FIG.3.
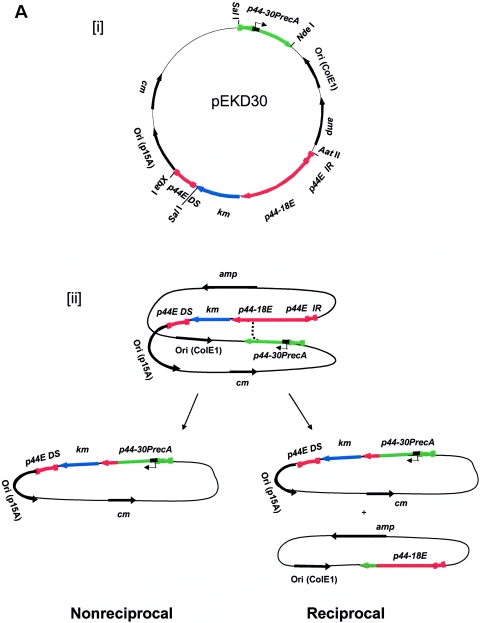
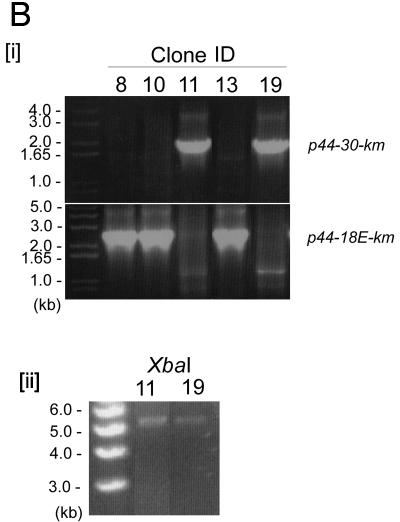
Analysis of a p44 recombination intermediate in E. coli using plasmid encoding p44 expression and donor loci. (A) Double-origin plasmid pEKD30 and E. coli system design. [i] Plasmid pEKD30 carries the recipient site of the p44 expression locus p44E upstream region (p44E IR)- p44-18E-km-p44E downstream sequence (p44E DS) and the donor site p44-30PrecA in a direct orientation. The donor p44-30PrecA has an E. coli recA gene promoter in the hypervariable region (bent arrow). The plasmid carries two more antibiotic-resistant genes (cm and amp) and two compatible replication origins (P15A and ColE). The restriction enzyme cleavage sites are shown. If p44-30PrecA recombines to p44-18E, km is transcribed from the recA promoter, allowing isolation of the recombination intermediates in the presence of Km. [ii] Experimental design. If nonreciprocal recombination occurs between p44-30PrecA and p44-18E, only one type of plasmid (5.7 kb) that carries km with upstream p44-30PrecA is expected to be isolated in the presence of Km. If reciprocal recombination occurs between the donor and the recipient sequences, two plasmids should be generated: one identical to the plasmid generated by the nonreciprocal recombination (5.7 kb) and another that carries p44-18E and amp (3.6 kb). Thus, in nonreciprocal recombination, Kmr E. coli strains are Ams, while in reciprocal recombination Kmr E. coli strains are Amr. [iii] Sequence alignment of 5′- and 3′-end conserved regions of donor p44-30D and recipient p44-18E in the plasmid pEKD30. The different nucleotides between p44-30D and p44-18E conserved regions are shaded in light gray. (B) Analysis of the Kmr Ams plasmids isolated from E. coli strain JC7623 with an active RecF pathway. [i] PCR amplification using the primer pair located upstream of p44-30PrecA and downstream of km, respectively, showed a band of the expected size for the recombined p44-30PrecA-km structure in Kmr Ams clones 11 and 19. The remaining three Kmr Ams clones had the original p44-18-km structure. [ii] The two PCR positive plasmids from clones 11 and 19 were analyzed by digestion with XbaI to determine the size of the recombined plasmid. As predicted from the restriction sites shown in Fig. 3Ai, XbaI digestion generated a single 5.7-kb band from the recombined p44-30-km plasmid. [iii] The sequence between the two SalI sites in clones 11 and 19, which confirmed the recombination between p44-30PrecA and p44-18E.