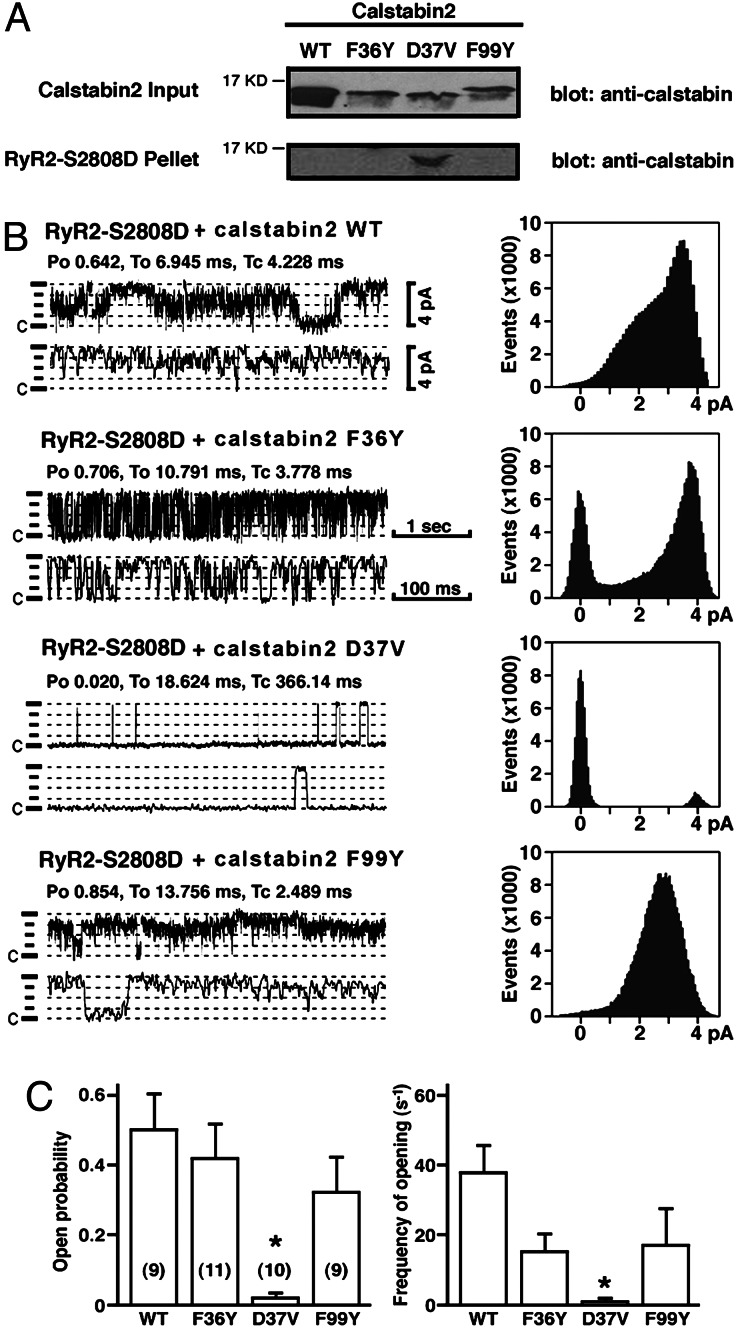
Fig. 3.
Calstabin2–D37V binds and modulates function of mutant RyR2–S2808D, which mimics chronically PKA-phosphorylated RyR2. (A) Immunoblots showing that calstabin2–D37V bound to RyR2–S2808D (which mimics chronically PKA-phosphorylated RyR2), whereas WT calstabin2 and mutants F36Y and F99Y did not. (B) Single-channel measurements showing that calstabin2–D37V restored normal function to RyR2–S2808D, whereas WT calstabin2, calstabin2–F36Y, and calstabin2–F99Y did not. (C) Bar graphs showing relative reduction in open probability and frequency of openings of RyR2–S2808D channels to which mutant calstabin2 were added as indicated. Calstabin2–D37V significantly reduced open probability and frequency of channel openings compared with WT calstabin2, calstabin2–F36Y, and calstabin2–F99Y.