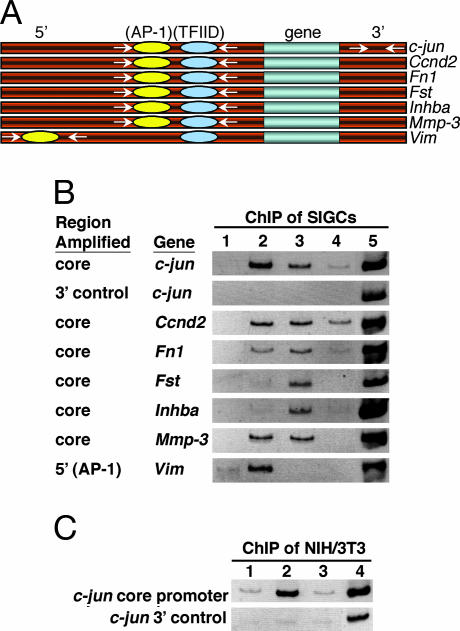
Fig. 5.
Direct association of TFIID and c-Jun with target gene promoters. (A) Schematic representation of genomic loci analyzed by ChIP. At core promoter regions, only AP-1- and TFIID-binding sites are shown. For promoters (c-jun, Ccnd2, and Fst) that lack canonical TATA-box elements, TFIID-binding sites are depicted upstream of transcriptional start sites (not shown). For promoters (c-jun, Ccnd2, Fst, Inhba, and Vim) that have multiple predicted c-Jun/AP-1-binding sites, only one site is represented. Primer pairs (arrows) used to amplify a 5′ distal enhancer, core promoters, and a 3′ control region are shown. A box is used to represent each gene. (B) ChIP assays using stable f-TAF4b SIGC cells from genomic regions illustrated in A. Lane 1, control antibody; lane 2, anti-c-Jun; lane 3, anti-Flag; lane 4, anti-TAF4; lane 5, input. (C) ChIP assays from a stable f-TAF4b NIH/3T3 cell line. Lane 1, control antibody; lane 2, anti-c-Jun; lane 3; anti-Flag; lane 4, input. Inverted images of ethidium-bromide-stained PCR products are shown.