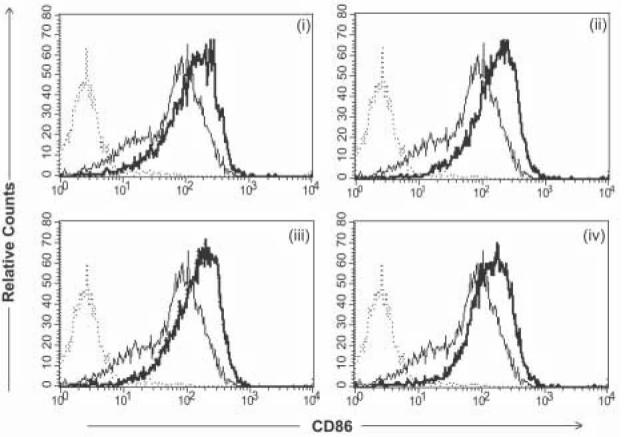
Figure 3.
Phenotypic analysis of CD86 expression following transduction with various targeted derivatives of Ad-FBAP-GFP. Primary human monocyte-derived DC were incubated with protein/peptide-NA-virus complexes of interest, at a multiplicity of infection of 2000 viral genome units (vg) per cell, and CD86 expression was analyzed by flow cytometry 48 hours later. AdFBAP-GFP virus was targeted using the following reagents: (i) a DC-SIGN specific monoclonal antibody (DC-SIGN), (ii) a nonamer peptide that binds to ChemR23 with nanomolar affinity (chemerin FAFS), (iii) a low-affinity and relatively non-selective αvβ3 integrin-binding (FnFn10), (iv) a high- affinity and highly selective αvβ3 integrin-binding peptide (3JCLI4). In each panel, the thin/light line denotes CD86 staining of unmanipulated DC (not exposed to virus) and the dark/thick line shows the CD86 expression profile of cells that were transduced with the indicated protein/peptide-NA-virus complexes. Results shown are representative of 3 independent experiments, each of which generated similar results.