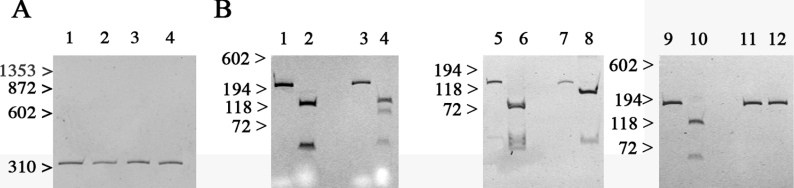
Figure 1. EBV-immortalized B-cells from patients express a mutated RyR.
Polyacrylamide gels showing PCR-amplification of cDNA using the primer pairs indicated in the Experimental section. (A) Amplification of cDNA spanning RYR1 exons 38–40 from control (lane 1), R999H (lane 2), P3527S (lane 3) and V4849I (lane 4) yields a band of 338 bp corresponding to the expected cDNA product, and none from genomic DNA amplification. (B) Lanes 1–4, amplification of exon 24 of the RYR1 gene for the R999H substitution: lanes 1 and 3, undigested cDNA; lanes 2 and 4, cDNA after digestion with BstU I; lanes 1 and 2, control; lanes 3 and 4, patient harbouring the heterozygous R999H substitution. Lanes 5–8, amplification of exon 71 of the RYR1 gene for the P3527S substitution: lanes 5 and 7, undigested cDNA; lanes 6 and 8, cDNA after digestion with HhaI; lanes 5 and 6, control; lanes 7 and 8, patient harbouring the homozygous P3527S substitution. Lanes 9–12, amplification of exon 101 for V4849I substitution: lanes 9 and 11, undigested cDNA; lanes 10 and 12, cDNA after digestion with AccI; lanes 9 and 10, control; lanes 11 and 12, patient harbouring the homozygous V4849I substitution.