Figure 3.
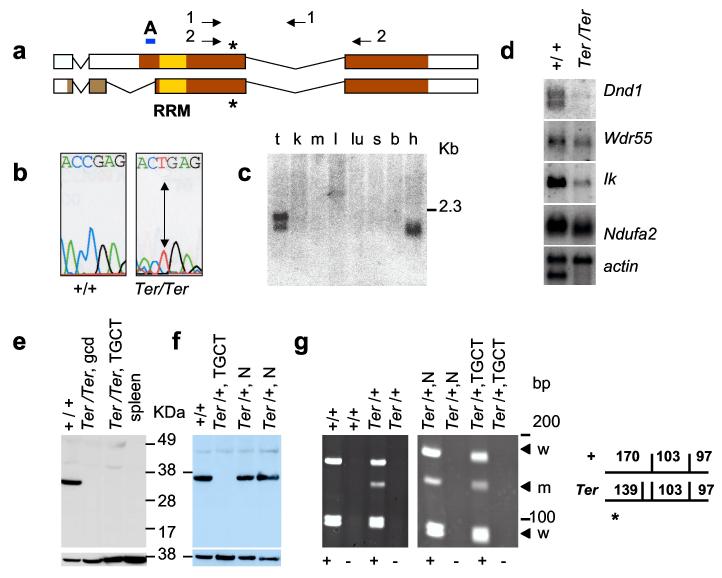
Expression of Dnd1 in normal tissues and TGCTs. (a) Comparison of DND1 isoforms with accession numbers BC034897 (top) and AY321066 (bottom). Colored regions indicate protein coding regions; yellow box marks RRM. Asterisk indicates amino acids 178 and 190, of the two isoforms, that is mutated (R178X) in Ter. Arrows indicate primers 4.13a (1) and A25 (2). A indicates the region used as peptide epitope to generate anti-DND1 antibody. (b) C to T mutation in Ter/Ter introduces stop codon. (c) Mouse tissue Northern blot for Dnd1. mRNAs are from testes (t), kidney (k), muscle (m), liver (l), lung (lu), spleen (s), brain (b) and heart (h). (d) Northern blot of mRNA from 129-+/+ testes and 129-Ter/Ter tumours. (e) Western blotting with anti-DND1 antibody of tissue lysates from normal (+/+) testes of 129-+/+, germ cell deficient (gcd) testes of B6.129-Ter/Ter congenic strain, bilateral TGCTs from 129-Ter/Ter mice, and spleen of 129-+/+. Lower panel shows control for loading using anti-β-actin. (f) Western blot with anti-DND1 of normal testes of 129-+/+ (+/+), tumour in the testes of 129-Ter/+ (Ter/+, TGCT), the normal contralateral testes (Ter/+, N), and normal testes of another 129-Ter/+ mouse (Ter/+, N). Lower panel shows the same blot re-hybridized with mouse anti-β-actin. (g) (left) RT-PCR of RNA from normal testes of 129-+/+ and 129-Ter/+ mice using primers A25 (2 in Fig. 3a) followed by Dde1 digestion. This produces fragments of 170, 103 and 97 bp from the + allele and 139, 103, 97 and 31 bp (not seen on gel) from the Ter allele. For controls, PCR reactions were performed on samples which included (+) or did not include Superscript II (-) during RT, as indicated below the panels. (right) Total RNA from normal and TGCT-bearing testes of the same 129-Ter/+ mouse was amplified by RT-PCR followed by Dde1 digestion and electrophoresis. The arrows indicate the wild-type (w) and Ter (m) allele.
