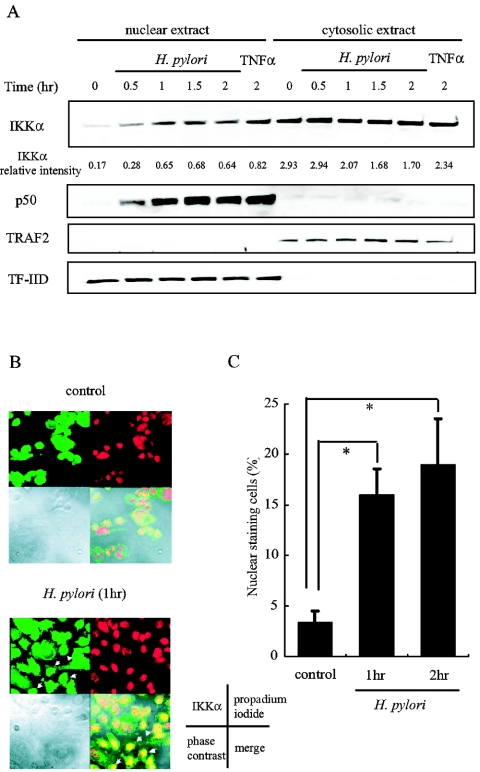
FIG. 3.
H. pylori infection induces IKKα nuclear translocation in AGS cells. (A) AGS cells were infected with H. pylori for the indicated time or treated with TNF-α for 2 h. The cells were fractioned into nuclear and cytosolic extracts. Aliquots of these extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting for IKKα and p50. Antibodies directed against TRAF2 and TF-IID were used to verify the integrity of the fractionation procedure and to ensure equal loading. A representative of three independent experiments with similar results is shown. (B) AGS cells seeded in 4-well chamber slides were left untreated or were infected with H. pylori for 1 h. The cells were immunostained with the anti-IKKα antibody and visualized by staining with Alexa Fluor 488. The nucleus was stained with propidium iodide. Phase-contrast images and merged images are shown. Arrows indicate the cells with IKKα nuclear staining. (C) AGS cells were infected with H. pylori for the indicated time, and IKKα nuclear translocation was assessed by immunofluorescence. The percentages of cells with IKKα nuclear staining cells are calculated from the observation of 300 cells in three independent experiments and are indicated as the means ± SD. *, P < 0.05.