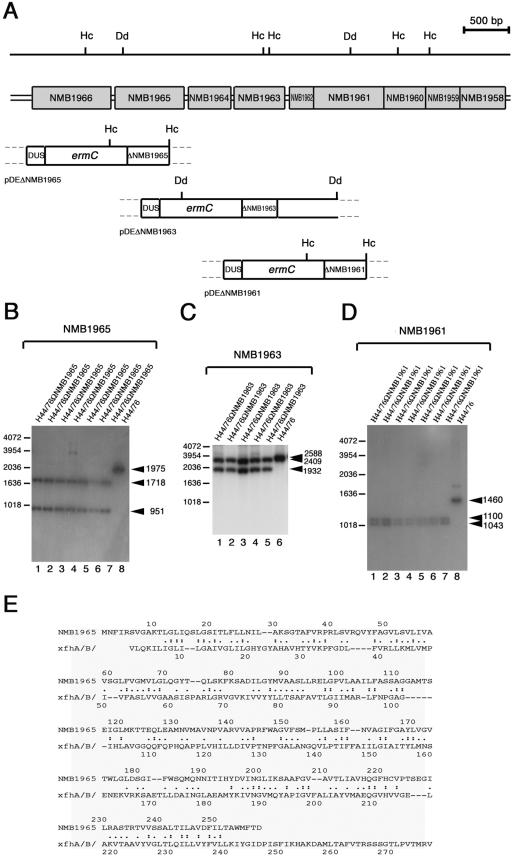
FIG.4.
Knockout of NMB1965, NMB1963, and NMB1961 in H44/76 and alignment of deduced amino acid sequences. (A) Experimental design for NMB1965, NMB1963, and NMB1961 disruption by single crossing-over. The genetic and physical map of the NMB1966-to-NMB1958 region is indicated above the map of the genetic determinants of pDEΔNMB1965, pDEΔNMB1963, and pDEΔNMB1961 used for the gene disruption. Hc, HincII restriction sites; Dd, DdeI restriction sites. The genetic determinants of pDEΔNMB1965, pDEΔNMB1963, and pDEΔNMB1961 are as follows: (i) ermC, the erythromycin resistance gene used as a selective marker for transformation; (ii) ΔNMB1965 (in pDEΔNMB1965), a BamHI-restricted 482-bp DNA fragment spanning the central part of NMB1965; (iii) ΔNMB1963 (in pDEΔNMB1963), a BamHI-restricted 417-bp DNA fragment spanning the central part of NMB1963; (iv) ΔNMB1961 (in pDEΔNMB1961), a BamHI-restricted 481-bp DNA fragment spanning the central part of NMB1961; (v) a DNA fragment containing a DUS, required for efficient DNA uptake during transformation. (B to D) Southern blot analysis demonstrating the inactivation of NMB1965 (B), NMB1963 (C), and NMB1961 (D). Chromosomal DNA was extracted from the parental strain, H44/76 (lane 8 in B and D and lane 6 in C), and from several recombinant strains transformed either with pDEΔNMB1965 (lanes 1 to 7, B), pDEΔNMB1963 (lanes 1 to 5, C) or with pDEΔNMB1961 (lanes 1 to 7, D). The HincII-restricted (B and D) or DdeI-restricted (C) chromosomal DNAs were analyzed by Southern blotting using as probes the 32P-labeled NMB1965-specific (B), the NMB1963-specific (C), or the NMB1961-specific (D) DNA fragments cloned in pDEΔNMB1965, pDEΔNMB1963, or pDEΔNMB1961, respectively. Arrows on the right of each panel indicate NMB1965-specific (B), NMB1963-specific (C), or NMB1961-specific (D) fragments whose sizes were deduced on the basis of the relative migration of DNA ladders (bars on the left of each panel). (E) Smith-Waterman alignment between the NMB1965 deduced protein sequence and the proton/glutamate symport protein from Pyrococcus horikoshii. Identities (:) and synonym substitutions (.) are reported.