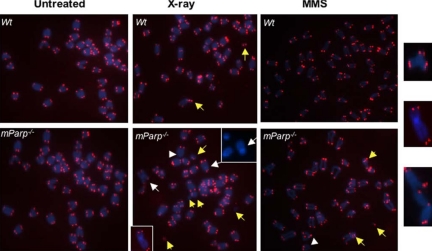
Figure 9.
PARP1 deficiency leads to chromosome end-to-end fusions or telomere signal free ends in primary MEFs after DNA damage in vivo. Telomeric-FISH analysis of metaphase spreads of untreated, 5-Gy x-ray- or 2 mM MMS–treated early passage of primary wild-type (wt) or mParp–/– proliferating MEFs. Un-treated wild-type and mParp–/– MEFs showed normal telomeric DNA signals (in red) and chromosomes (in blue). Although chromosome breakages were detectable in wild-type MEFs 24 h after DNA damage, telomere signal free ends (arrowheads), chromosome or chromatid end-to-end fusions or telomere associations (white arrows, enlarged images at far-right), and chromosome breakages or frag-ments (yellow arrows) were found more frequently in x-ray– or MMS-treated mParp–/– MEFs.