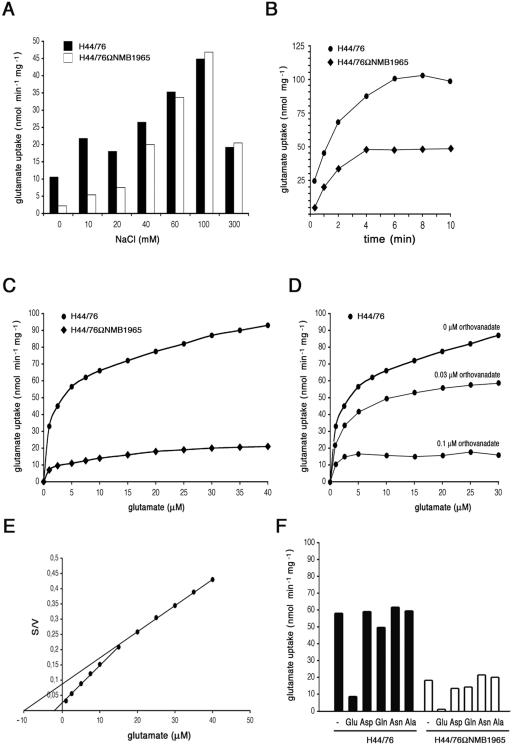
FIG. 5.
Effects of NMB1965 genetic inactivation on l-glutamate import. (A) Effects of sodium ion concentration on l-glutamate uptake by H44/76 and H44/76ΩNMB1965 (permease defective). The assay was performed as detailed in Materials and Methods using a final l-glutamate concentration of 0.5 μM and the indicated NaCl concentration. The transport assays were terminated after 20 s. (B) Time course of l-glutamate uptake. The assay was performed in the presence of 20 μM l-[3,4-3H]glutamic acid and a final NaCl concentration of 20 mM. (C) Concentration dependence of l-glutamate import by strains H44/76 and H44/76ΩNMB1965. The assay (20 s) was performed using a final NaCl concentration of 20 mM. (D) Effects of sodium orthovanadate addition on l-glutamate uptake. Transport assays were carried out as in panel C. (E) Reciprocal transformation of the saturation data of panel C relative to H44/76; S is expressed as micromolar concentrations, and V is expressed as nanomoles min−1 mg cell protein−1. (F) l-glutamate uptake (20 s) was determined using a final l-glutamate concentration of 5 μM and a final NaCl concentration of 20 mM, either in the absence or in the presence of 100-fold molar excess of l-glutamate, l-aspartate, l-glutamine, l-asparagine, or l-alanine.