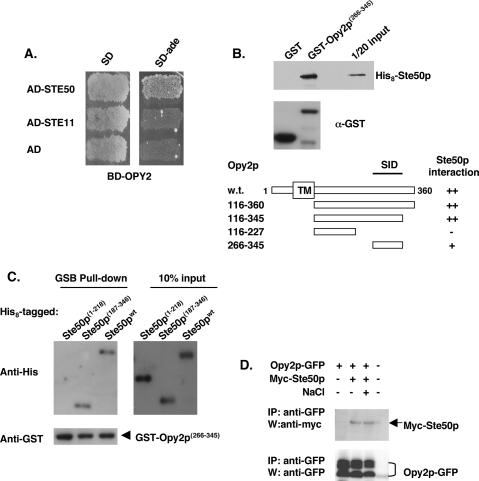
Figure 8.
Opy2p interacts with Ste50p. (A) Opy2p interacts with Ste50p in a yeast two-hybrid assay. (B) Mapping the SID of Opy2p. Bacterially expressed GST fusion proteins as indicated were purified onto glutathione-Sepharose beads; the beads were then blocked with 2% BSA, incubated with bacterial extract containing His8-tagged Ste50p, washed, and suspended in SDS-PAGE sample buffer. The presence of His8-tagged Ste50p was detected by an anti-His antibody, and visualized using the ECL detection system. The levels of the GST fusion proteins used in the binding assay were monitored by the anti-GST antibody. (Top) An amount of ∼5% input of the His 8-tagged Ste50p used in the assay is shown. (Bottom) Schematic representation of using various fragments of Opy2p, analyzed in the same way as described above, to map the SID of Opy2p. (C) Opy2p interacts with the C-terminal RA-like domain of Ste50p. Resin-binding assay using bacterially expressed GST-Opy2p SID and various His8-tagged Ste50p and fragments as indicated under the same conditions as described in B. (D) Opy2p interacts with Ste50p in vivo. GFP-tagged Opy2p was immunoprecipitated from cell extracts containing Myc-tagged Ste50p, and the presence of Myc-Ste50p in the immunocomplex was analyzed by Western blotting with an antibody against the Myc epitope (shown in the top panel). The relative amount of Opy2p in the immunoprecipitate was revealed by Western blotting with an antibody against GFP. (NaCl) Treatment of cells with 0.5 M NaCl for 5 min before harvest for the preparation of cells extracts.