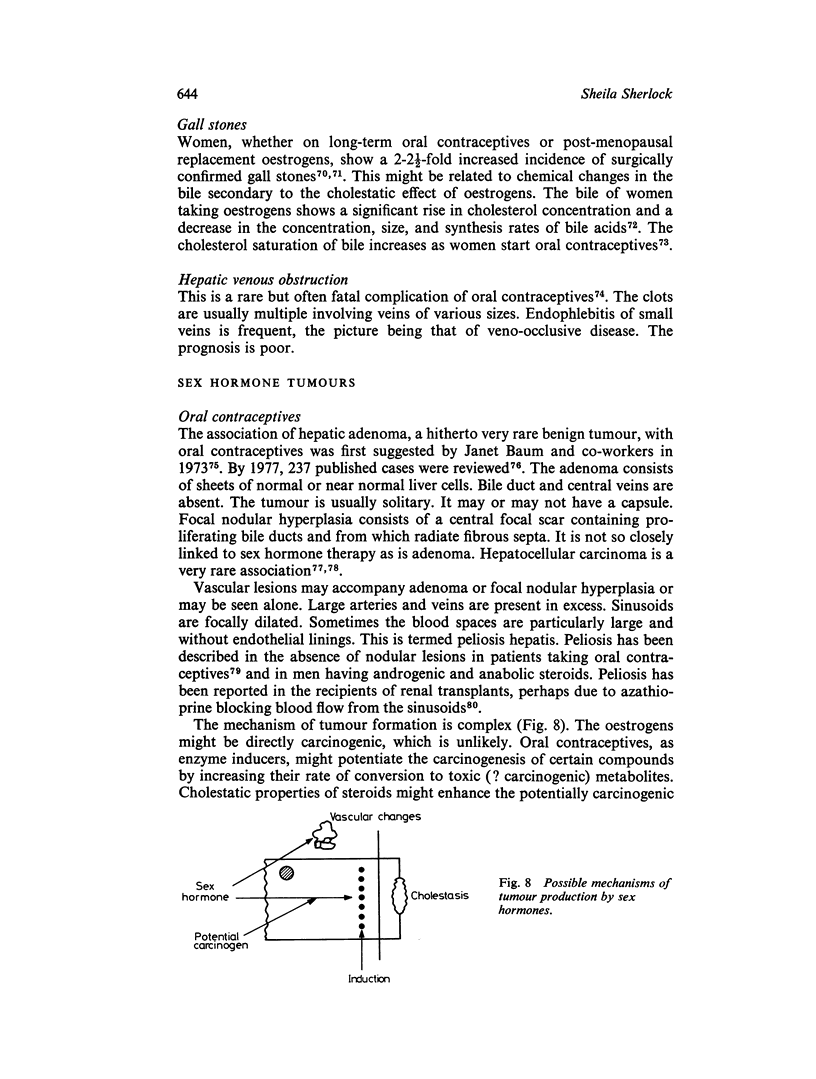




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeyda J., Barnardo D., Baker H., Levene G. M., Landells J. W. Structural and functional abnormalities of the liver in psoriasis before and during methotrexate therapy. Br J Dermatol. 1972 Dec;87(6):623–631. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1972.tb07453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpert L. I. Veno-occlusive disease of the liver associated with oral contraceptives: case report and review of literature. Hum Pathol. 1976 Nov;7(6):709–718. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(76)80082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baerg R. D., Kimberg D. V. Centrilobular hepatic necrosis and acute renal failure in "solvent sniffers". Ann Intern Med. 1970 Nov;73(5):713–720. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-73-5-713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum J. K., Bookstein J. J., Holtz F., Klein E. W. Possible association between benign hepatomas and oral contraceptives. Lancet. 1973 Oct 27;2(7835):926–929. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92594-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennion L. J., Ginsberg R. L., Gernick M. B., Bennett P. H. Effects of oral contraceptives on the gallbladder bile of normal women. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jan 22;294(4):189–192. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197601222940403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black M., Mitchell J. R., Zimmerman H. J., Ishak K. G., Epler G. R. Isoniazid-associated hepatitis in 114 patients. Gastroenterology. 1975 Aug;69(2):289–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonkowsky H. L., Mudge G. H., McMurtry R. J. Chronic hepatic inflammation and fibrosis due to low doses of paracetamol. Lancet. 1978 May 13;1(8072):1016–1018. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckstein A. H., Attia A. A. Oxacillin hepatitis. Two patients with liver biopsy, and review of the literature. Am J Med. 1978 Mar;64(3):519–522. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90246-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. K., Detmer D. E. Proper management of hepatic adenoma associated with oral contraceptives. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1977 May;144(5):703–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. Liver pathology in hycanthone hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jul;75(1):103–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crome P., Vale J. A., Volans G. N., Widdop B., Goulding R. Oral methionine in the treatment of severe paracetamol (Acetaminophen) overdose. Lancet. 1976 Oct 16;2(7990):829–830. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91211-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl M. G., Gregory M. M., Scheuer P. J. Liver damage due to methotrexate in patients with psoriasis. Br Med J. 1971 Mar 20;1(5750):625–630. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5750.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M., Portmann B., Searle M., Wright R., Williams R. Histological evidence of carcinoma in a hepatic tumour associated with oral contraceptives. Br Med J. 1975 Nov 29;4(5995):496–498. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5995.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degott C., Rueff B., Kreis H., Duboust A., Potet F., Benhamou J. P. Peliosis hepatis in recipients of renal transplants. Gut. 1978 Aug;19(8):748–753. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.8.748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M. F., Nimmo J., Prescott L. F. Experimental paracetamol-induced hepatic necrosis: a histopathological study. J Pathol. 1971 Apr;103(4):225–229. doi: 10.1002/path.1711030404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujovne C. A., Zimmerman H. J. Cytotoxicity of phenothiazines on Chang liver cells as measured by enzyme leakage. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Jun;131(2):583–587. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-33931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson H. A., Henderson B., Benton B. Liver-cell adenomas associated with use of oral contraceptives. N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 26;294(9):470–472. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602262940904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson H. A., Reynolds T. B., Henderson B., Benton B. Regression of liver cell adenomas associated with oral contraceptives. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Feb;86(2):180–182. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-2-180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell G. C., Joshua D. E., Uren R. F., Baird P. J., Perkins K. W., Kronenberg H. Androgen-induced hepatoma. Lancet. 1975 Feb 22;1(7904):430–432. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91494-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forker E. L. The effect of estrogen on bile formation in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1969 Apr;48(4):654–663. doi: 10.1172/JCI106023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouts J. R. The stimulation and inhibition of hepatic microsomal drug-metabolizing enzymes with special reference to effects of environmental contaminants. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;17(3):804–809. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(70)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garibaldi R. A., Drusin R. E., Ferebee S. H., Gregg M. B. Isoniazid-associated hepatitis. Report of an outbreak. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 Sep;106(3):357–365. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.106.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. L. Letter: Aspirin hepatotoxicity. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Jun;80(6):773–773. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-6-773_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski M., Stenram U., Bergqvist A. Focal nodular hyperplasia of the liver, benign hepatomas, oral contraceptives and other drugs affecting the liver. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1975 Nov;83(6):615–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb01388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. L., Threlfall E. J., Rowe B., Pinegar J. A., Gibson G. L. Lactose-fermenting Salmonella indiana from turkeys in Britain. Lancet. 1978 Dec 2;2(8101):1197–1198. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92175-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn A. N., Douglas A. P., James O. The spectrum of paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose: clinical and epidemiological studies. Postgrad Med J. 1978 Jun;54(632):400–404. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.54.632.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman W. H., Mushin W. W. Jaundice after repeated exposure to halothane: a further analysis of reports to the Committee on Safety of Medicines. Br Med J. 1978 Nov 25;2(6150):1455–1456. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6150.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishak K. G., Kirchner J. P., Dhar J. K. Granulomas and cholestatic--hepatocellular injury associated with phenylbutazone. Report of two cases. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Jul;22(7):611–617. doi: 10.1007/BF01073079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. K., Tolman K. G. Chronic liver disease and acetaminophen. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Sep;87(3):302–304. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-3-302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew M. C., Van Coller B., Prowse C. M., Skikne B., Wolfsdorf J. I., Isdale J., Krawitz S., Altman H., Levin S. E., Bothwell T. H. Occurrence of primary hepatocellular cancer and peliosis hepatis after treatment with androgenic steroids. S Afr Med J. 1976 Jul 24;50(32):1233–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatskin G. Hepatic tumors: possible relationship to use of oral contraceptives. Gastroenterology. 1977 Aug;73(2):386–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatskin G., Kimberg D. V. Recurrent hepatitis attributable to halothane sensitization in an anesthetist. N Engl J Med. 1969 Mar 6;280(10):515–522. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196903062801001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. M., 2nd, Casarella W. J., Johnson P. M., Wolff M. The clinical, radiologic, and pathologic characterization of benign hepatic neoplasms. Alleged association with oral contraceptives. Medicine (Baltimore) 1978 May;57(3):223–237. doi: 10.1097/00005792-197805000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRusso N. F., Hoffman N. E., Korman M. G., Hofmann A. F., Cowen A. E. Determinants of fasting and postprandial serum bile acid levels in healthy man. Am J Dig Dis. 1978 May;23(5):385–391. doi: 10.1007/BF01072919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. J., Carney C. N., Lapis J. L., Higgins T., Fallon H. J. Diphenylhydantoin-induced hepatic necrosis. A case study. Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):422–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees A. W., Allan G. W., Smith J., Tyrrell W. F., Fallon R. J. Toxicity form rifampicin plus isoniazid and rifampicin plus ethambutol therapy. Tubercle. 1971 Sep;52(3):182–190. doi: 10.1016/0041-3879(71)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi A. J., Sherlock S., Walker D. Phenylbutazone and isoniazid metabolism in patients with liver disease in relation to previous drug therapy. Lancet. 1968 Jun 15;1(7555):1275–1279. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunzer M. R., Huang S. N., Ward K. M., Sherlock S. Jaundice due to erythromycin estolate. Gastroenterology. 1975 May;68(5 Pt 1):1284–1291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunzer M., Huang S. N., Ginsburg J., Ahmed M., Sherlock S. Jaundice due to carbimazole. Gut. 1975 Nov;16(11):913–917. doi: 10.1136/gut.16.11.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddrey W. C., Boitnott J. K. Drug-induced chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1977 Jun;72(6):1348–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean A. E., McLean E. Diet and toxicity. Br Med Bull. 1969 Sep;25(3):278–281. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miguet J. P., Mavier P., Soussy C. J., Dhumeaux D. Induction of hepatic microsomal enzymes after brief administration of rifampicin in man. Gastroenterology. 1977 May;72(5 Pt 1):924–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. J., Dwyer J., Klatskin G. Halothane hepatitis: benign resolution of a severe lesion. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Aug;89(2):212–215. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-2-212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. R., Jollows D. J. Progress in hepatology. Metabolic activation of drugs to toxic substances. Gastroenterology. 1975 Feb;68(2):392–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. R., Nelson S. D., Thorgeirsson S. S., McMurtry R. J., Dybing E. Metabolic activation: biochemical basis for many drug-induced liver injuries. Prog Liver Dis. 1976;5:259–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. R., Zimmerman H. J., Ishak K. G., Thorgeirsson U. P., Timbrell J. A., Snodgrass W. R., Nelson S. D. Isoniazid liver injury: clinical spectrum, pathology, and probable pathogenesis. Ann Intern Med. 1976 Feb;84(2):181–192. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-84-2-181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moult P. J., Sherlock S. Halothane-related hepatitis. A clinical study of twenty-six cases. Q J Med. 1975 Jan;44(173):99–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyfors A., Hopwood D. Liver ultrastructure in psoriatics related to methotrexate therapy. 1. A prospective study of findings in hepatocytes from 24 patients before and after methotrexate treatment. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1977 Nov;85(6):787–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyfors A. Liver biopsies from psoriatics related to methotrexate therapy. 3. Findings in post-methotrexate liver biopsies from 160 psoriatics. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1977 Jul;85(4):511–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb03882.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien E. T., Yeoman W. B., Hobby J. A. Hepatorenal damage from toluene in a "glue sniffer". Br Med J. 1971 Apr 3;2(5752):29–30. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5752.29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Gorman T., Koff R. S. Salicylate hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1977 Apr;72(4 Pt 1):726–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paronetto F., Popper H. Lymphocyte stimulation induced by halothane in patients with hepatitis following exposure to halothane. N Engl J Med. 1970 Aug 6;283(6):277–280. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197008062830602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pertsemlidis D., Panveliwalla D., Ahrens E. H., Jr Effects of clofibrate and of an estrogen-progestin combination on fasting biliary lipids and cholic acid kinetics in man. Gastroenterology. 1974 Apr;66(4):565–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pessayre D., Bentata M., Degott C., Nouel O., Miguet J. P., Rueff B., Benhamou J. P. Isoniazid-rifampin fulminant hepatitis. A possible consequence of the enhancement of isoniazid hepatotoxicity by enzyme induction. Gastroenterology. 1977 Feb;72(2):284–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. J., Oda M., Mak E., Fisher M. M., Jeejeebhoy K. N. Microfilament dysfunction as a possible cause of intrahepatic cholestasis. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jul;69(1):48–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F., Newton R. W., Swainson C. P., Wright N., Forrest A. R., Matthew H. Successful treatment of severe paracetamol overdosage with cysteamine. Lancet. 1974 Apr 6;1(7858):588–592. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92649-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F., Park J., Ballantyne A., Adriaenssens P., Proudfoot A. T. Treatment of paracetamol (acetaminophen) poisoning with N-acetylcysteine. Lancet. 1977 Aug 27;2(8035):432–434. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)90612-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F., Roscoe P., Wright N., Brown S. S. Plasma-paracetamol half-life and hepatic necrosis in patients with paracetamol overdosage. Lancet. 1971 Mar 13;1(7698):519–522. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91125-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C. D., Gibbs A. R., Williams W. J. Halothane macrophage migration inhibtiion factor test in halothane-associated hepatitis. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Apr;30(4):312–316. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.4.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot A. T., Park J. Changing pattern of drugs used for self-poisoning. Br Med J. 1978 Jan 14;1(6105):90–93. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6105.90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot A. T., Wright N. Acute paracetamol poisoning. Br Med J. 1970 Sep 5;3(5722):557–558. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5722.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramseur W. L., Cooper M. R. Asymptomatic liver cell adenomas. Another case of resolution after discontinuation of oral contraceptive use. JAMA. 1978 Apr 21;239(16):1647–1648. doi: 10.1001/jama.239.16.1647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. K., Wilkinson G. R., Branch R. A., Schenker S. Effect of age and parenchymal liver disease on the disposition and elimination of chlordiazepoxide (librium). Gastroenterology. 1978 Sep;75(3):479–485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodman J. S., Deutsch D. J., Gutman S. I. Methyldopa Hepatitis. A report of six cases and review of the literature. Am J Med. 1976 Jun;60(7):941–948. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90564-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg D. M., Neelon F. A. Acetaminophen and liver disease. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Jan;88(1):129–129. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-1-129_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels A. M., Carey M. C. Effects of chlorpromazine hydrochloride and its metabolites on Mg2+- and Na+,K+-ATPase activities of canalicular-enriched rat liver plasma membranes. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jun;74(6):1183–1190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuer P. J., Summerfield J. A., Lal S., Sherlock S. Rifampicin hepatitis. A clinical and histological study. Lancet. 1974 Mar 16;1(7855):421–425. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92381-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer I. L., Weiner J. M., McPeak C. M., Thursby M. W. Oral contraceptives in acute viral hepatitis. JAMA. 1975 Sep 1;233(9):979–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmon F. R. Effects of estrogens on the liver. Gastroenterology. 1978 Sep;75(3):512–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotolongo R. P., Neefe L. I., Rudzki C., Ishak K. G. Hypersensitivity reaction to sulfasalazine with severe hepatotoxicity. Gastroenterology. 1978 Jul;75(1):95–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swank L. A., Chejfec G., Nemchausky B. A. Allopurinol-induced granulomatous hepatitis with cholangitis and a sarcoid-like reaction. Arch Intern Med. 1978 Jun;138(6):997–998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toghill P. J., Smith P. G., Benton P., Brown R. C., Matthews H. L. Methyldopa liver damage. Br Med J. 1974 Aug 31;3(5930):545–548. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5930.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowell J., Peto R., Smith A. C. Controlled trial of repeated halothane anaesthetics in patients with carcinoma of the uterine cervix treated with radium. Lancet. 1975 Apr 12;1(7911):821–824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utili R., Boitnott J. K., Zimmerman H. J. Dantrolene-associated hepatic injury. Incidence and character. Gastroenterology. 1977 Apr;72(4 Pt 1):610–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergani D., Tsantoulas D., Eddleston A. L., Davis M., Williams R. Sensitisation to halothane-altered liver components in severe hepatic necrosis after halothane anaesthesia. Lancet. 1978 Oct 14;2(8094):801–803. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92585-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton B., Simpson B. R., Strunin L., Doniach D., Perrin J., Appleyard A. J. Unexplained hepatitis following halothane. Br Med J. 1976 May 15;1(6019):1171–1176. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6019.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaby D., Ogle S. J., Paradinas F. J., Randell J. B., Murray-Lyon I. M. Liver damage from long-term methyltestosterone. Lancet. 1977 Aug 6;2(8032):262–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. R., Schenker S. Effects of liver disease on drug disposition in man. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Dec 15;25(24):2675–2681. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90256-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. T. Hepatic metabolism of drugs. Gut. 1972 Jul;13(7):579–585. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.7.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler K., Poulsen H. Liver disease with periportal sinusoidal dilatation. A possible complication to contraceptive steroids. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1975;10(7):699–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R., Eade O. E., Chisholm M., Hawksley M., Lloyd B., Moles T. M., Edwards J. C., GArdner M. J. Controlled prospective study of the effect on liver function of multiple exposures to halothane. Lancet. 1975 Apr 12;1(7911):817–820. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)93000-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


