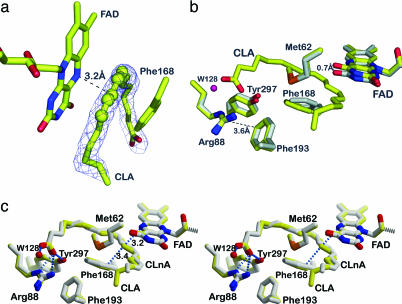
Fig. 2.
Substrate binding to PAI. (a) The σA-weighted mFo − DFc omit electron density map of 10,12-CLA is contoured at 2σ. CLA adopts a U-shaped form. Atoms C9–C13 are shown as spheres to visualize the planarity of the double bond system. (b) Conformational changes in the PAI–CLA complex. Superposition of the active sites of apo-PAI (gray) and bound to CLA (yellow). Phe-168, FAD, and Tyr-270 undergo small conformational change upon substrate binding. The side chain of Phe-168 becomes coplanar with the conjugated double bonds of CLA. The FAD isoalloxazine ring is shifted backwards to accommodate the fatty acid. The OH-group of Tyr-270 moves toward the carboxylate of CLA. (c) Structure of PAI in complex with (11E, 13E, 15Z)–CLnA (gray). The PAI–CLA complex (yellow) is shown for reference in this stereo figure. The conjugated triene bond system is planar (atoms C10–C16), and the fatty acid molecule is more strongly bent compared with CLA.