FIGURE 1.
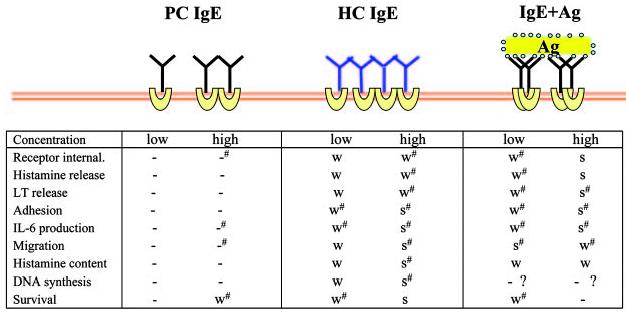
Biological effects by various modes of stimulation via the Fc∊RI. Experiments using mouse BMMCs are summarized. Concentrations of stimuli are as follows: PC IgE (H1 DNP-∊-206) and HC IgE (SPE-7), 0.5 μg/ml (low) and 5 μg/ml (high); and IgE+Ag (DNP21-BSA), 1 ng/ml (low) and 100 ng/ml (high). Notice that biological events are listed in a rough order of occurrences and that receptor aggregation presumably occurs in all modes of stimulation, except for low PC IgE concentrations. -, not detected, -#, very weak; W, weak; W#, weak∼moderate; S#, moderate∼strong; and S, strong. References: receptor internalization (24, 44, 50); histamine release (14, 21, 22, 24, 26, 27, 43, 44, 50); leukotriene release (21, 22, 24); adhesion (28, 56); IL-6 production (21, 22, 24, 43, 44, 50, 51); migration (29); histamine content (23, 24, 57); DNA synthesis (21, 22, 24, 86); and survival (21, 22, 24, 43, 44, 50, 51, 58-62). In Ref. 60, MC9 mouse mast cells were used. In Ref. 62, BMMCs were stimulated with anti-TNP IgE (hybridoma supernatants) and TNP4.8-BSA (1 μg/ml). However, it is not clear whether the used Ag concentration corresponds to weak or strong stimulus.
