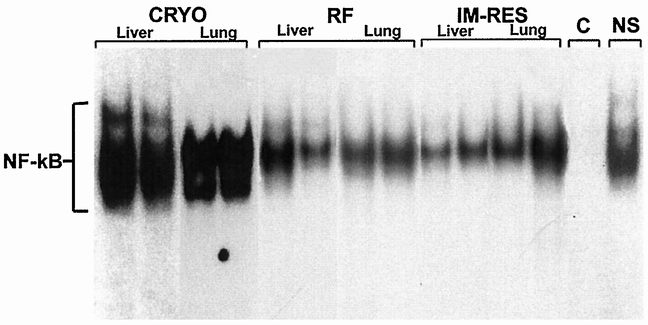
Figure 5. Composite electrophoretic mobility shift assay gel performed on tissue taken from the nonablated liver and lung from representative animals undergoing cryoablation (cryo) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) killed 1 hour after treatment. Each lane represents a single animal experiment. These results demonstrate activated nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) in liver and lung tissue extracts from animals undergoing cryoablation but not from animals undergoing RFA. Also, immediate resection (IM-res) of the cryoablated liver before thawing prevented activation of NF-κB in liver and lung tissue. Addition of 50 ng unlabeled, specific NF-κB oligonucleotide markedly diminished all three bands (cold competition = C). The addition of 50 ng unlabeled oligonucleotide that did not contain the NF-κB motif (nonspecific competition = NS) did not affect NF-κB binding. These results confirm the authenticity of detected protein bands in NF-κB analysis.
