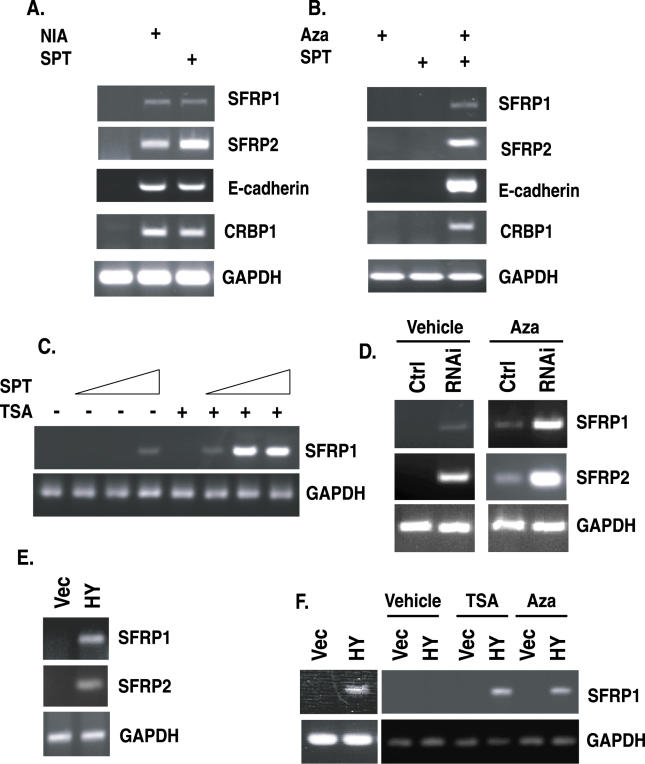
Figure 2. Pharmacologic and Dominant Negative Inhibition of SIRT1 Cause Re-Expression of TSGs and Synergize with 5-Deoxy-Azacytidine or TSA.
(A) Pharmacologic inhibition of SIRT1 causes TSG re-expression. MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 15 mM NIA or 300 μM SPT for 21 h, RNA was isolated, and RT-PCR was performed with intron−spanning primers specific for the indicated genes. Control samples in which no reverse transcriptase was added were analyzed separately, and all were negative for amplification of the indicated genes.
(B) Combined treatment with low doses of Aza and SPT synergizes in the re-expression of TSGs. MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with either 50 nM Aza (+), 100 μM SPT (+) or with both Aza and SPT (++), and 34 h later, RT-PCR was performed for the indicated genes as described in (A).
(C) Combined treatment with SPT and TSA synergize in the re-expression of genes. MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with either 0, 50, 100, or 120 μM SPT alone for 34 h, or the treatment was followed by treatment with 300 nM TSA for 3 h prior to RNA isolation and RT-PCR analysis.
(D) SIRT1 protein knockdown synergizes with low doses of Aza for gene re-expression. MDA-MB-231 cells were infected with low titers of virus for shRNA specific for SIRT1. Aza (100 nM) was added 24 h prior to RNA isolation, and RT-PCR analysis was performed for the genes SFRP1, SFRP2, and GAPDH as described in (A).
(E) Dominant negative inhibition of SIRT1 leads to TSG re-expression in MCF7 cells. MCF7 cells were infected with virus encoding either pBabe (vec) or the catalytically inactive SIRT1H363Y (HY) mutant, and RT-PCR was performed as described in (A).
(F) Dominant negative inhibition of SIRT1 leads to TSG re-expression and synergizes with TSA and Aza. As shown in the left panel, MDA-MB-231 cells were infected with a control (vec) or mutant SIRT1 virus (HY), and RT-PCR was performed as described in (A). MDA-MB-231 cells were infected with low titers of pBabe or pBabe-SIRT1H363Y retrovirus and subsequently treated with 100 nM Aza for 24 h or with 300 nM TSA for 3 h prior to harvest, and RT-PCR was performed.