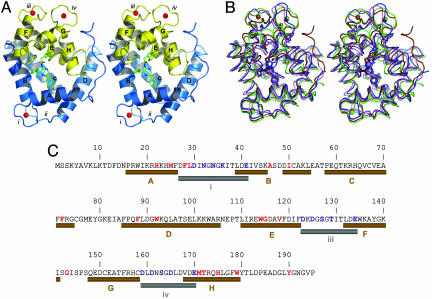
Fig. 2.
The spatial structure of Ca2+-discharged obelin and its comparison with other ligand-dependent confirmation states shown in Fig. 1. (A) Stereoview of the overall crystal structure of Ca2+-discharged obelin. The stick model in the center of the protein is the coelenteramide molecule. The helices are marked by capital letters A–H. Numbers i–iv designate the loops. Calcium ions are shown as red balls. (B) Stereoview of the superimposition of different obelin conformation states: II, blue; III, brown; IV, pink; and V, green. The 2-hydroperoxycoelenterazine and coelenteramide molecules are displayed by the stick models in the center of the protein; the calcium ions are shown as balls. The 2-hydroperoxycoelenterazine, coelenteramide, and calcium are colored according to the conformation state. (C) Sequence of the obelin from O. longissima (45). The residues comprising the coelenteramide binding cavity or participating in calcium binding are marked with red and blue, respectively. The helices and loops involved in the binding of Ca2+ are shown as brown and gray cylinders, respectively, according to the structure of Ca2+-discharged obelin.