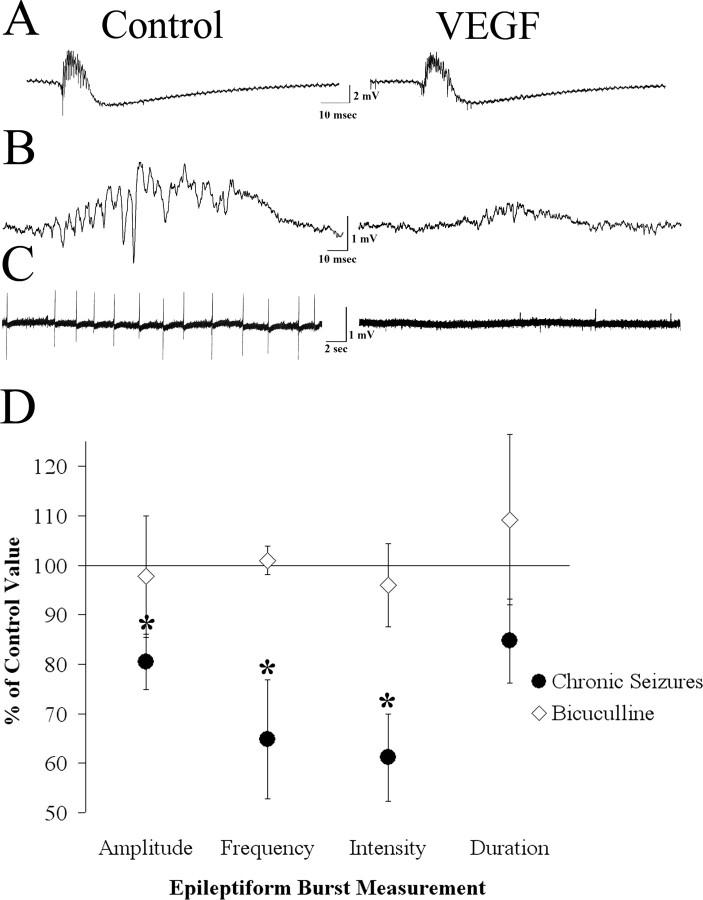
Figure 6.
Differential effects of VEGF on spontaneous epileptiform burst discharges recorded in area CA3 in slices from epileptic and normal rats. A, Representative example of spontaneous burst discharges recorded from slices made from normal adult rats that were exposed to the GABAA receptor antagonist bicuculline (10 μm) demonstrates the similarity of epileptiform bursts before and after VEGF application. B, Examples of spontaneous CA3 burst discharges in a slice made from an epileptic rat (slices were made during the period of recurrent seizures after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus; see Materials and Methods) show reduced burst discharges after the slice was exposed to VEGF.C, One-minute-long recordings made in a slice from an epileptic rat demonstrate reduced burst frequency after bath application of VEGF. D, The average change in burst amplitude frequency, duration, and intensity (measured using the coastline bursting index; see Materials and Methods) after VEGF administration is represented as a percentage of control. VEGF significantly reduced amplitude, frequency, and intensity but not the duration of the bursts (n = 11). *p < 0.05. However, paired Student's t tests did not show a significant reduction in any of these measures when epileptiform bursts were induced by bicuculline bath application (n = 7).