Abstract
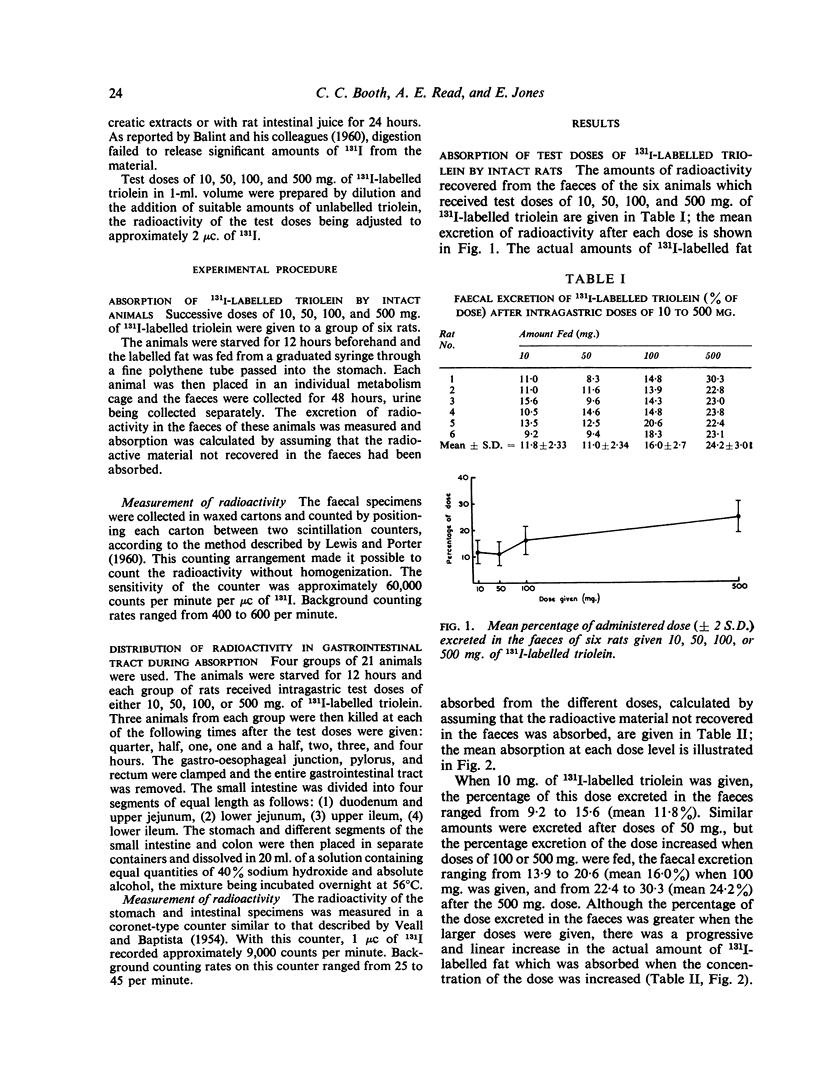
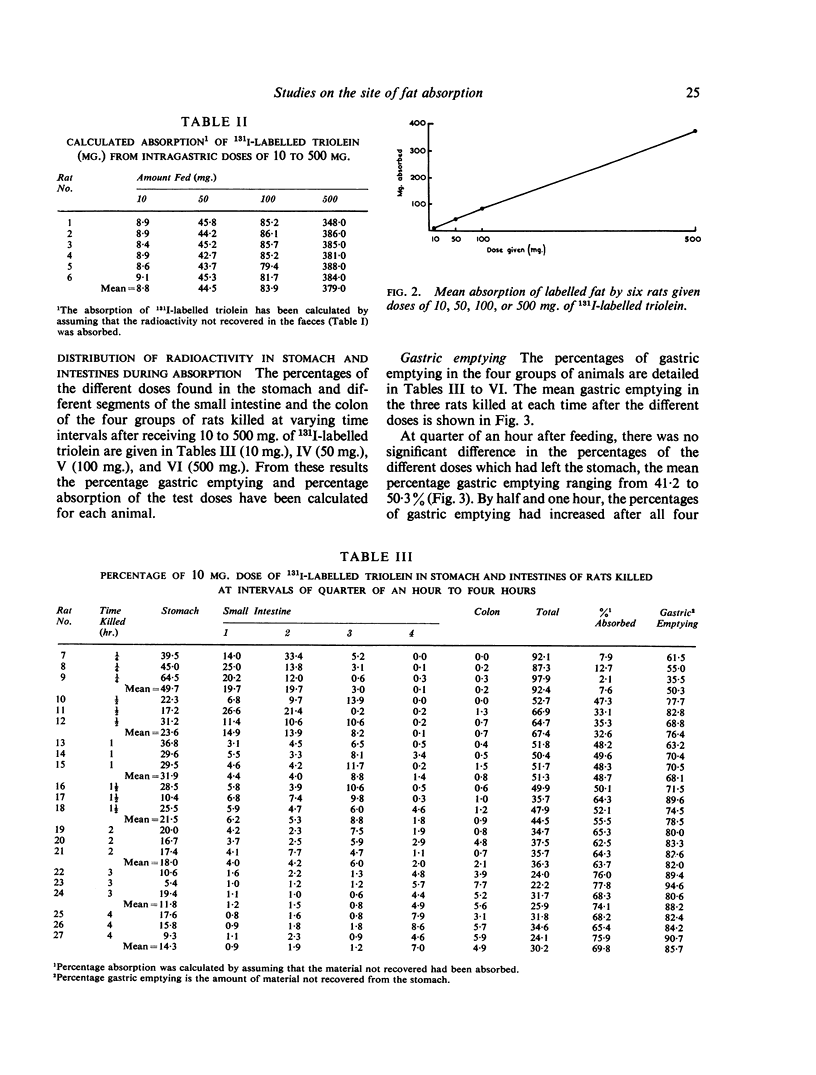
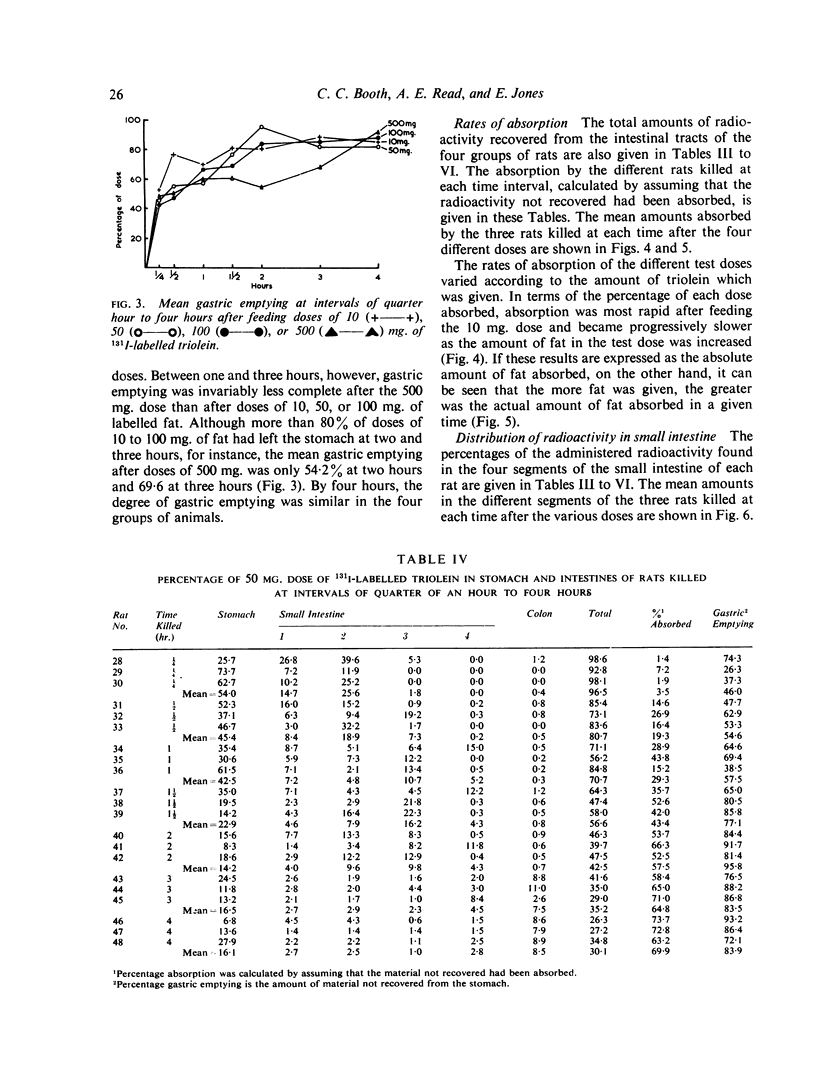
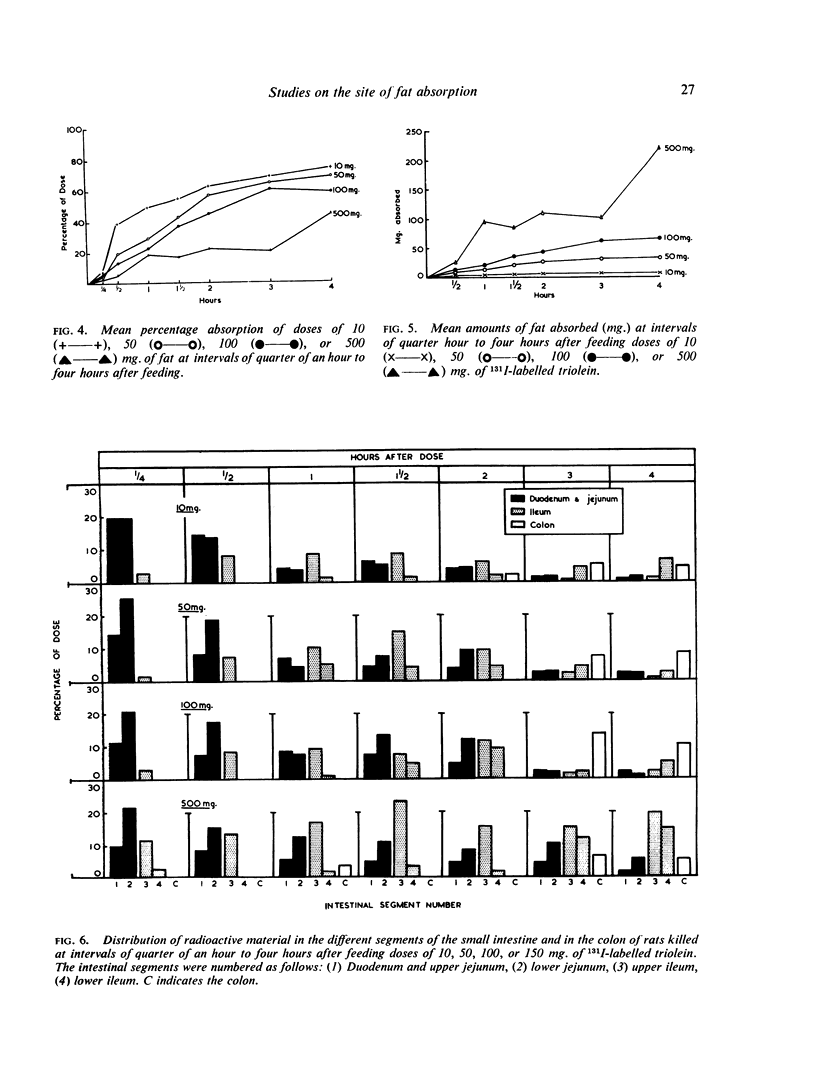
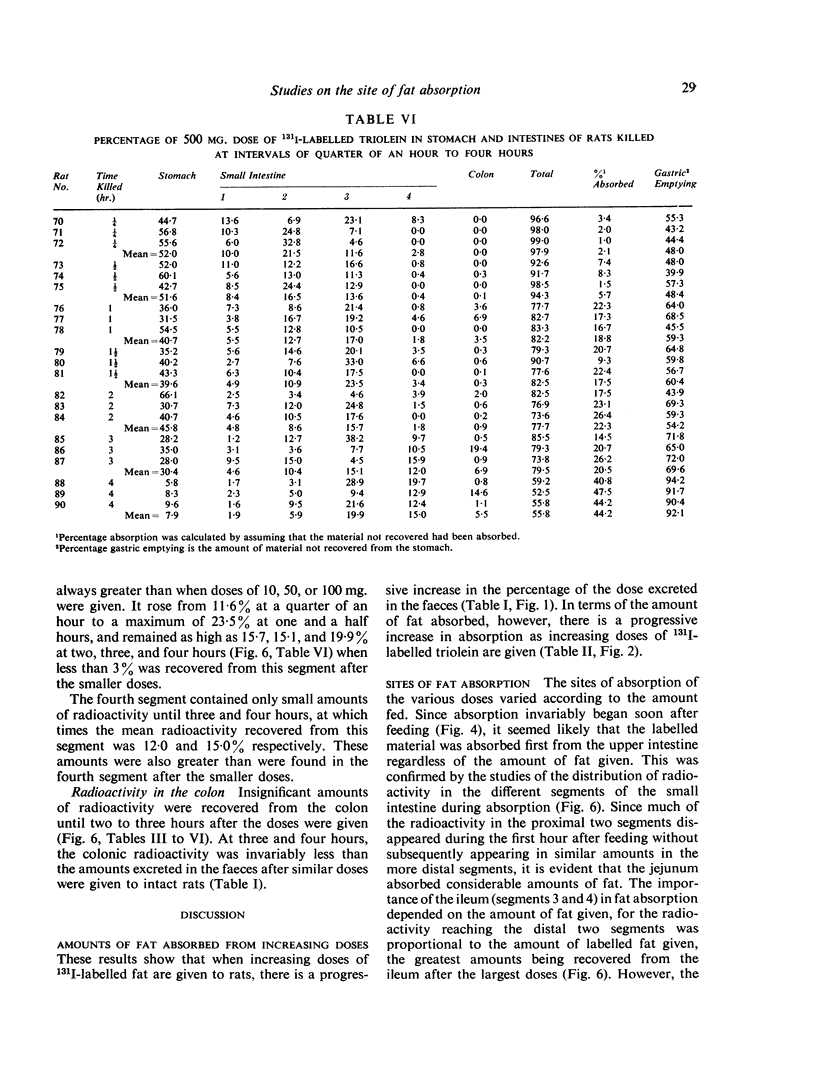
These studies on fat absorption in rats show that a small dose was relatively rapidly absorbed in the jejunum. With larger doses it was also absorbed in the ileum. When larger doses were given the jejunum responded to the increased load with an increased absorption, and fat was also absorbed in the ileum.
Full text
PDF
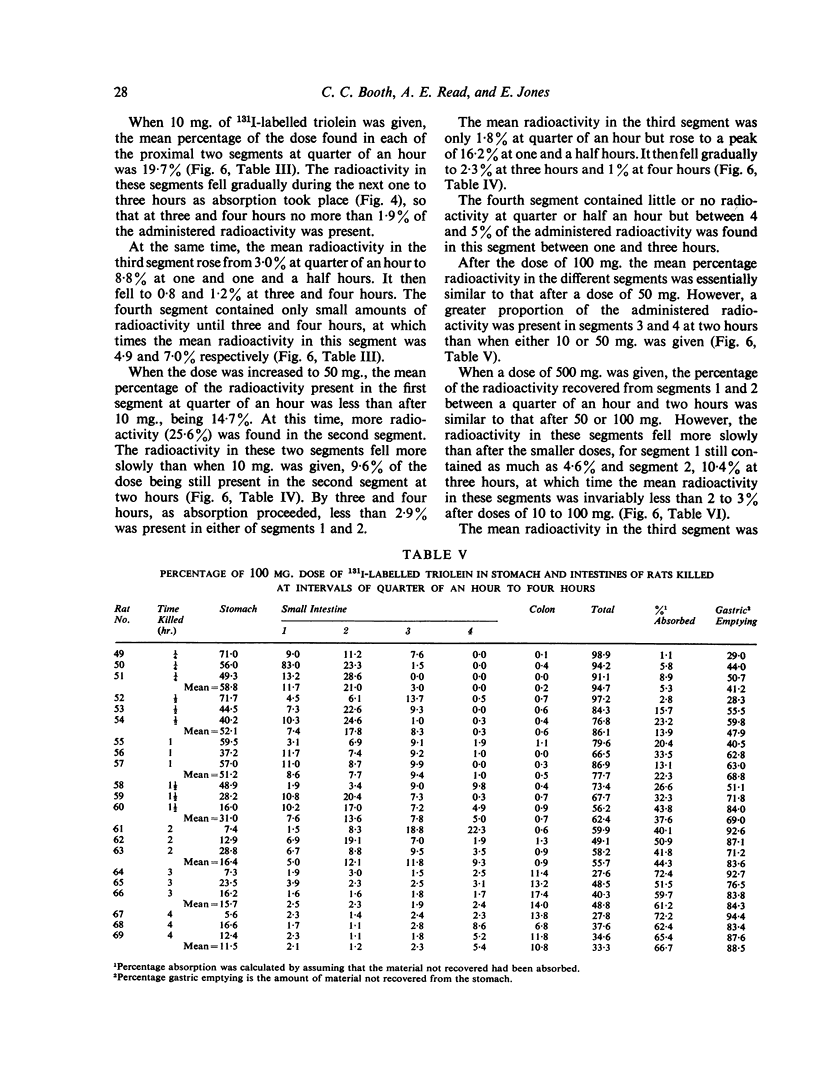


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALINT J., PENDOWER J., RAMSEY N. W. The stability of radio-iodinated olive oil. Clin Sci. 1960 May;19:321–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENSON J. A., Jr, CHANDLER G. N., VANSTEENHUYSE F. E., GAGNON J. O. Studies concerning the site of fat absorption in the small intestine of the rat. Gastroenterology. 1956 Jan;30(1):53–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOOTH C. C., MOLLIN D. L. The site of absorption of vitamin B12 in man. Lancet. 1959 Jan 3;1(7062):18–21. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)90979-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORGSTROM B., DAHLQVIST A., LUNDH G., SJOVALL J. Studies of intestinal digestion and absorption in the human. J Clin Invest. 1957 Oct;36(10):1521–1536. doi: 10.1172/JCI103549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUMMINS A. J., JUSSILA R. Comparison of glucose absorption rates in the upper and lower human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1955 Dec;29(6):982-92; discussion, 1003-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON A. M., ISSELBACHER K. J. The esterification of palmitate-1-C14 by homogenates of intestinal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39:150–160. doi: 10.1172/JCI104014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAVARGER P., GERLACH J. Variations dans le mode de résorption des differentes graisses et acides gras chez le rat. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1953;11(3):239–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazer A. C. Differentiation in the absorption of olive oil and oleic acid in the rat. J Physiol. 1943 Dec 31;102(3):306–312. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1943.sp004036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREMEN A. J., LINNER J. H., NELSON C. H. An experimental evaluation of the nutritional importance of proximal and distal small intestine. Ann Surg. 1954 Sep;140(3):439–448. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195409000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUBRAN M., PEARSON J. D. A screening test for steatorrhoea using 131I-labelled triolein. J Clin Pathol. 1958 Mar;11(2):165–169. doi: 10.1136/jcp.11.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. M., Porter I. H. Erythrocyte Survival in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1960 Mar;19(1):54–58. doi: 10.1136/ard.19.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKINS R. A., DIMITRIADOU A., BOOTH C. C. The rates and sites of absorption of 131 I-labelled albumin and sodium 131 I in the rat. Clin Sci. 1960 Nov;19:595–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNELL P. C., SPRAY G. H. The simultaneous measurement of absorption and transit in the gastro-intestinal tract of the rat. J Physiol. 1956 Feb 28;131(2):452–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER D. A. The absorption, transport, and deposition of fat; application of a new method for the determination of I 131-lipid activity in dogs and man. II. Am J Dig Dis. 1958 Sep;3(9):682–708. doi: 10.1007/BF02231240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN HANDEL E., ZILVERSMIT D. B. Limitation of radioiodine as a label for fat. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Dec;52(6):831–839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VEALL N., BAPTISTA A. M. A multi-tube gamma counting apparatus for small samples. Br J Radiol. 1954 Mar;27(315):198–199. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-27-315-198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


