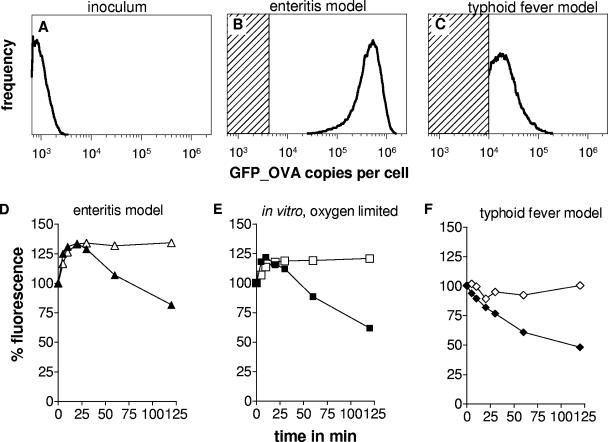
FIG. 1.
GFP_OVA content in Salmonella cells carrying a transcriptional PrpsA-gfp_ova fusion during enteritis and typhoid fever, as determined by flow cytometry. (A) Mice were infected with initially nonfluorescing Salmonella cells from a stationary in vitro culture. Salmonella were recovered 8 h after oral infection from infected ceca (Β) or 4 days after systemic infection from spleen (C). The shaded areas represent GFP_OVA levels below the detection threshold in the respective tissue homogenates. Similar data were obtained in three independent experiments. To assess GFP maturation and degradation, Salmonella cells expressing stable GFP (open symbols) or nonstable GFP_OVA (solid symbols) were freshly prepared from infected ceca (D), in vitro cultures with limited aeration (E), or infected spleen (F) and incubated in fully aerated LB medium containing chloramphenicol to block de novo synthesis. At different time intervals, GFP fluorescence was determined by flow cytometry.