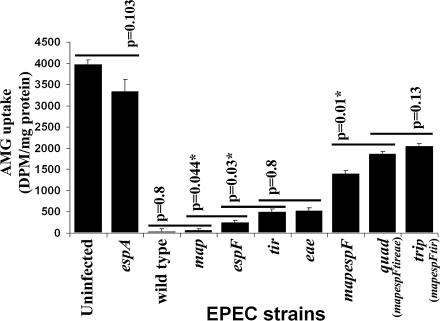
Fig. 5.
Map, EspF, Tir, and Intimin function together to inhibit SGLT-1 function. Differentiated Caco-2 cells were infected for 6 h with wild-type EPEC, the espA translocator mutant, or strains deleted for one or more of the map, espF, tir, and eae (Intimin) genes before assessing SGLT-1 activity by measuring uptake of the nonmetabolizable glucose analog 14C-labeled AMG [in disintegrations per minute (DPM)]. This reveals (i) minor roles for EspF, Tir, and Intimin, (ii) redundant cooperative roles for Map and EspF, (iii) a role for Tir–Intimin interaction, and (iv) that all four proteins function together to inhibit SGLT-1 function (n = 3; mean ± SE). Statistical significance (∗) between indicated pairs (horizontal lines) determined by Student’s t test. Note the ≈50% loss of SGLT-1 activity with quad/trip mutant (differ only in Intimin expression) is due to a slow Map/EspF/Tir/Intimin-independent mechanism (Fig. 4D).