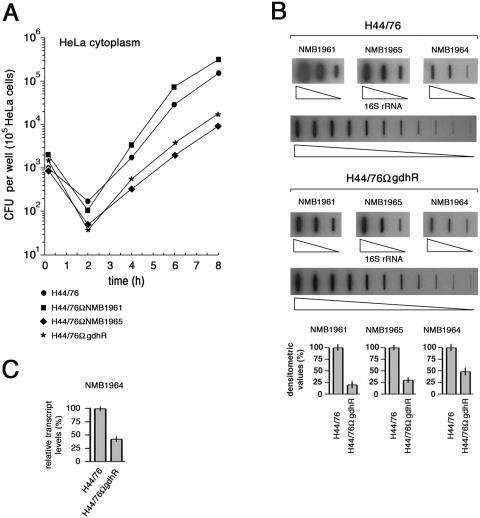
FIG. 7.
Effects of genetic inactivation of NMB1965, NMB1961, or gdhR on HeLa cell invasion and intracellular survival. (A) After allowing meningococci to invade for 1 h, intracellular viability was assessed immediately after gentamicin treatment (0 h) and every 2 h post-gentamicin treatment. Intracellular viability is expressed as the average number of viable bacteria (CFU) per epithelial cell for H44/76 and derivative strains H44/76ΩgdhR, H44/76ΩNMB1965 (permease defective), and H44/76ΩNMB1961 (VacJ-like defective). (B) Slot blot analysis of NMB1965-, NMB1964-, and NMB1961-specific transcripts in the intracellular environment. Top, total RNAs were extracted from about 5 × 107 to 5 × 108 intracellular meningococci (strains H44/76 and H44/76ΩgdhR) following saponin lysis of infected HeLa cells at different times after 8 h of gentamicin treatment and were used to generate gene-specific 32P-labeled cDNA probes as detailed in the Materials and Methods section. The 32P-labeled cDNA probes were hybridized to different amounts (4, 20, and 100 ng) of denatured NMB1965-, NMB1964-, or NMB1961-specific fragments. For the 16S rRNA gene-specific fragment, twofold serial dilutions (from 0.05 to 50 ng) were used. Bottom, densitometry analysis of the slot blot. For NMB1965, NMB1964, and NMB1961, the relative transcript levels in H44/76 are arbitrarily assumed to be equal to 100%. Values represent means from five independent experiments, each with triplicate samples, using RNA preparations from distinct infection assays. Bars indicate standard deviations. (C) Semiquantitative analysis of the NMB1964-specific transcript in H44/76 and H44/76ΩgdhR by RT real-time PCR experiment. The RNA was extracted from intracellular meningococci as described above. Results were normalized to 16S rRNA levels. Transcript levels in H44/76 are arbitrarily assumed to be equal to 100%. Values represent means from five independent experiments with triplicate samples using distinct cDNA preparations for each RNA sample ± standard deviations.