Figure 7.
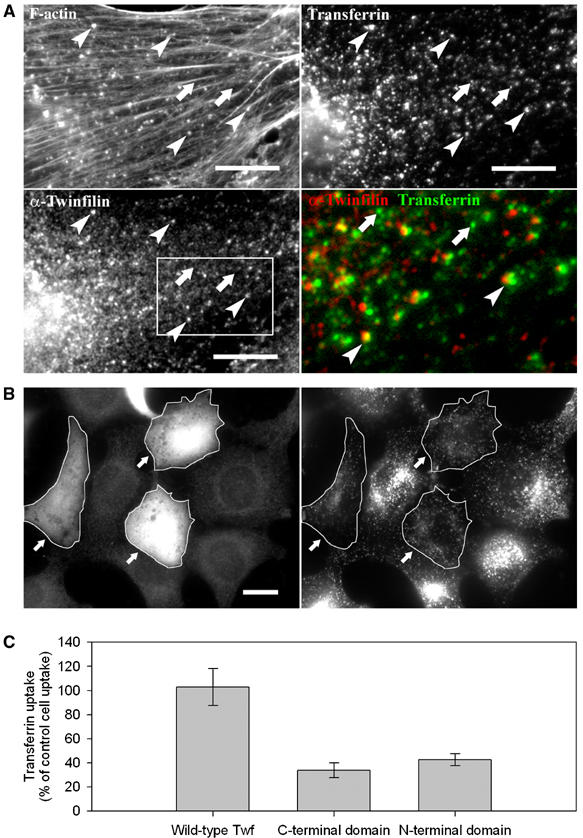
Twinfilin is involved in receptor-mediated endocytosis. (A) Endogenous twinfilin-1 localizes to F-actin-rich transferrin particles (examples indicated with arrowheads), but is absent from transferrin particles that are not associated with F-actin (arrows). NIH 3T3 cells were incubated for 20 min in 15 μg/ml rhodamine-transferrin (upper right panel), and stained with phalloidin (upper left panel), and anti-twinfilin-1 antibody (bottom left panel). A higher magnification overlay of twinfilin (red) and transferrin (green) from the boxed region is presented in the bottom right panel. Bar: 5 μm. (B) Overexpression of twinfilin's N-terminal ADF-H domain results in defects in receptor-mediated endocytosis. After 20 min incubation in 15 μg/ml transferrin, wild-type cells showed efficient uptake and accumulation of transferrin to the perinuclear region. In contrast, the cells overexpressing twinfilin's isolated ADF-H domain (arrows) showed punctate cytoplasmic staining and reduced transferrin uptake. Bar: 5 μm. (C) Intensity of rhodamine-transferrin fluorescence was quantified by TINA software from 10 cells overexpressing wild-type twinfilin, N-terminal ADF-H domain, or C-terminal half of the protein and compared with the intensity of rhodamine fluorescence of an adjacent wild-type cell from the same frame. The efficiency of transferrin uptake was reduced to approximately 30 and 40% in cells overexpressing twinfilin's C-terminal half and N-terminal ADF-H domain, respectively. Transferrin uptake in cells overexpressing full-length twinfilin was very similar as compared to wild-type cells. s.e.m.s are indicated in the graph.
