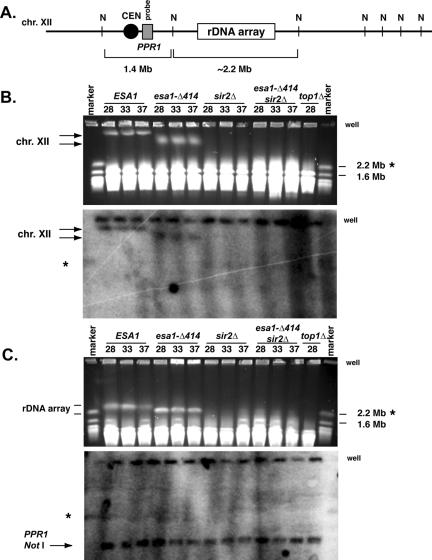
Figure 5.
The rDNA array is affected by esa1 mutants. (A) The 2.2+-Mb rDNA array as diagrammed resides on the right arm of chromosome XII, the largest S. cerevisiae chromosome (not drawn to scale). NotI restriction enzyme sites (N) flank the array and the region containing the PPR1 gene (gray box). A chromosomal NotI digest liberates a 2.2+-Mb fragment containing the rDNA array and a 1.4-Mb fragment containing the PPR1 gene. (B) The esa1-414 mutant exhibited altered chromatin structure of chromosome XII as evidenced by pulsed-field gel electrophoretic mobility. Whole chromosome preparations from ESA1 (LPY4909), esa1-414 (LPY4911), sir2Δ (LPY4978), and top1–8 (AMR53) strains incubated at the temperatures indicated (28, 33, and 37°C) were subjected to pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and analyzed by ethidium bromide staining (top) and Southern blotting (bottom) with a PPR1 probe, as diagrammed in A. In the esa1-414 mutant, chromosome XII (as identified in the Southern blot) displayed an altered electrophoretic mobility at all temperatures compared with wild-type (left arrows), which was distinct from the sir2Δ and top1-8 strains, where chromosome XII failed to enter the gel. (C) The altered electrophoretic mobility of chromosome XII in the esa1-414 mutant is due to the rDNA array. Whole chromosome preparations as in B were digested with NotI, subjected to pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, and analyzed by ethidium bromide staining (top) and Southern blotting (bottom) with the PPR1 probe. The rDNA array has an altered electrophoretic mobility in the esa1-414 mutant compared with wild-type, as evidenced by ethidium bromide staining (top arrows). However, the PPR1 NotI fragment (bottom arrow, Southern) migrated equivalently in all strains, including in the sir2Δ and top1-8 strains. In both B and C relevant marker sizes are indicated to the right. Asterisks indicate the marker chromosome XII and the wells are indicated. In B and C, the wells are detected by the PPR1 probe, because not all chromosomal material enters the gels.