Abstract
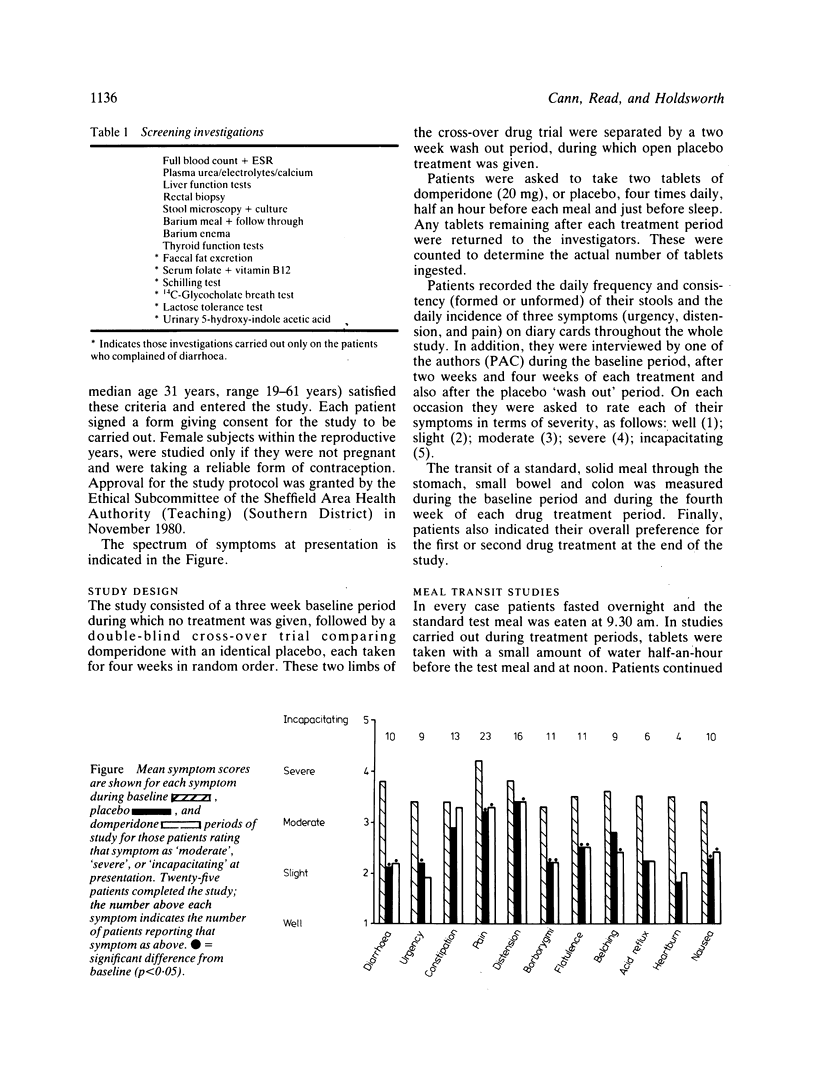
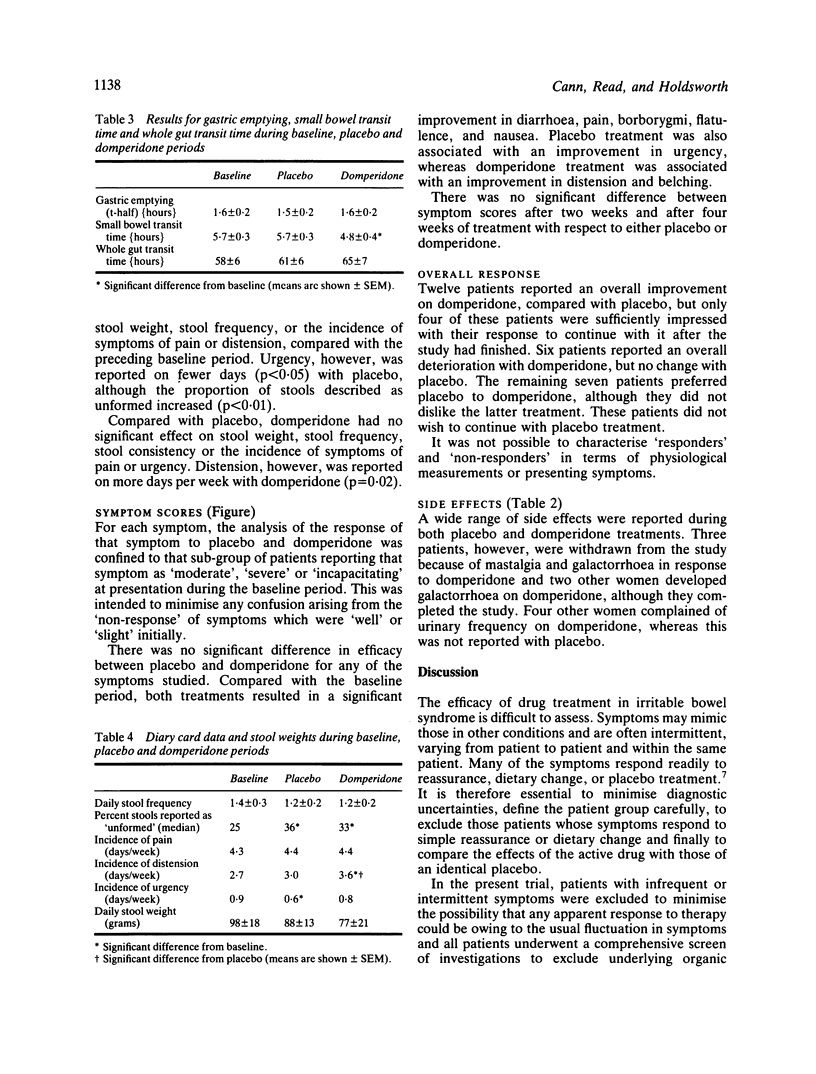
Symptom scores, stool data, and the transit of a standard, solid meal were measured in 25 patients with irritable bowel syndrome during baseline conditions and after four weeks treatment with placebo and domperidone in the form of a double-blind cross-over trial. All patients had previously undergone a comprehensive series of diagnostic investigations and had failed to respond to dietary supplementation with coarse wheat bran (10-30 g daily). Compared with placebo treatment, domperidone had no significant effect on gastric emptying, small bowel or whole gut transit times, stool weight, frequency, or consistency. Most symptoms improved significantly with both placebo and domperidone treatments, compared with the baseline period, but there was no significant difference between placebo and domperidone for any of the symptoms. Abdominal distension, however, was reported on more days per week during domperidone treatment (p = 0.02). The findings in this study do not support the use of domperidone in the management of irritable bowel syndrome.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeyens R., van de Velde E., De Schepper A., Wollaert F., Reyntjens A. Effects of intravenous and oral domperidone on the motor function of the stomach and small intestine. Postgrad Med J. 1979;55 (Suppl 1):19–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. H., Jr, Levitt M. D., Prentiss R. Investigation of small bowel transit time in man utilizing pulmonary hydrogen (H2) measurements. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Apr;85(4):546–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camanni F., Genazzani A. R., Massara F., La Rosa R., Cocchi D., Müller E. E. Prolactin-releasing effect of domperidone in normoprolactinemic and hyperprolactinemic subjects. Neuroendocrinology. 1980;30(1):2–6. doi: 10.1159/000122965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann P. A., Read N. W., Brown C., Hobson N., Holdsworth C. D. Irritable bowel syndrome: relationship of disorders in the transit of a single solid meal to symptom patterns. Gut. 1983 May;24(5):405–411. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.5.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Schepper A., Wollaert F., Reyntjens A. Effects of oral domperidone on gastric emptying and motility. A double-blind comparison with placebo and metoclopramide. Arzneimittelforschung. 1978;28(7):1196–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding J. F. Domperidone treatment in the irritable bowel syndrome. Digestion. 1982;23(2):125–127. doi: 10.1159/000198701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton J. M., Lennard-Jones J. E., Young A. C. A ne method for studying gut transit times using radioopaque markers. Gut. 1969 Oct;10(10):842–847. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.10.842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milo R. Use of the peripheral dopamine antagonist, domperidone, in the management of gastro-intestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Curr Med Res Opin. 1980;6(9):577–584. doi: 10.1185/03007998009109491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostick D. G., Howe K., Green G., Dymock I. W., Cowley D. J. Simple clinical method of measuring gastric emptying of solid meals. Gut. 1976 Mar;17(3):189–191. doi: 10.1136/gut.17.3.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read N. W., Miles C. A., Fisher D., Holgate A. M., Kime N. D., Mitchell M. A., Reeve A. M., Roche T. B., Walker M. Transit of a meal through the stomach, small intestine, and colon in normal subjects and its role in the pathogenesis of diarrhea. Gastroenterology. 1980 Dec;79(6):1276–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyntjens A. J., Niemegeers C. J., Van Nueten J. M., Laduron P., Heykants J., Schellekens K. H., Marsboom R., Jageneau A., Broekaert A., Janssen P. A. Domperidone, a novel and safe gastrokinetic anti-nauseant for the treatment of dyspepsia and vomiting. Arzneimittelforschung. 1978;28(7):1194–1196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


