Abstract
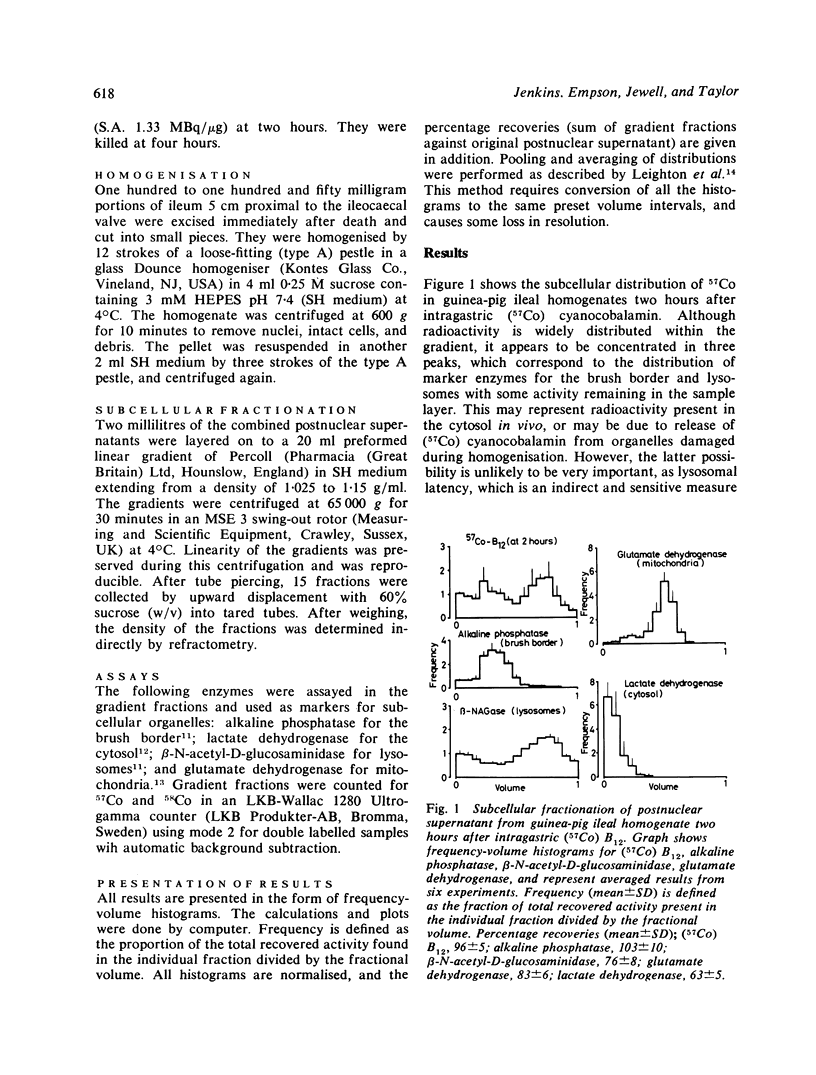
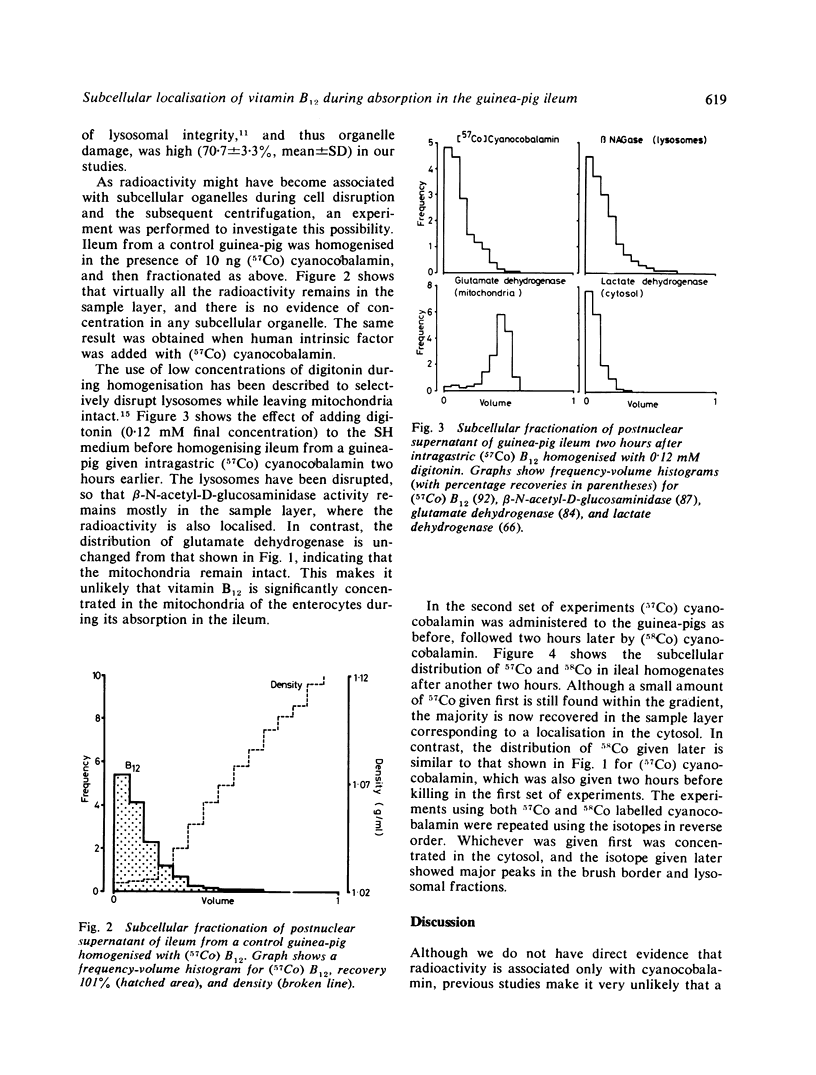
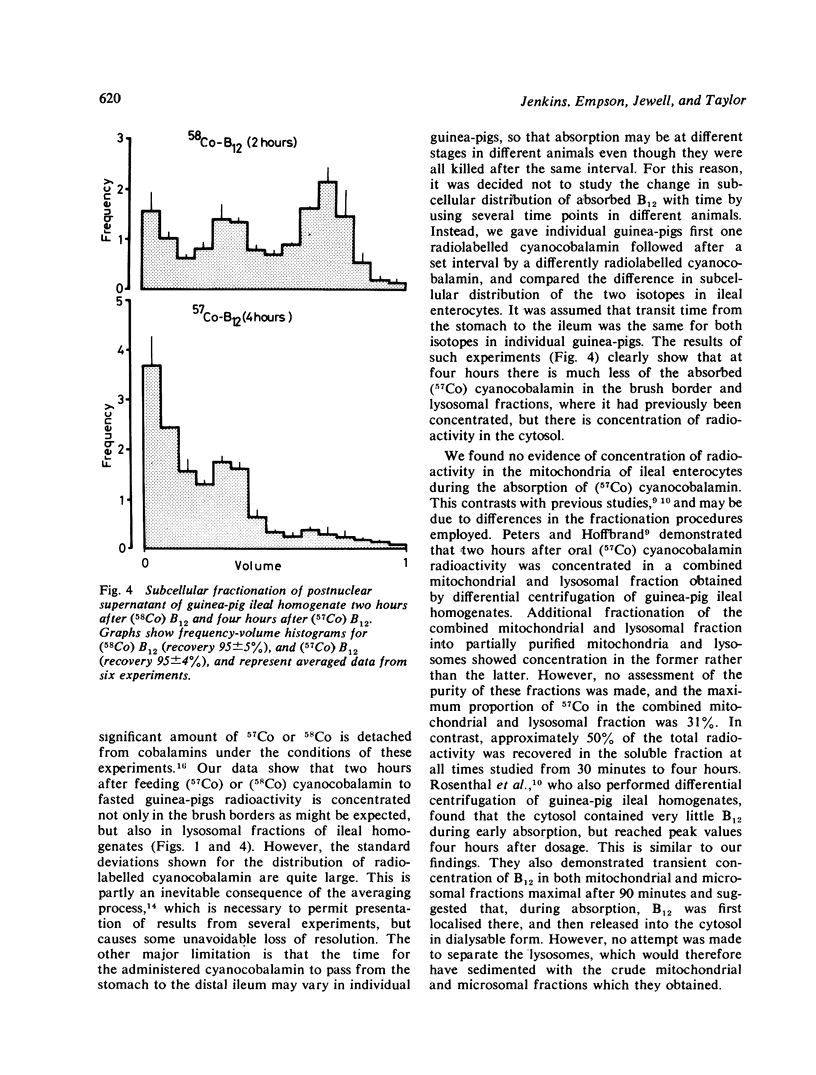
The subcellular distribution of vitamin B12 was studied during its absorption in the guinea-pig ileum. Animals were fed either (57Co) or (58Co) cyanocobalamin and killed two or four hours later. At two hours labelled cyanocobalamin was concentrated in brush border and lysosomal fractions of ileal homogenates, with some remaining in the sample layer. In contrast, at four hours labelled cyanocobalamin was concentrated predominantly in the cytosol with much smaller peaks in the brush border and lysosomal fractions. These findings are consistent with vitamin B12 absorption by receptor-mediated endocytosis. It is suggested that, after binding at the brush border, vitamin B12 is first sequestrated within lysosomes, and then released into the cytosol, from where it leaves the cell to enter the portal blood.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOOTH C. C., CHANARIN I., ANDERSON B. B., MOLLIN D. L. The site of absorption and tissue distribution of orally administered 56Co-labelled vitamin B12 in the rat. Br J Haematol. 1957 Jul;3(3):253–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1957.tb05794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper B. A., White J. J. Absence of intrinsic factor from human portal plasma during 57CoB12 absorption in man. Br J Haematol. 1968 Jan;14(1):73–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb01474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. M., Jr, Mackenzie I. L., Trier J. S. Intrinsic factor-mediated attachment of vitamin B12 to brush borders and microvillous membranes of hamster intestine. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jul;46(7):1215–1228. doi: 10.1172/JCI105615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis G., Goldberg D. M. Optimal conditions for the kinetic assay of serum glutamate dehydrogenase activity at 37 degrees C. Clin Chem. 1972 Jun;18(6):523–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton F., Poole B., Beaufay H., Baudhuin P., Coffey J. W., Fowler S., De Duve C. The large-scale separation of peroxisomes, mitochondria, and lysosomes from the livers of rats injected with triton WR-1339. Improved isolation procedures, automated analysis, biochemical and morphological properties of fractions. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):482–513. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie I. L., Donaldson R. M., Jr Vitamin B 12 absorption and the intestinal cell surface. Fed Proc. 1969 Jan-Feb;28(1):41–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmark P., Newman G. E., O'Brien J. R. Vitamin B12 in the rat kidney. Evidence for an association with lysosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Nov;141(1):121–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J. Analytical subcellular fractionation of jejunal biopsy specimens: methodology and characterization of the organelles in normal tissue. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Dec;51(6):557–574. doi: 10.1042/cs0510557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Heath J. R., Wansbrough-Jones M. H., Foe W. F. Enzyme activities and properties of lysosomes and brush borders in jejunal biopsies from control subjects and patients with coeliac disease. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975 Apr;48(4):259–267. doi: 10.1042/cs0480259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Hoffbrand A. V. Absorption of vitamin B 12 by the guinea-pig. I. Subcellular localization of vitamin B 12 in the ileal enterocyte during absorption. Br J Haematol. 1970 Sep;19(3):369–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01634.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Linnell J. C., Matthews D. M., Hoffbrand A. V. Absorption of vitamin B12 in the guinea-pig. 3. The forms of vitamin B12 in ileal mucosa and portal plasma in the fasting state and during absorption of cyanocobalamin. Br J Haematol. 1971 Mar;20(3):299–305. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb07040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T. J., Seymour C. A. Analytical subcellular fractionation of needle-biopsy specimens from human liver. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 15;174(2):435–446. doi: 10.1042/bj1740435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNELL P. C., SPRAY G. H., TAYLOR K. B. The site of absorption of vitamin B12 in the rat. Clin Sci. 1957 Nov;16(4):663–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal H. L., Cutler L., Sobieszczanska W. Uptake and transport of vitamin B12 in subcellular fractions of intestinal mucosa. Am J Physiol. 1970 Feb;218(2):358–362. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.2.358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUS W. CYTOCHEMICAL OBSERVATIONS ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LYSOSOMES AND PHAGOSOMES IN KIDNEY AND LIVER BY COMBINED STAINING FOR ACID PHOSPHATASE AND INTRAVENOUSLY INJECTED HORSERADISH PEROXIDASE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Mar;20:497–507. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20.3.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON T. H. Intestinal absorption of vitamin B12. Physiologist. 1963 Feb;6:11–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngdahl-Turner P., Rosenberg L. E., Allen R. H. Binding and uptake of transcobalamin II by human fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):133–141. doi: 10.1172/JCI108911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


