Abstract
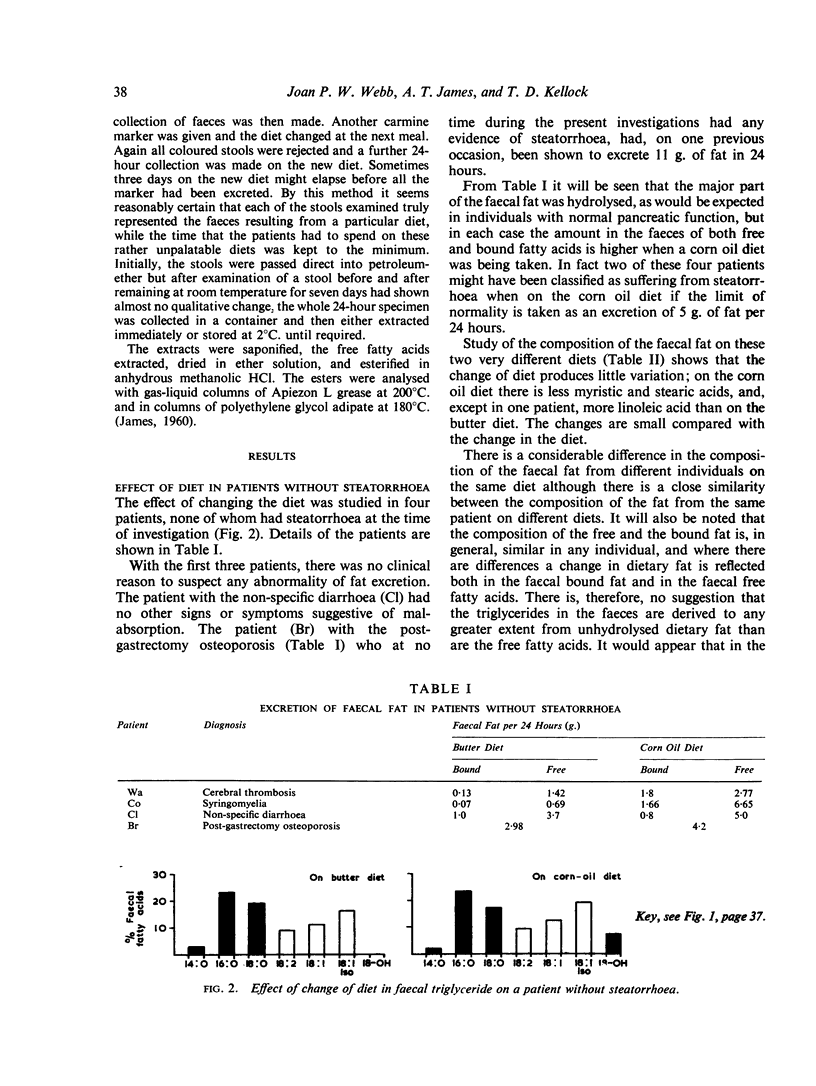
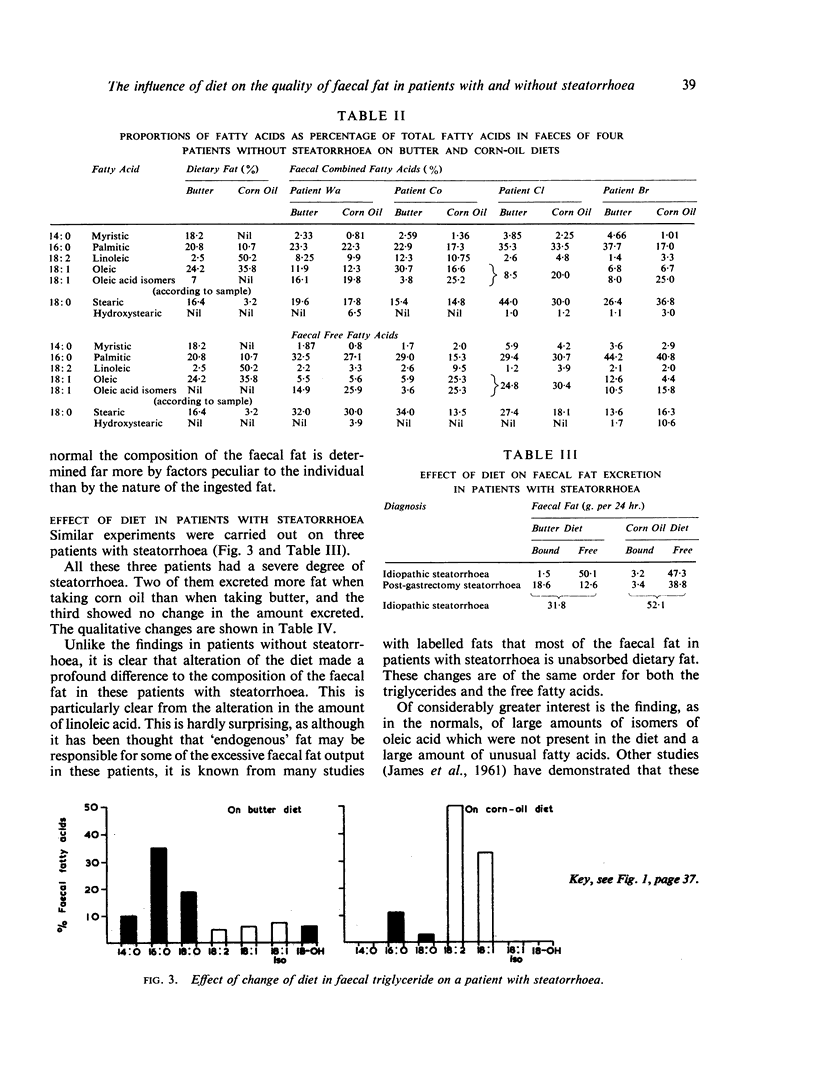
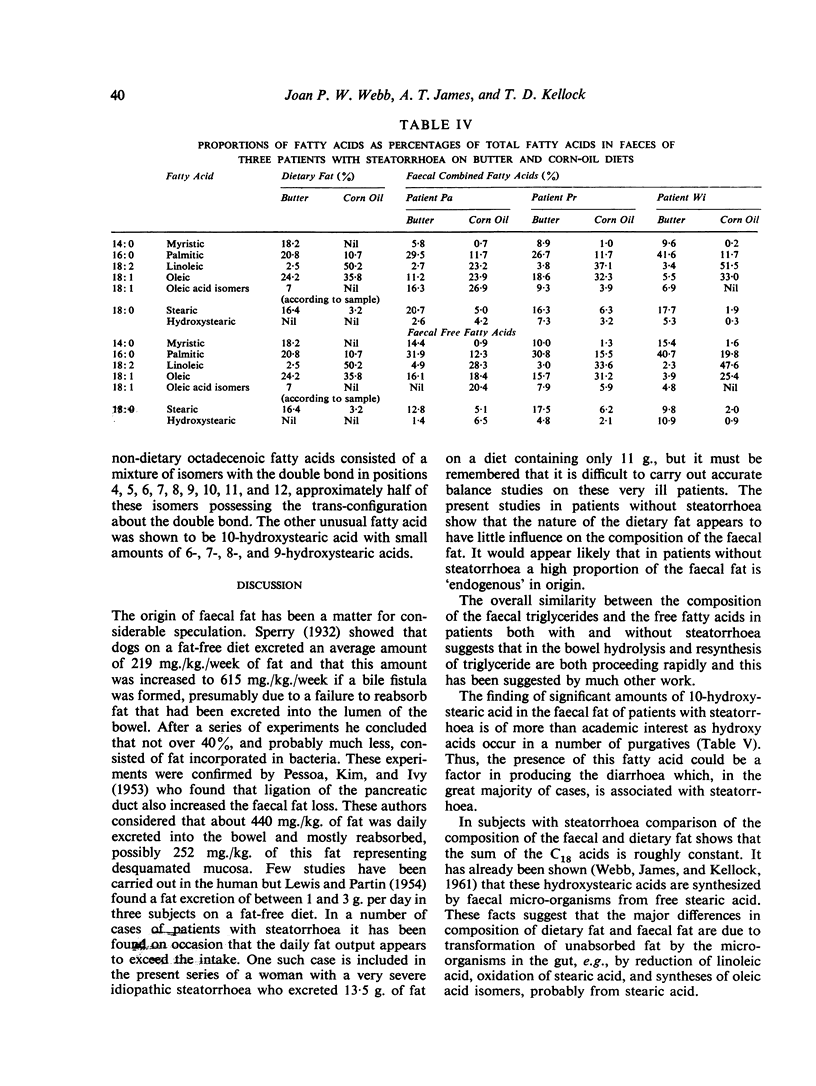
By the use of gas-liquid chromatography it has been shown that the quality of the faecal fat in individuals without steatorrhoea is little affected by changes in the quality of the dietary fat. Large amounts of non-dietary fatty acids have been identified in the faeces both of patients with and without steatorrhoea. These have been identified as a number of isomers of oleic acid and hydroxystearic acids, particularly 10-hydroxystearic acid.
Full text
PDF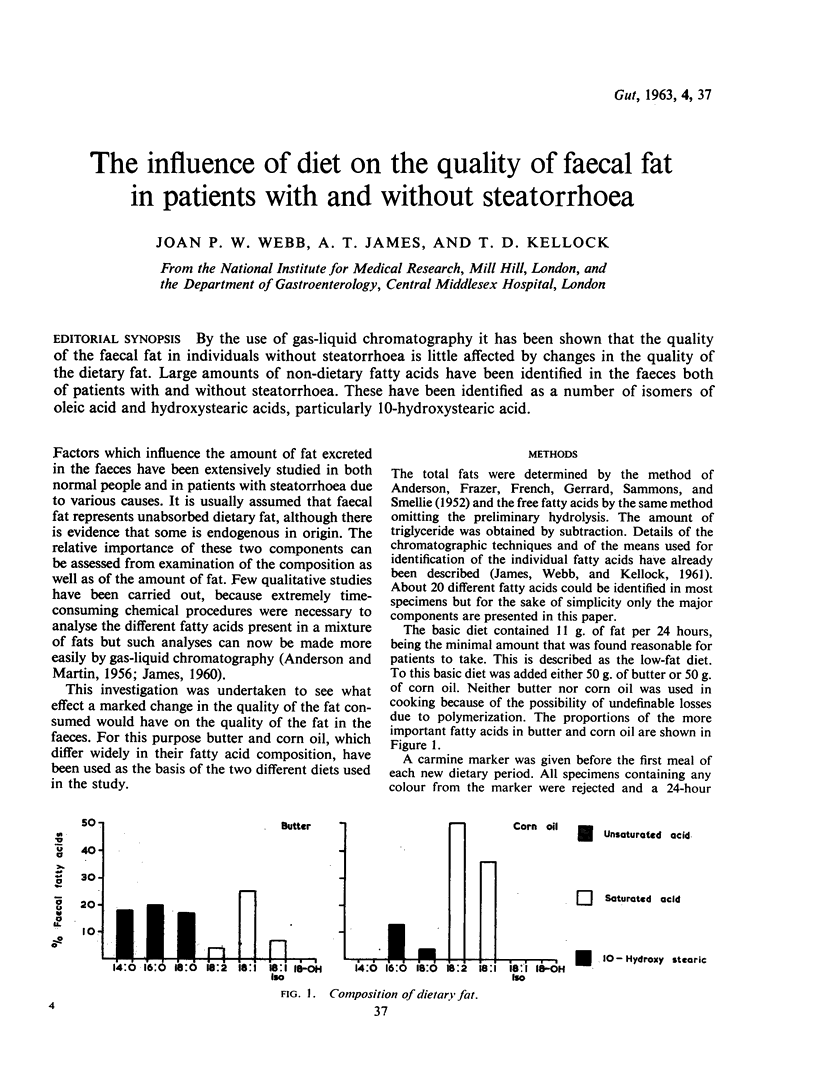

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON C. M., FRENCH J. M., SAMMONS H. G., FRAZER A. C., GERRARD J. W., SMELLIE J. M. Coeliac disease; gastrointestinal studies and the effect of dietary wheat flour. Lancet. 1952 Apr 26;1(6713):836–842. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(52)90795-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES A. T., MARTIN A. J. Gas-liquid chromatography: the separation and identification of the methyl esters of saturated and unsaturated acids from formic acid to n-octadecanoic acid. Biochem J. 1956 May;63(1):144–152. doi: 10.1042/bj0630144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES A. T., WEBB J. P., KELLOCK T. D. The occurrence of unusual fatty acids in faecal lipids from human beings with normal and abnormal fat absorption. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78:333–339. doi: 10.1042/bj0780333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS G. T., PARTIN H. C. Fecal fat on an essentially fat-free diet. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Jul;44(1):91–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PESSOA V. C., KIM K. S., IVY A. C. Fat absorption in absence of bile and pancreatic juice. Am J Physiol. 1953 Aug;174(2):209–218. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1953.174.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


