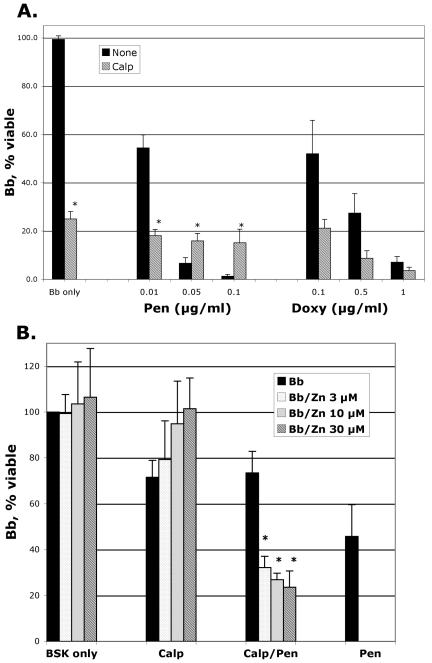
FIG. 2.
Calprotectin alters spirochete susceptibility to antibiotic killing. Spirochetes (5 × 106) were incubated for 48 h at 33°C in 0.05 ml BSK with 20% (vol/vol) assay buffer containing (A) penicillin (Pen) (0.01, 0.05, or 0.1 μg/ml), doxycycline (Doxy) (0.1, 0.5, or 1.0 μg/ml), and rCalp (300 μg/ml) in six to eight separate experiments or (B) penicillin (0.05 μg/ml), rCalp (300 μg/ml), and ZnCl2 (3, 10, or 30 μM) in three separate experiments. Percent viable spirochetes was determined by microscopic examination (dark-field or vital stain) at 48 h. Untreated spirochetes increased from 5 × 105 to (2 to 5) × 106 during the 48 h of incubation. The statistical significance between spirochete numbers in untreated versus rCalp incubations is a P value of 0.001; results with antibiotic alone or antibiotic with calprotectin for Pen G are as follows: 0.01 μg/ml, P = 0.001; 0.05 μg/ml, P = 0.02; 0.1 μg/ml, P = 0.04. For doxycycline: 0.1 μg/ml, not significant; 0.5 μg/ml, P = 0.04; 1 μg/ml, P = 0.04. The statistical significance between numbers of spirochetes incubated without Zn versus Zn (3 μM) is P = 0.04; for Zn (10 μM), P = 0.02; and for Zn (30 μM), P = 0.02.