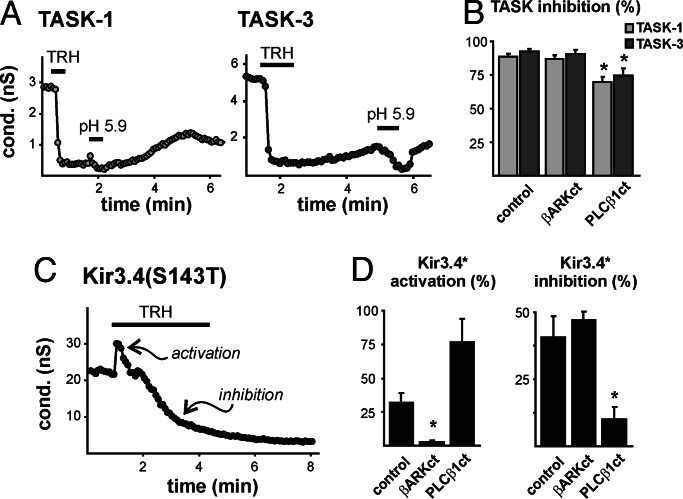
Fig. 1.
Inhibition of TASK and Kir3.4* channels is distinctly different. (A) Whole cell conductance (slope conductance between −130 mV and −60 mV) in HEK293 cells stably expressing TRHR1 receptor and transiently transfected with TASK-1 (Left) or TASK-3 (Right). TRH (200 nM) inhibited pH-sensitive TASK channels. (B) Averaged (±SEM) TRH-mediated TASK inhibition (% control) in cells transfected with βARK-ct, a Gβγ sink, or PLCβ1-ct, a Gαq sink (∗, P < 0.05 by ANOVA, n ≥ 5 per group). (C) Conductance in cells expressing a homomeric mutant Kir channel [Kir3.4(S143T), Kir3.4*] in 25 mM extracellular KCl. TRH caused fast activation of Kir3.4* conductance followed by a delayed inhibition. (D) Averaged (±SEM) TRH-induced activation (Left) and inhibition (Right) of Kir3.4* (% of control) was reduced in cells transfected with βARK-ct or PLCβ1-ct (∗, P < 0.05 by ANOVA, n ≥ 11 per group).