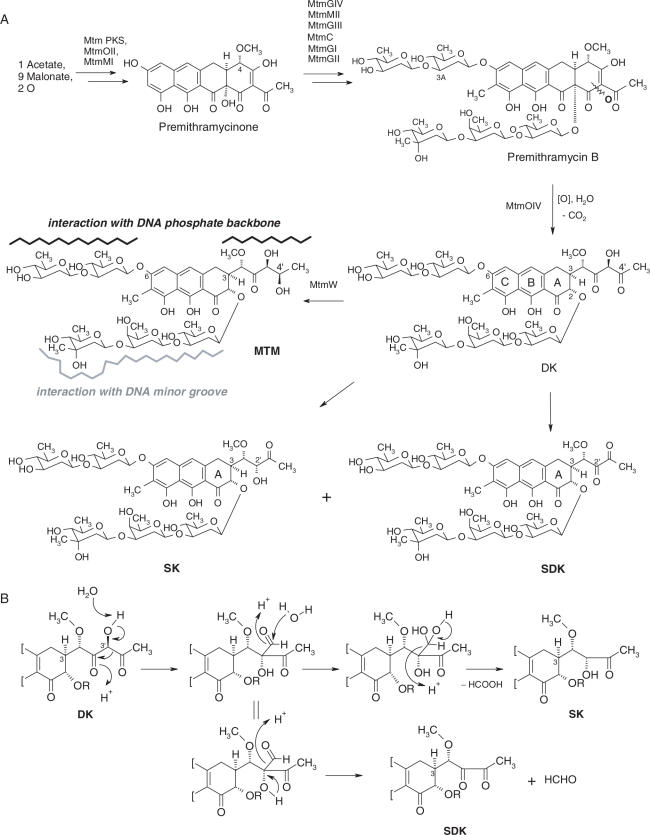
Figure 1.
Biosynthesis of the MTM analogs SDK and SK. (A) The oxygenase MtmOIV and ketoreductase MtmW catalyze the conversion of premithramycin B to mithramycin (MTM). Inactivation of MtmW prevents synthesis of MTM and results in accumulation of the intermediate product DK, which is then converted into SK and SDK. Regions of relevant MTM-DNA interaction are indicated. (B) Side chain rearrangements leading to formation of SK and SDK from the MtmOIV product DK.