FIG.2.
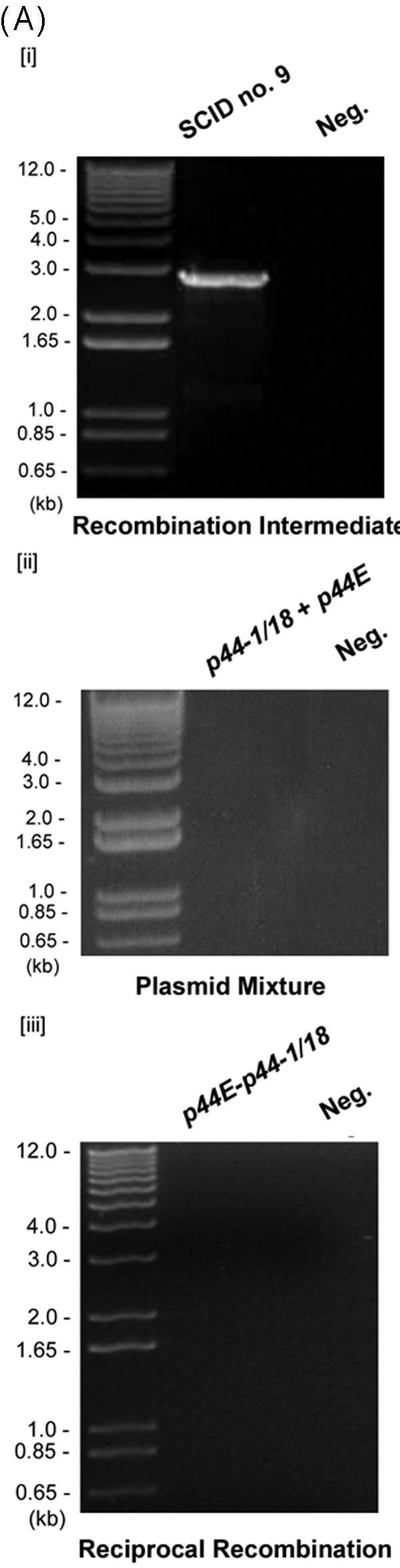
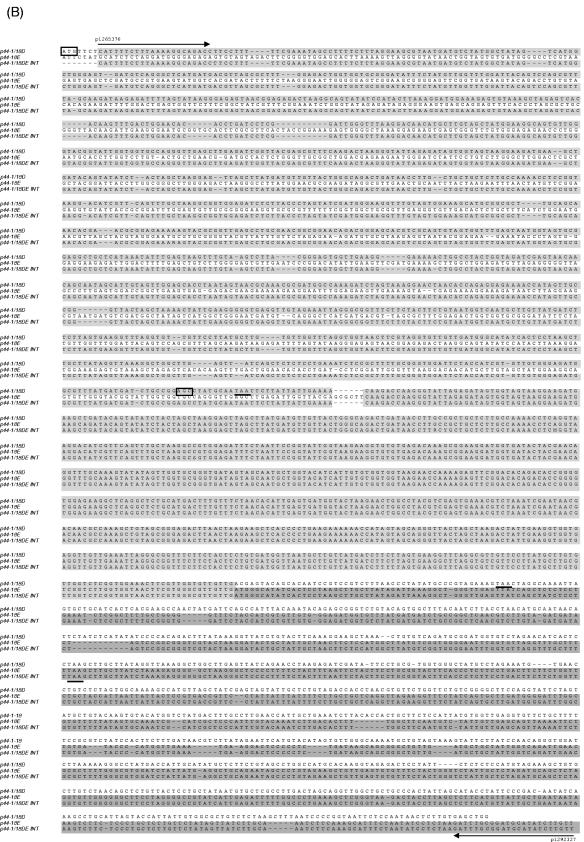
Analysis of the p44 recombination intermediate in A. phagocytophilum from an infected SCID mouse. (A) The half-crossover recombination intermediate was detected by PCR of peripheral blood leukocytes from an A. phagocytophilum-infected SCID mouse. [i] The ∼2.9-kb band was amplified by the primer pairs p1265450-p1292839 and p1265376-p1292327 (Fig. 1Aii) using Pfu DNA polymerase. [ii] No PCR product was detected with the same primer pairs from uninfected SCID mouse DNA spiked with plasmids containing p44-1/18 and p44E as a template. [iii] No PCR product was detected in peripheral blood leukocytes of infected mice with forward primers located in the intergenic region of p44E and omp-1N and with reverse primers located downstream of donor p44-1/18 locus (Fig. 1Ai). “Neg.” refers to a negative control with water as a template. (B) The nucleotide sequence of the half-crossover recombination duplex between p44E and p44-1/18D. The second set of primers used for the nested PCR are indicated by horizontal arrows and labeled with primer ID. p44-1/18DE INT is the intermediate structure containing donor site p44-1/18 and the recipient site p44E. The sequence is identical to that expected for a half-crossover recombination intermediate as illustrated in Fig. 1Aii. The light-shaded areas indicate sequence identity between the crossover structure and the putative donor p44-1/18 locus, and the dark shaded areas indicate identical sequence between the hybrid structure and the recipient p44E, or among all three structures. The boxed nucleotides are start codons for p44-1 and for p44-18. The stop codons are underlined. Dashes indicate sequence gaps that helped to determine the origins of conserved sequences in the recombination intermediate.