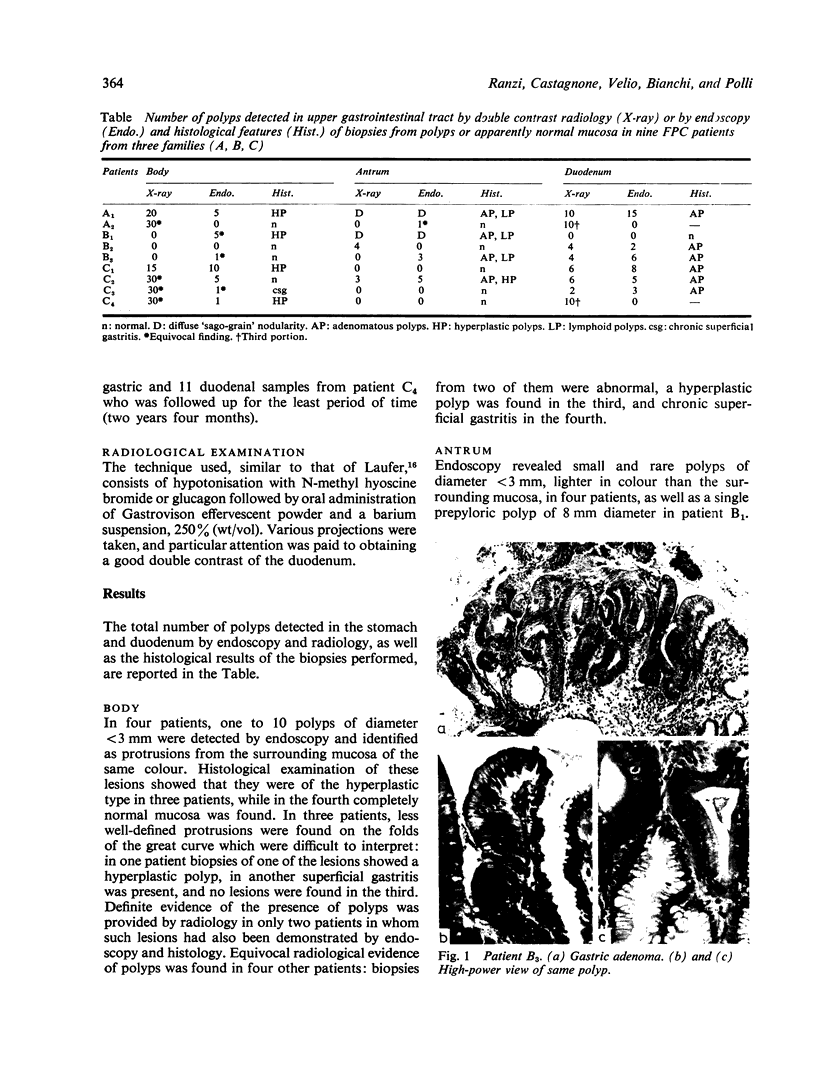
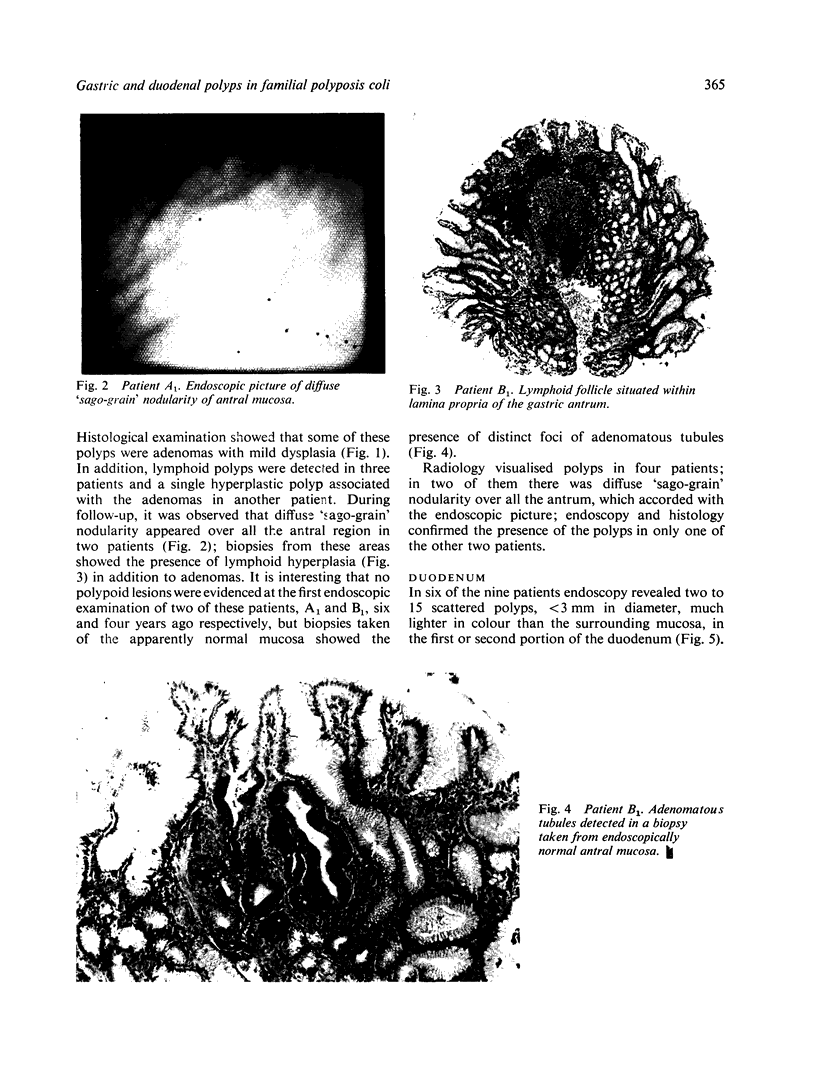
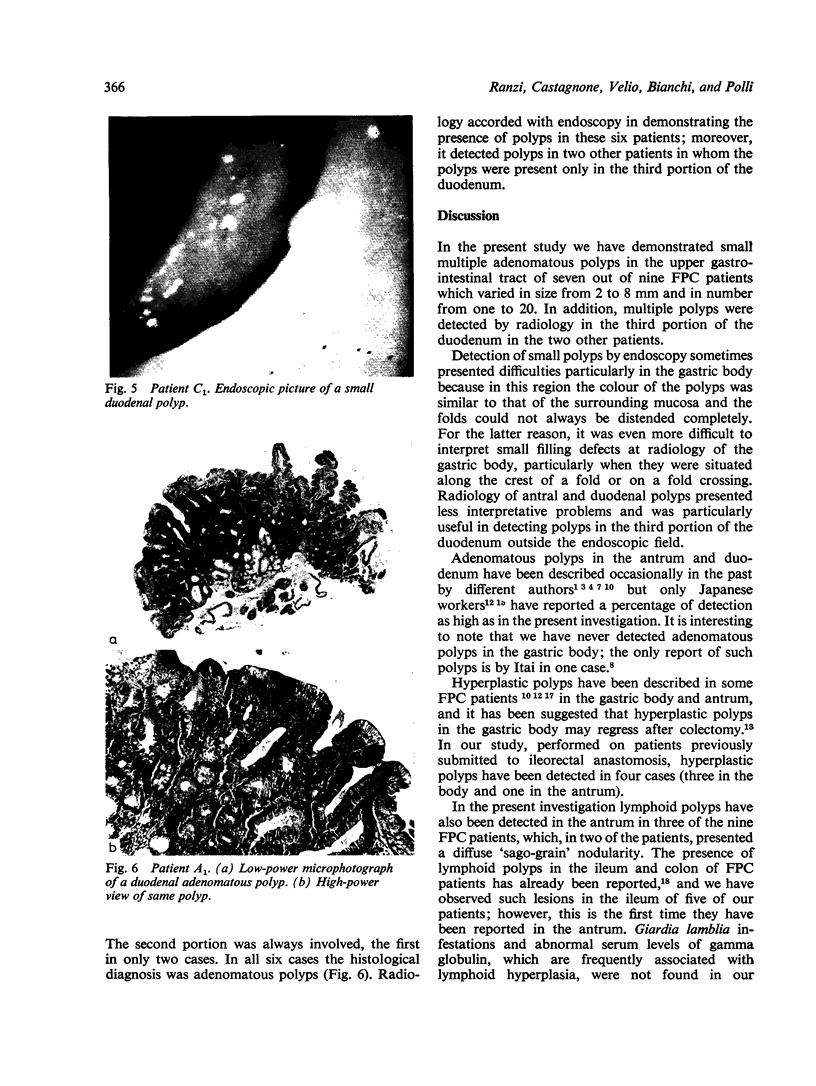
Abstract
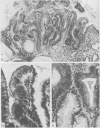
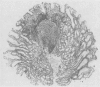
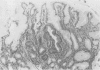
Endoscopy with multiple biopsies of the upper gastrointestinal tract was repeated yearly over a two to six year period in nine patients with familial polyposis coli from three families. Adenomatous polyps, one to 20 in number and 2-8 mm in size, were detected in the antrum and the first and second duodenal portions in seven patients, while hyperplastic polyps were detected in four patients in the gastric body. In two patients adenomatous tubules were observed in the biopsies of endoscopically normal mucosa from the same area where adenomatous polyps later developed. Lymphoid polyps were detected in the antrum in three cases. Double contrast radiology correlated poorly with endoscopy in the gastric body; it allowed detection of polyps in the third duodenal portion in two more patients. These results confirm that the incidence of adenomas in the upper gastrointestinal tract in familial polyposis coli may be higher than previously suspected.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOLEY S. J., McKINNON W. M., MARZULLI V. F. The management of familial gastrointestinal polyposis involving stomach and colon. Surgery. 1961 Oct;50:691–696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capron J. P., Descombes P., Dupas J. L., Delamarre J., Lorriaux A. La polypose gastrique dans le syndrome de Gardner. Etude radiologique et endoscopique de 6 cas. Arch Fr Mal App Dig. 1975 Jul-Aug;64(5):391–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denzler T. B., Harned R. K., Pergam C. J. Gastric polyps in familial polyposis coli. Radiology. 1979 Jan;130(1):63–66. doi: 10.1148/130.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann D. C., Goligher J. C. Polyposis of the stomach and small intestine in association with familia polyposis coli. Br J Surg. 1971 Feb;58(2):126–128. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800580212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itai Y., Kogure T., Okuyama Y., Muto T. Radiographic features of gastric polyps in familial adenomatosis coli. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1977 Jan;128(1):73–76. doi: 10.2214/ajr.128.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laufer I. A simple method for routine double-contrast study of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Radiology. 1975 Dec;117(3 Pt 1):513–518. doi: 10.1148/117.3.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melmed R. N., Bouchier I. A. Duodenal involvement in Gardner's syndrome. Gut. 1972 Jul;13(7):524–527. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.7.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks T. G., Bussey H. F., Lockhart-Mummery H. E. Familial polyposis coli associated with extracolonic abnormalities. Gut. 1970 Apr;11(4):323–329. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.4.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnur P. L., David E., Brown P. W., Jr, Beahrs O. H., ReMine W. H., Harrison E. G., Jr Adenocarcinoma of the duodenum and the Gardner syndrome. JAMA. 1973 Mar 12;223(11):1229–1232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull L. N., Jr, Fitts C. T. Lymphoid polyposis associated with familial polyposis and Gardner's syndrome. Ann Surg. 1974 Sep;180(3):319–322. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197409000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzanne J., Camelot G., Miguet J. P., Carbillet J. P., Gillet M., Carayon P., Gisselbrecht H. Syndrome de Gardner et adénocarcinome duodénal. Etude d'un cas et revue de la littérature. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 1977;1(5):455–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tim L. O., Bank S., Marks I. N., Novis B. H., Botha J. C., Odes H. S., Helman C. A., Barbezat G. O. Benign lymphoid hyperplasia of the gastric antrum - another cause of "etat mammelonne". Br J Radiol. 1977 Jan;50(589):29–31. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-50-589-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushio K., Sasagawa M., Doi H., Yamada T., Ichikawa H., Hojo K., Koyama Y., Sano R. Lesions associated with familial polyposis coli: studies of lesions of lesions of the stomach, duodenum, bones, and teeth. Gastrointest Radiol. 1976;1(1):67–80. doi: 10.1007/BF02256344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsunomiya J., Maki T., Iwama T., Matsunaga Y., Ichikawa T. Gastric lesion of familial polyposis coli. Cancer. 1974 Sep;34(3):745–754. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197409)34:3<745::aid-cncr2820340333>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe H., Enjoji M., Yao T., Ohsato K. Gastric lesions in familial adenomatosis coli: their incidence and histologic analysis. Hum Pathol. 1978 May;9(3):269–283. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(78)80085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao T., Ida M., Ohsato K., Watanabe H., Omae T. Duodenal lesions in familial polyposis of the colon. Gastroenterology. 1977 Nov;73(5):1086–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemoto R. H., Slayback J. B., Byron R. L., Jr, Rosen R. B. Familial polyposis of the entire gastrointestinal tract. Arch Surg. 1969 Oct;99(4):427–434. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1969.01340160007003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]