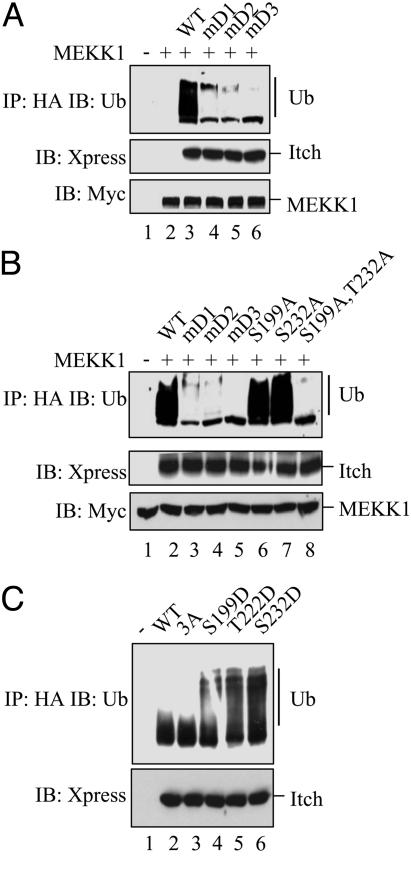
Fig. 3.
The JNK1 phosphoacceptor sites and the D domain are required for JNK1-mediated Itch activation. (A) D domain mutations prevent Itch activation by JNK1. Xpress-tagged WT Itch or D domain mutants were coexpressed in HEK293 cells with Myc-tagged MEKK1. (Top) Itch proteins were immunoprecipitated with anti-Xpress antibody and subjected to self-ubiquitylation in vitro. The extent of Itch ubiquitylation was examined by immunoblotting of gel-separated reaction mixtures with anti-Ub antibody. (Middle and Bottom) Itch and MEKK1 levels were examined by immunoblotting of unfractionated cell lysates with anti-Xpress (Middle) or anti-Myc (Bottom) antibodies. (B) JNK1-mediated phosphorylation is required for Itch activation. Xpress-tagged WT Itch, D domain (mD1, mD2, and mD3), and JNK1 phosphoacceptor site (S199A and T222A) mutants were expressed in HEK293 cells along with Myc-tagged MEKK1. (Top) Xpress-tagged Itch proteins were immunoprecipitated and subjected to self-ubiquitylation in vitro, and gels were separated and ubiquitylation was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-Ub antibody. (Middle and Bottom) Unfractionated cell lysates were immunoblotted with anti-Xpress (Middle) or anti-Myc (Bottom) antibodies. (C) Phosphomimic substitution mutations activate Itch. Xpress-tagged WT Itch and mutants that either abolish (S199A, T222A, and S232A) or mimic (S199D, T222D, or S232D) its JNK1 phosphoacceptor sites were expressed in HEK293 cells. After immunoprecipitation with anti-Xpress, self-ubiquitylation activity of the Itch proteins was examined as described for A.