Figure 2.
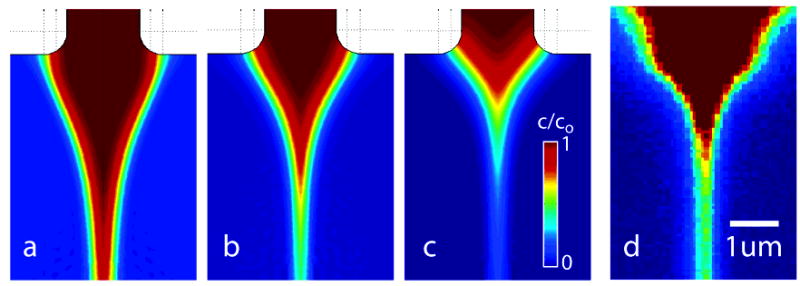
Scalar images of sample concentration (a–c). Three conditions of flow rate ratios, Qc/Qs (center channel/side channels), decreasing from left to right; from simulation. (a) Qc/Qs = 0.02 condition with center stream that is overly thick, in which mixing time is dominated by lateral diffusion in the focused stream. The concentration reaches 10% of co at x(c10%) = 22 μm downstream of the exit plane of the center nozzle. (b) An optimally sized stream, Qc/Qs = 0.01, x(c10%) = 8.2 μm, and (c) the Qc/Qs = 0.005 condition, x(c10%) = 4.3 μm, where diffusion time is again greater than optimum and dominated by the relatively slow convective diffusion process in the two-dimensional focusing region. (d) Fluorescence image from confocal scanning microscope of an optimally focused stream (with similar false color map), Qc/Qs = 0.01 and Qc ≈ 1 nL/s. The fluorescent agent is a 10 μM solution of 2 MD dextran-conjugated fluorescein in 10 mM PBS and mixing with 10 mM PBS buffer.
