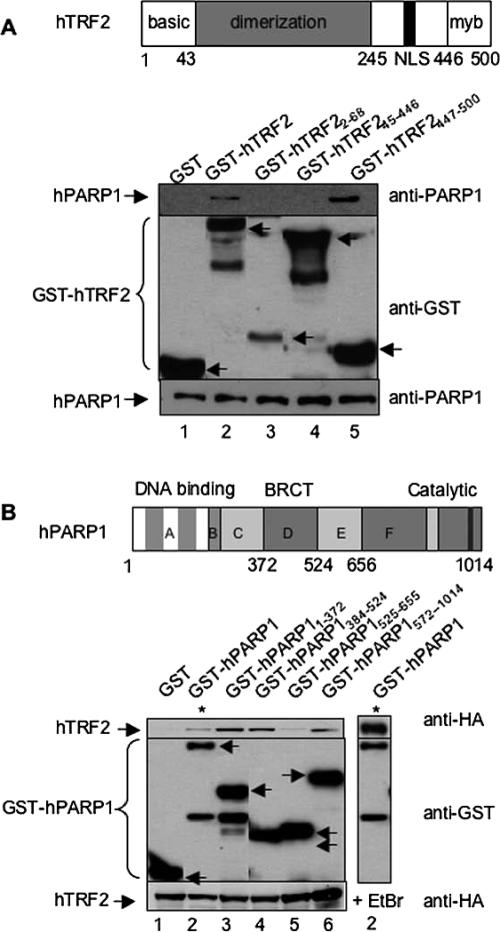
Figure 2.
The Myb domain of hTRF2 interacts with hPARP1. (A) Interaction between GST-hTRF2 full-length or deletion constructs and endogenous hPARP1 in Cos-7 cells. Top panel, schematic representation of human TRF2. Bottom panel, GST, GST-hTRF2, and GST-hTRF2 deletion mutants expressed in Cos-7 cells were subjected to GST pulldown then examined by Western blot using, consecutively, mouse anti-hPARP1 (BD Transduction Laboratoriess, top) and rabbit anti-GST (Upstate, middle) antibodies. (B) Interaction between GST-hPARP1 full-length or deletion constructs and His-Tev-HA hTFR2 in Cos-7 cells. Top panel, schematic representation of human PARP1. Bottom panel, GST, GST-hPARP1 full-length, and GST-hPARP1 deletion mutants along with His-Tev-HA hTFR2 were expressed in Cos-7 cells. Cell lysates were subjected to GST pull-down in the absence (lanes 1–6) or presence (lane 7) of 12.5 μg/ml ethidium bromide and subsequently examined by Western blot using mouse anti-HA.11 (BAbCo, top), then rabbit anti-GST (middle) antibodies. To show the level of endogenous PARP1 or His-Tev-HA hTFR2 in each sample, 40 μg of whole cell lysates were subjected to Western blot with mouse anti-hPARP1 or mouse anti-HA antibodies, respectively (bottom). Arrows indicate the position of GST or GST fusion proteins. Bottom bands are protein degradation products.