Figure 1.
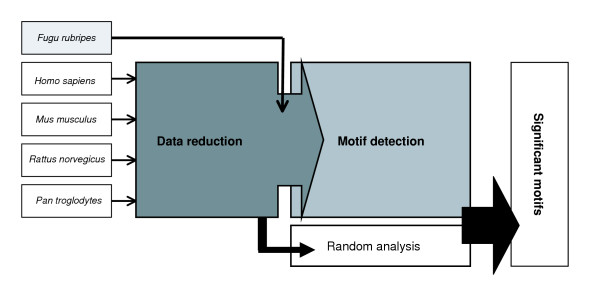
Schematic representation of the two-step procedure for phylogenetic footprinting. In the data reduction step, regions conserved among closely related (mammalian) orthologs are selected. Subsequently, these strongly conserved sequences are combined with a more distant ortholog (for example, Fugu); this set of genes is then subjected to motif detection. Finally, significantly conserved blocks are identified using a threshold defined by a random analysis.
