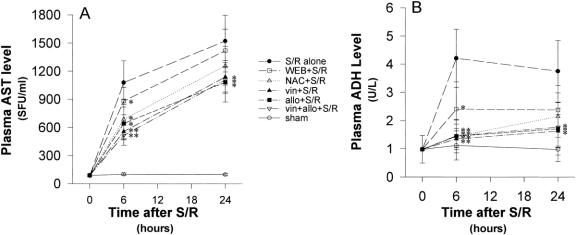
Figure 6. (A) Plasma aspartate aminotransferase (AST) levels continued to rise for the first 24 hours after shock/resuscitation (S/R) for all groups with substantial elevation in the first 6 hours. However, this early elevation was significantly blunted in the allopurinol, N-acetylcysteine, and WEB 2170 groups. At 24 hours, allopurinol and vinblastine treatment blunted the elevated AST levels compared with the S/R alone group. (B) Plasma alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) levels in the S/R rats rose rapidly in the first 6 hours and then started to decline but remained elevated at 24 hours. In contrast, the allopurinol and N-acetylcysteine groups showed a steady increase in ADH levels. At 6 hours, treatment with allopurinol, N-acetylcysteine, WEB 2170, and vinblastine significantly blunted the rise in ADH levels compared with the S/R alone group. At 24 hours, the allopurinol and vinblastine-treated groups had significantly lower ADH levels than the S/R alone group. *P < .05 versus S/R alone; **P < .001 versus S/R alone.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.