Abstract
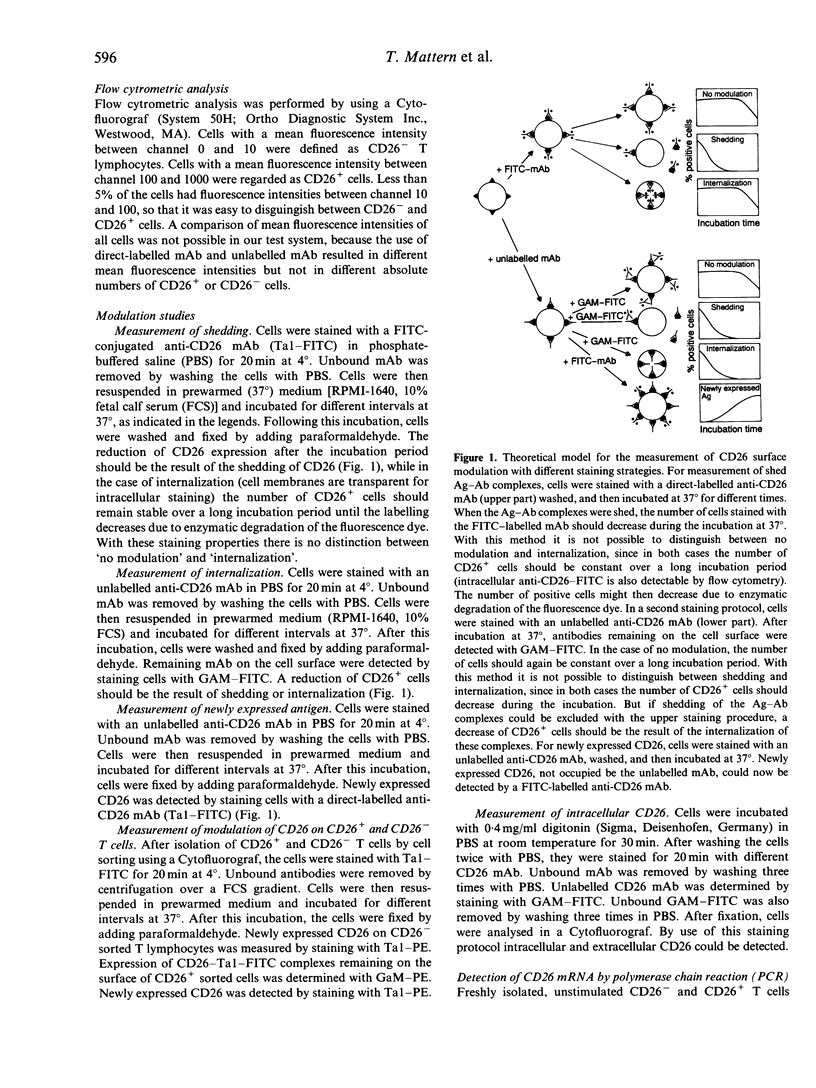
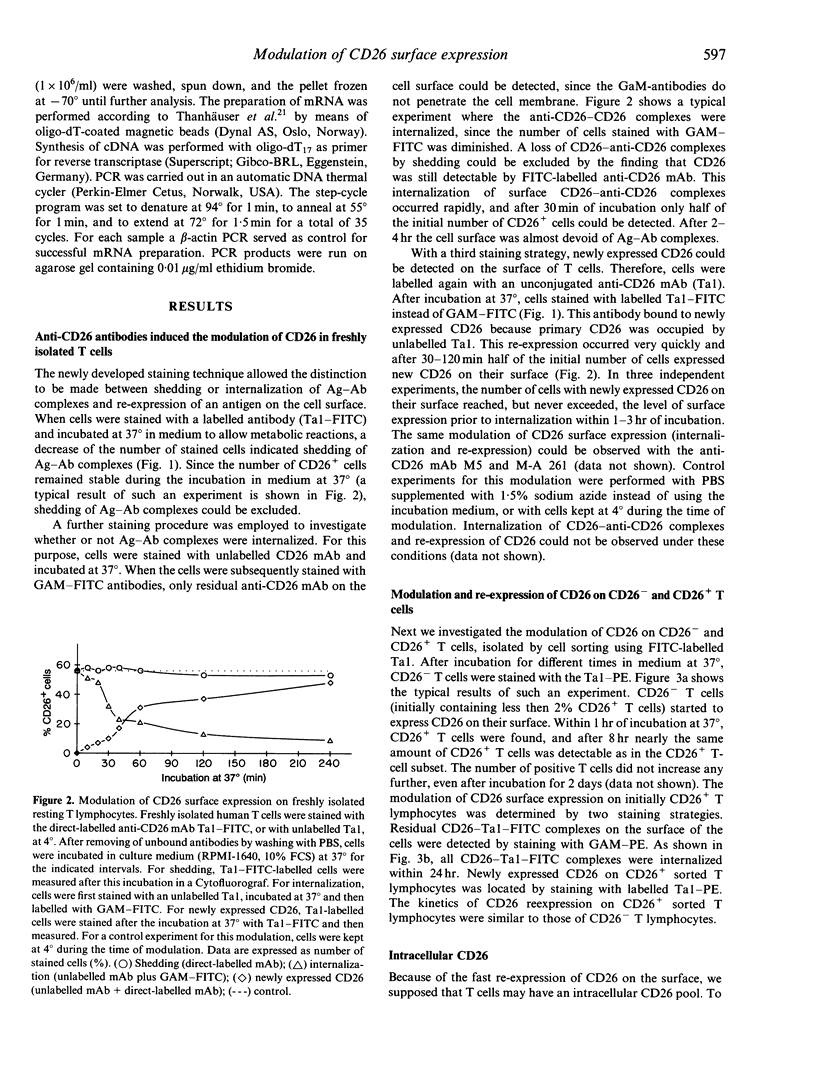
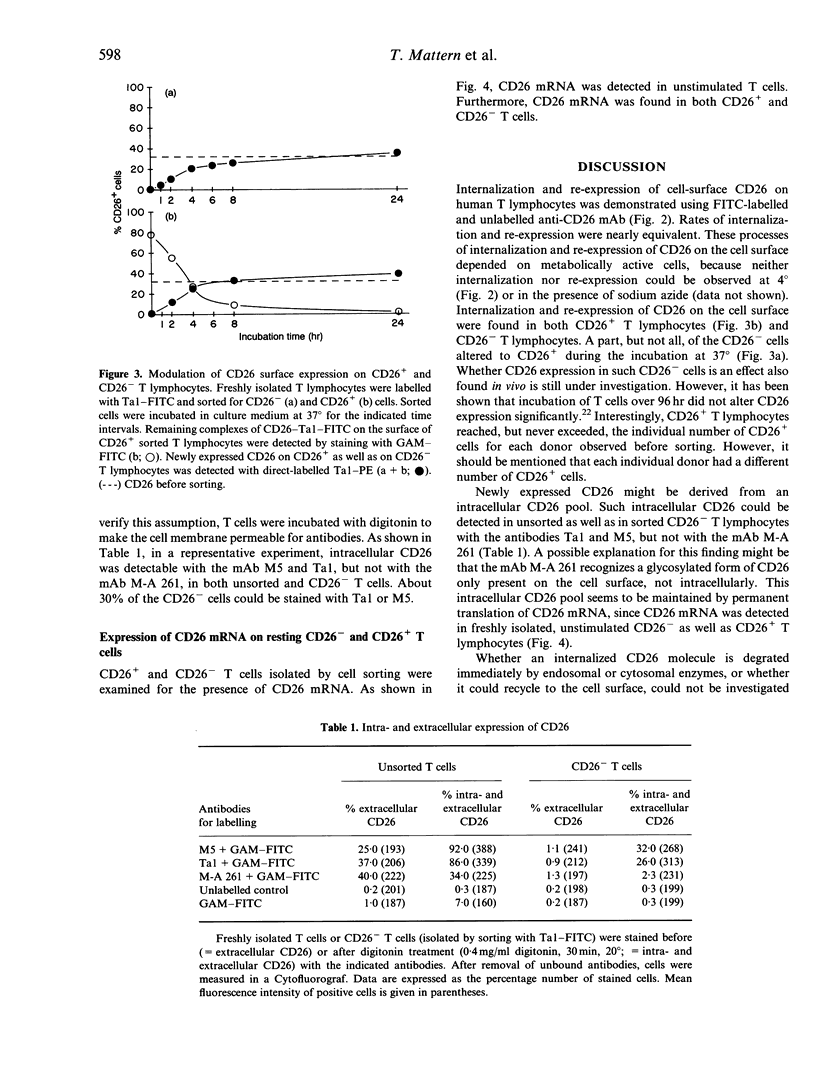
The ability of different anti-CD26 monoclonal antibodies to modulate the expression of CD26 on human T lymphocytes was investigated. By means of a new non-radioactive method using fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labelled and unlabelled anti-CD26 monoclonal antibodies and flow cytometry, we measured the internalization and re-expression of CD26 on freshly isolated resting human T lymphocytes. The modulation of CD26 surface expression takes place in primarily CD26+ as well as in CD26- T lymphocytes, indicating the presence of an intracellular CD26 pool. In fact, with two different anti-CD26 monoclonal antibodies (Ta1 and M5) intracellular CD26 was detected out of which newly expressed CD26 might have originated. This intracellular CD26 pool appears to be maintained by continuous translation of CD26 mRNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bierer B. E., Barbosa J., Herrmann S., Burakoff S. J. Interaction of CD2 with its ligand, LFA-3, in human T cell proliferation. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3358–3363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchsel R., Kreisel W., Fringes B., Hanski C., Reutter W., Gerok W. Localization and turnover of dipeptidylpeptidase IV in the domains of rat liver plasma membrane. Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;40(1):53–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callebaut C., Krust B., Jacotot E., Hovanessian A. G. T cell activation antigen, CD26, as a cofactor for entry of HIV in CD4+ cells. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):2045–2050. doi: 10.1126/science.7903479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M., Bieber M., Levy R., Teng N. N. Influence of avidity and idiotope recognition on the modulation of surface immunoglobulin on malignant human B cells by rat monoclonal anti-idiotype antibodies. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2983–2988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang N. H., Torimoto Y., Deusch K., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Comitogenic effect of solid-phase immobilized anti-1F7 on human CD4 T cell activation via CD3 and CD2 pathways. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4092–4100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang N. H., Torimoto Y., Shimamura K., Tanaka T., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. 1F7 (CD26): a marker of thymic maturation involved in the differential regulation of the CD3 and CD2 pathways of human thymocyte activation. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):2825–2832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang N. H., Torimoto Y., Sugita K., Daley J. F., Schow P., Prado C., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Cell surface modulation of CD26 by anti-1F7 monoclonal antibody. Analysis of surface expression and human T cell activation. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):3963–3971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Fu S. M., Hansen J. A. Human T cell activation. II. A new activation pathway used by a major T cell population via a disulfide-bonded dimer of a 44 kilodalton polypeptide (9.3 antigen). J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1513–1524. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegen M., Camerini D., Fleischer B. Function of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (CD26, Tp103) in transfected human T cells. Cell Immunol. 1993 Feb;146(2):249–260. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1993.1024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. R., Trowbridge I. S. Internalization and processing of transferrin and the transferrin receptor in human carcinoma A431 cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):508–521. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisel W., Hanski C., Tran-Thi T. A., Katz N., Decker K., Reutter W., Gerok W. Remodeling of a rat hepatocyte plasma membrane glycoprotein. De- and reglycosylation of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11736–11742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisel W., Hildebrandt H., Mössner W., Tauber R., Reutter W. Oligosaccharide reprocessing and recycling of a cell surface glycoprotein in cultured rat hepatocytes. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1993 Apr;374(4):255–263. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1993.374.1-6.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisel W., Volk B. A., Büchsel R., Reutter W. Different half-lives of the carbohydrate and protein moieties of a 110,000-dalton glycoprotein isolated from plasma membranes of rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1828–1831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter K., Stieger B., Klumperman J., Ginsel L., Hauri H. P. Endocytosis, recycling, and lysosomal delivery of brush border hydrolases in cultured human intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3503–3512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattern T., Ansorge S., Flad H. D., Ulmer A. J. Anti-CD26 monoclonal antibodies can reversibly arrest human T lymphocytes in the late G1 phase of the cell cycle. Immunobiology. 1993 Jun;188(1-2):36–50. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80485-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattern T., Scholz W., Feller A. C., Flad H. D., Ulmer A. J. Expression of CD26 (dipeptidyl peptidase IV) on resting and activated human T-lymphocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1991 Jun;33(6):737–748. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1991.tb02548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison M. E., Vijayasaradhi S., Engelstein D., Albino A. P., Houghton A. N. A marker for neoplastic progression of human melanocytes is a cell surface ectopeptidase. J Exp Med. 1993 Apr 1;177(4):1135–1143. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.4.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz E., Blazquez M. V., Madueño J. A., Rubio G., Peña J. CD26 induces T-cell proliferation by tyrosine protein phosphorylation. Immunology. 1992 Sep;77(1):43–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J., Stockert E., Boyse E. A., Kim J. H. Antigenic modulation. Loss of TL antigen from cells exposed to TL antibody. Study of the phenomenon in vitro. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):523–539. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesando J. M., Hoffman P., Abed M. Antibody-induced antigenic modulation is antigen dependent: characterization of 22 proteins on a malignant human B cell line. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3689–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold D., Bank U., Bühling F., Neubert K., Mattern T., Ulmer A. J., Flad H. D., Ansorge S. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (CD26) on human lymphocytes. Synthetic inhibitors of and antibodies against dipeptidyl peptidase IV suppress the proliferation of pokeweed mitogen-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and IL-2 and IL-6 production. Immunobiology. 1993 Aug;188(4-5):403–414. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader W. P., Miczek A. D., West C. A., Samsonoff W. A. Evidence for receptor-mediated uptake of adenosine deaminase in rabbit kidney. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Dec;36(12):1481–1487. doi: 10.1177/36.12.2461411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. L., Ciechanover A., Merritt S., Turkewitz A. Antibody-induced receptor loss. Different fates for asialoglycoproteins and the asialoglycoprotein receptor in HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15225–15232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanhäuser A., Reiling N., Böhle A., Toellner K. M., Duchrow M., Scheel D., Schlüter C., Ernst M., Flad H. D., Ulmer A. J. Pentoxifylline: a potent inhibitor of IL-2 and IFN-gamma biosynthesis and BCG-induced cytotoxicity. Immunology. 1993 Sep;80(1):151–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer A. J., Mattern T., Feller A. C., Heymann E., Flad H. D. CD26 antigen is a surface dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV) as characterized by monoclonal antibodies clone TII-19-4-7 and 4EL1C7. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Apr;31(4):429–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J. P., De Mey J. R., Goossens J. G. OKT3: a monoclonal anti-human T lymphocyte antibody with potent mitogenic properties. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2708–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk B. A., Kreisel W., Köttgen E., Gerok W., Reutter W. Heterogeneous turnover of terminal and core sugars within the carbohydrate chain of dipeptidylaminopeptidase IV isolated from rat liver plasma membrane. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 31;163(1):150–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



