Figure 1.
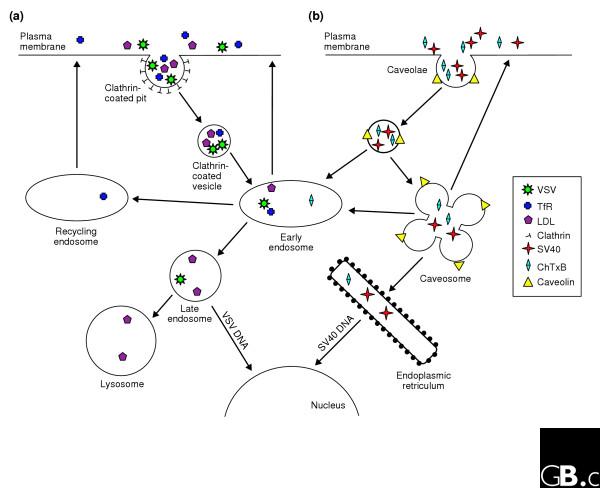
Schematic representation of two endocytosis pathways. (a) Cargo trafficking mediated by clathrin-dependent endocytosis. This pathway is typically initiated by the recruitment of cargo into clathrin-coated pits at the plasma membrane. After pinching off from the plasma membrane, clathrin-coated vesicles are transported to the early endosome. Here cargo is sorted for delivery to the degradative pathway, that is, the late endosome and lysosome, or is recycled to the plasma membrane directly, or via the recycling endosome. (b) Caveolae-dependent endocytosis. This pathway starts at the plasma membrane. After leaving the plasma membrane caveolar vesicles can either briefly fuse with early endosomes or fuse with caveosomes. From caveosomes, cargo can either traffic to the endoplasmic reticulum or early endosomes, or back to the plasma membrane. Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) and transferrin receptor (TfR) enter cells via the clathrin-mediated pathway, whereas simian virus 40 (SV40) and cholera toxin B subunit (ChTxB) use the caveolae and raft-mediated pathway. LDL, low density lipoprotein.
