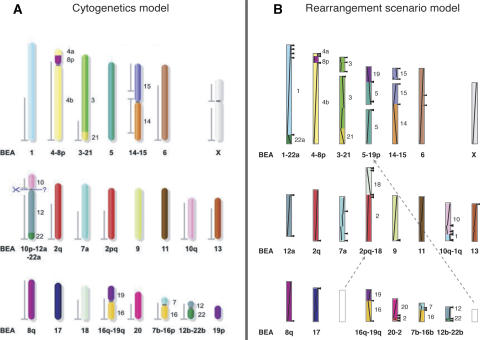
Figure 1.
Putative genome architecture of the boreoeutherian ancestor from (A) cytogenetics model using over 80 eutherian genomes (Froenicke et al. 2006) and (B) a rearrangement scenario model using human–mouse–rat–cat–cattle–dog–pig (Murphy et al. 2005). In B, the black arrowheads to the right of the ancestral chromosomes indicate unresolved/weak adjacencies, and the diagonal line segments indicate original position and orientation on human. This is the same reconstruction as in Murphy et al. (2005), but reformatted, rescaled, and recolored to facilitate comparison. The two dashed arrows show the location in the rearrangement model of two of the ancestral chromosomes from the cytogenetics model. These two chromosomes are only weakly associated with two other chromosomes in the rearrangement model.