Abstract
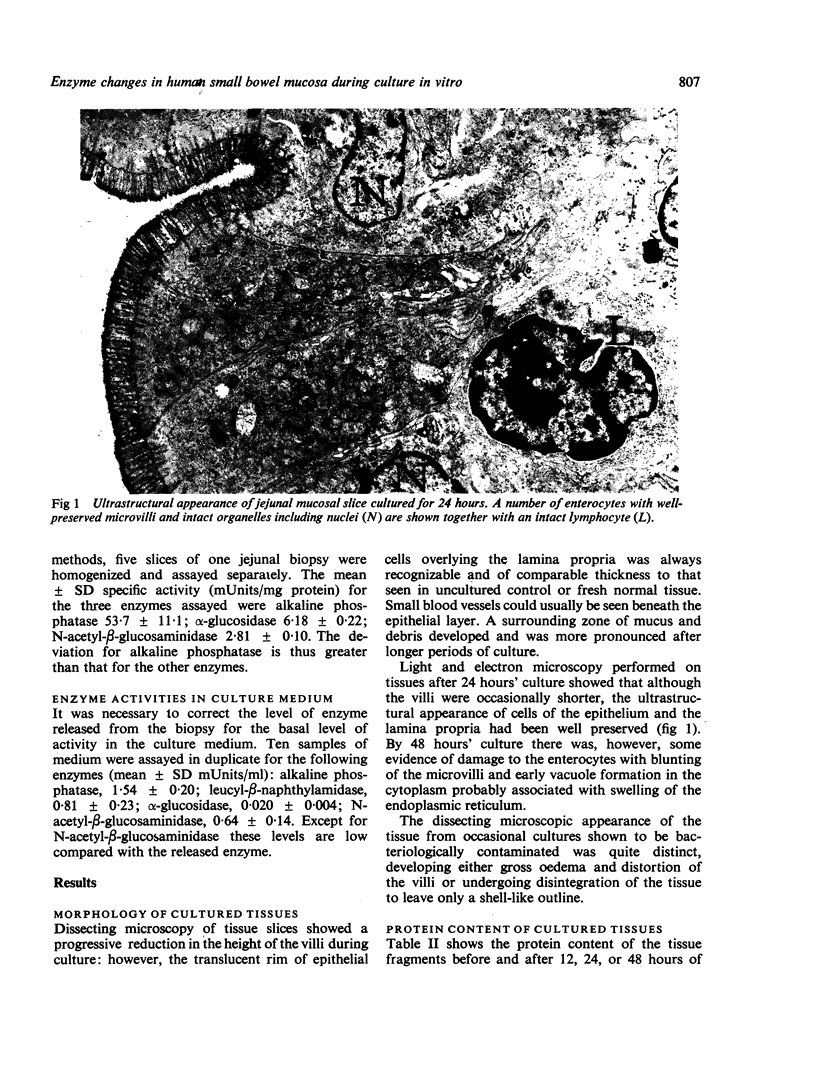
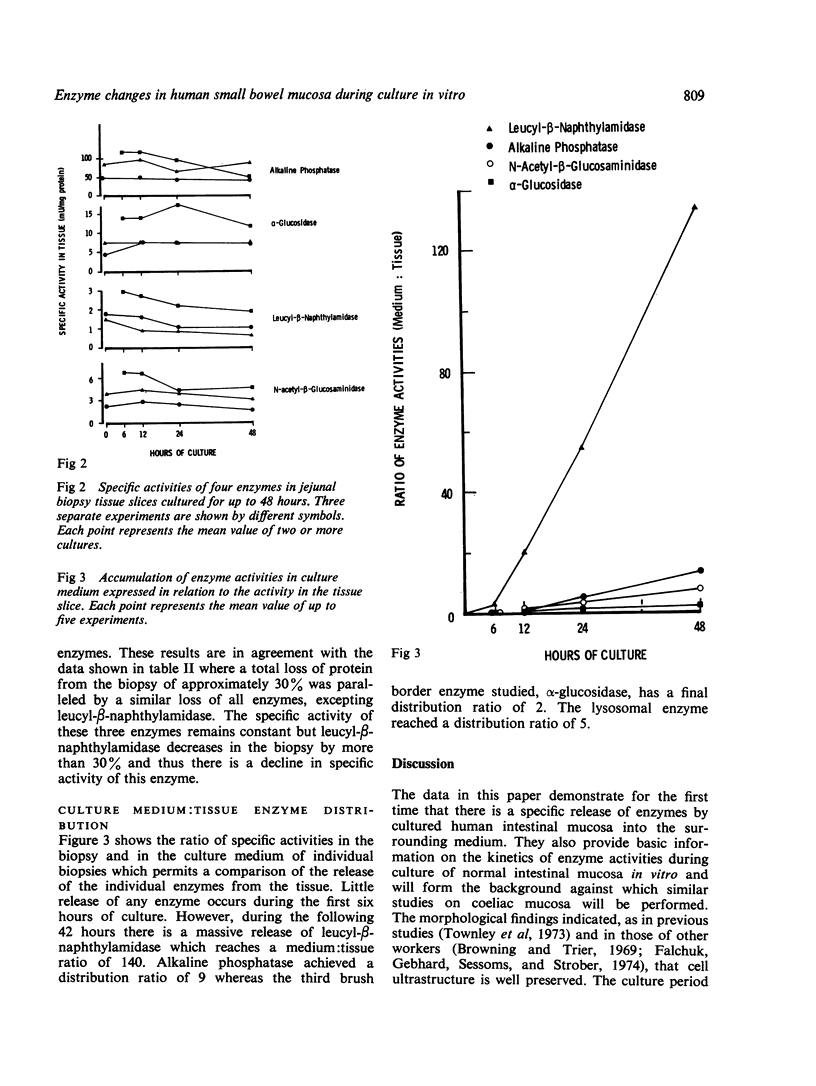
Human jejunal biopsy slices were maintained in culture for up to 48 hours. At 24 hours there was good morphological preservation but by 48 hours there was ultrastructural evidence of damage to the enterocytes. During culture the tissue had lost a certain amount of protein. At the same time the levels of three brush border enzymes (alkaline phosphatase, α-glucosidase, and leucyl-β-naphthylamidase) and one lysosomal enzyme (N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase) showed a progressive decrease. Alkaline phosphatase, α-glucosidase, and N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase accumulated in the medium throughout the experimental period to give a medium:tissue distribution ratio of between 2 and 9. Leucyl-β-naphthylamidase had a medium:tissue ratio of 140 after 48 hours of culture suggesting a selective secretion of this enzyme by the tissue.
Full text
PDF

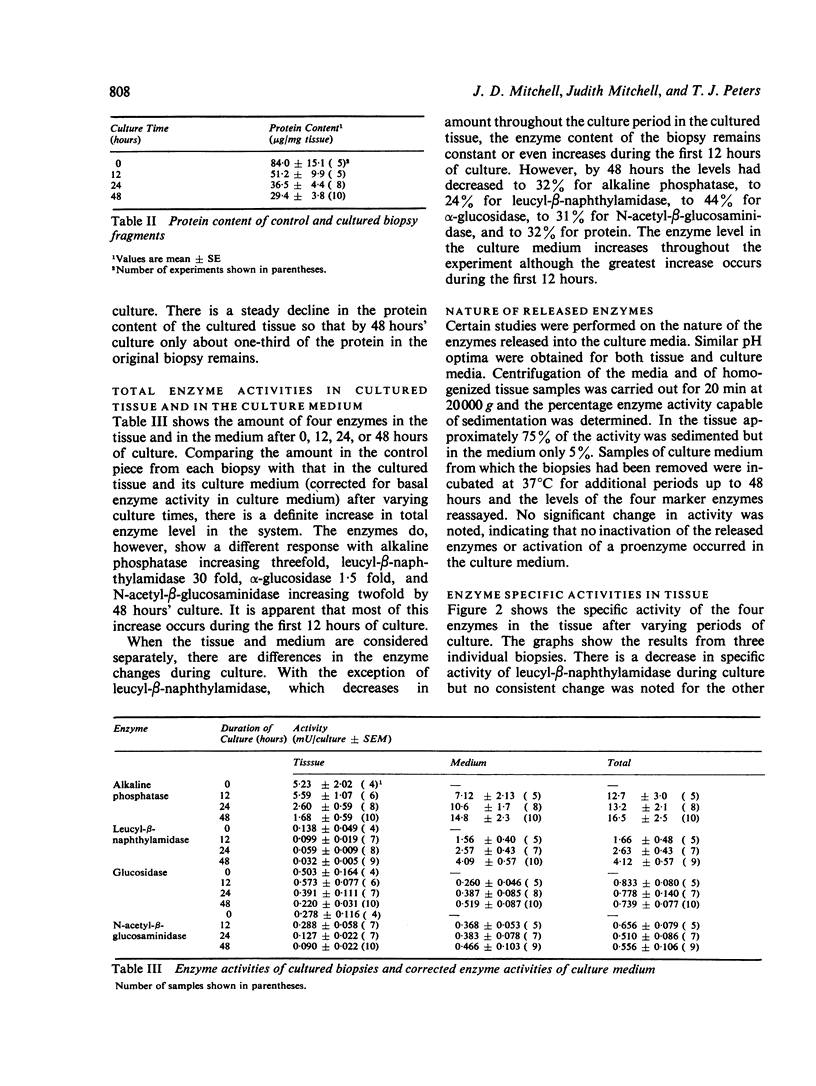


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpers D. H. The relation of size to the relative rates of degradation of intestinal brush border proteins. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2621–2630. doi: 10.1172/JCI107080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth C. C. Enterocyte in coeliac disease. 1. Br Med J. 1970 Sep 26;3(5725):725–731. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5725.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers W. E., Finkenstaedt J. T., de Duve C. Lysosomes in lymphoid tissue. I. The measurement of hydrolytic activities in whole homogenates. J Cell Biol. 1967 Feb;32(2):325–337. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning T. H., Trier J. S. Organ culture of mucosal biopsies of human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1969 Aug;48(8):1423–1432. doi: 10.1172/JCI106108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck W. P., Hall F. F., Ratliff C. R. Hormonal control of intestinal alkaline phosphatase secretion in the dog. Gastroenterology. 1973 Sep;65(3):445–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichholz A. Studies on the organization of the brush border in intestinal epithelial cells. V. Subfractionation of enzymatic activities of the microvillus membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug;163(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falchuk Z. M., Gebhard R. L., Sessoms C., Strober W. An in vitro model of gluten-sensitive enteropathy. Effect of gliadin on intestinal epithelial cells of patients with gluten-sensitive enteropathy in organ culture. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):487–500. doi: 10.1172/JCI107582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götze H., Adelson J. W., Hadorn H. B., Portmann R., Troesch V. Hormone-elicited enzyme release by the small intestinal wall. Gut. 1972 Jun;13(6):471–476. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.6.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Pathologic mechanisms in neutrophil-mediated injury. Am J Pathol. 1972 Sep;68(3):593–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F., Donaldson R. M., Jr, Trier J. S. Organ culture of rabbit small intestine: prolonged in vitro steady state protein synthesis and secretion and secretory IgA secretion. Gastroenterology. 1972 Oct;63(4):541–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb P. M., Strober W., Falchuk Z. M., Laster L. Incorporation of L-leucine-14C into immunoglobulins by jejunal biopsies of patients with celiac sprue and other gastrointestinal diseases. J Clin Invest. 1971 Mar;50(3):559–569. doi: 10.1172/JCI106525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. D., Bhathal P., Cornell H., Townley R. R. Gluten enteropathy in vitro: a culture system for the study of coeliac disease. Gut. 1972 Oct;13(10):848–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss S., Lobley R. W., Holmes R. Enterokinase in human duodenal juice following secretin and pancreozymin and its relationship to bile salts and trypsin. Gut. 1972 Oct;13(10):851–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Doe W. F., Heath J. R., Mitchell J. D. Lysosomal acid hydrolase activity in intestinal biopsies from control subjects and patients with coeliac disease. Gut. 1973 May;14(5):430–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Müller M., De Duve C. Lysosomes of the arterial wall. I. Isolation and subcellular fractionation of cells from normal rabbit aorta. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1117–1139. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riecken E. O., Stewart J. S., Booth C. C., Pearse A. G. A histochemical study on the role of lysosomal enzymes in idiopathic steatorrhoea before and during a gluten-free diet. Gut. 1966 Aug;7(4):317–332. doi: 10.1136/gut.7.4.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townley R. R., Cornell H. J., Bhathal P. S., Mitchell J. D. Toxicity of wheat gliadin fractions in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1973 Jun 16;1(7816):1363–1364. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91679-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UGOLEV A. M. MEMBRANE (CONTACT) DIGESTION. Physiol Rev. 1965 Jul;45:555–595. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.3.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshaw A. L., Laster L. Protein synthesis by human intestinal mucosa: variations with diseases of the gut. J Surg Res. 1973 Apr;14(4):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(73)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]