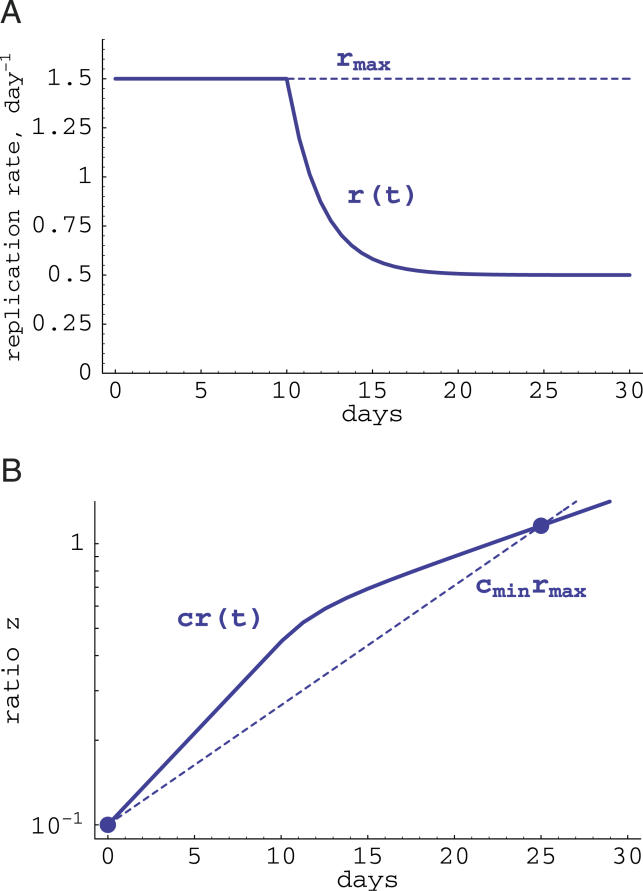
Figure 2. Estimating the Cost of a CTL Escape Mutation.
(A) Plots the hypothetical changes in the replication rate of the virus during the acute phase of infection. We assume that initially (until time Tr) the virus population expands exponentially at rate rmax, and after t = Tr , the virus replication rate is reduced exponentially at rate λ to a smaller value rmin. Biologically this would correspond to the acute phase of SIV/HIV infection when the replication rate of the virus depends on the availability of target cells, which are depleted by the virus.
(B) Plots changes in the ratio z(t) calculated using Equation 8 with k(t) = 0 for the replication rate r(t) shown by a solid line in (A). For two measurements of the ratio z at ts = 0 and te = 25 d, we obtain a minimal estimate of the cost of the escape mutation assuming exponential virus growth with rmax = 1.5 d−1 (shown by dashed lines), i.e., cmin = 0.065 which is 65% of the actual fitness cost. Other parameters: rmin = 0.5 d−1, Tr = 10 d, λ = 0.5 d−1, z(0) = 0.1, c = 0.1.