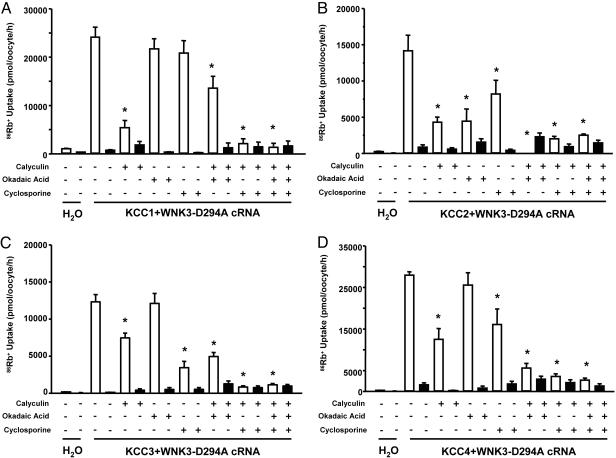
Fig. 4.
WNK3-D294A activates KCC1, KCC2, KCC3, and KCC4 via a phosphatase-dependent mechanism. Effect of protein phosphatase inhibitors upon 86Rb+ uptake in oocytes injected with KCC1 (A), KCC2 (B), KCC3 (C), and KCC4 (D). All groups were injected with cRNA concentration at 0.2 μg/μl, except for KCC1 (0.4 μg/μl). All groups were coinjected with WNK3-D294A cRNA at 0.1 μg/μl. Uptakes were performed in isotonic conditions in oocytes that were exposed to Cl−-containing medium (open bars) or Cl−-depleted medium (filled bars). Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of 20 oocytes from two different frogs. Protein phosphatase inhibitors used were as follows: calyculin A (at 100 nM), okadaic acid (at 1 nM), and cyclosporine A (at 25 μM). ∗, significantly different from the uptake observed in the corresponding control (absence of protein phosphatase inhibitors, P < 0.01).